Uterine bleeding: causes, symptoms, first aid, treatment
Uterine bleeding is a discharge of blood from the vagina, characterized by profusion and duration. This pathological condition poses a danger to the life and health of a woman, is a sign of serious diseases of the reproductive system.
To save the patient, it is important to immediately provide her with first aid, to find out the cause of the bleeding.
Natural bleeding from the vagina is called menstruation. Menstrual bleeding is cyclical, repeated at regular intervals. The period between periods usually lasts 25 - 30 days.
Vaginal blood should not come out more than 8 days, otherwise we can talk about pathology. Violation of the menstrual cycle is a reason to immediately consult a gynecologist. The doctor will find out the cause of the pathological phenomenon, help get rid of the disease at an early stage, until complications arise.
Content
- Causes of uterine bleeding
- Symptoms of uterine bleeding
- Types of uterine bleeding
- Dysfunctional bleeding
- Organic bleeding
- Breakthrough bleeding
- Bleeding due to pregnancy and childbirth
- First emergency aid before the arrival of doctors
- Drug therapy
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Related Videos
Causes of uterine bleeding
The likelihood of uterine bleeding depends on the age of the patient. In girls from 12 to 18 years old, abundant discharge of blood from the vagina is a consequence of hormonal imbalance. BUT hormonal disruptions at a young age arise from:
- physical injury or emotional distress;
- deterioration of the endocrine glands;
- malnutrition, vitamin deficiency in the body;
- pregnancy with complications, difficult childbirth;
- genital tuberculosis;
- blood clotting disorders;
- transferred severe infectious diseases.
In women of mature age, uterine bleeding is a rare occurrence, usually associated with dysfunction of the ovaries. In this case, the provocateurs of the pathological condition are:
- stress, overwork, nervous strain, mental disorders;
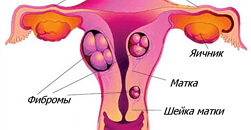
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- advanced endometritis;
- polyps of the uterus;
- oncology of the uterus or cervix;
- tumor formations in the ovaries;
- ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, medical or instrumental abortion;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive organs;
- climate change, unfavorable environmental situation in the place of residence, harmful working conditions;
- taking medications that can disrupt the systemic work of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
Uterine bleeding is often observed in women in period of menopause. This is due to a decrease in the synthesis of gonadotropin by the pituitary gland.
As a result, the level of sex hormones in the female body begins to jump, gets lost menstrual cycle, the formation of follicles in the ovaries is disrupted. Common causes of bleeding from the uterus at the age of extinction of reproductive function are:
- uterine fibroids;
- endometriosis;
- polyposis of the uterus;
- hormone-dependent ovarian tumors.
Symptoms of uterine bleeding
Common signs of abnormal uterine bleeding are:
- weakness;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- blanching of the skin;
- tachycardia of the heart;
- lowering blood pressure.
Specific symptoms of uterine bleeding are:
- profuse flow of blood from the vagina;
- the presence of clots in blood discharge;
- changing the gasket every 2 hours, even more often;
- the duration of bleeding is more than 8 days;
- increased bleeding after intercourse;
- painless bleeding with a dysfunctional origin of pathology;
- non-coincidence of the onset of bleeding with the period of menstruation.
The duration of menstruation normally does not exceed 8 days, and bleeding that lasts longer than normal is pathological. Vaginal bleeding should be considered unhealthy, the period between which is less than 21 days.
Read also:Menopause in women: symptoms and treatment
When menstruation per day flows out 80 - 120 ml of blood, with uterine bleeding, the daily blood volume is more than 120 ml.
Types of uterine bleeding
Bleeding from the uterus, depending on the age of the patients, is divided into five types.
- During infancy. In the first week of life, a newborn girl may experience minor bleeding from the vagina. This is not a pathological phenomenon, the child does not need medical intervention. Infant bleeding is caused by a sharp change in the hormonal background in a girl who was born, and they disappear on their own.
- Before puberty. During this period, vaginal bleeding in girls is rare. The cause of the pathological condition is most often a hormone-dependent tumor of the ovary, due to which the sex gland synthesizes too many hormones. As a result, the girl has a false maturation of the reproductive system.
- During puberty. Uterine bleeding during puberty between 12 and 18 years of age is called juvenile.
- During the reproductive period. Bleeding from the uterus observed between 18 and 45 years old is organic, dysfunctional, breakthrough, and also caused by pregnancy and childbirth.
- In the climacteric period. During the period of extinction of the reproductive function, bleeding from the vagina is most often associated with pathologies of the genital organs or with a decrease in the synthesis of hormones.
Dysfunctional bleeding
This type of uterine bleeding, seen during the reproductive period, is the most common. The pathological condition is diagnosed in both girls and older women during menopause. The reason for dysfunctional blood discharge is a failure in the synthesis of sex hormones by the endocrine glands.
Endocrine system, including the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, ovaries and adrenal glands, controls the production of sex hormones. If the work of this complex system fails, then the menstrual cycle, the duration and abundance of menstruation changes, the likelihood of infertility increases and spontaneous abortion. Therefore, for any changes in the menstrual cycle, you should immediately contact your gynecologist.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is ovulatory and anovulatory. Ovulatory bleeding is manifested by a change in the duration and abundance of blood flow during menstruation. Anovulatory bleeding is observed more often, due to the lack of ovulation due to a violation of the synthesis of sex hormones.
Organic bleeding
Such bleeding is caused either by severe pathologies of the reproductive organs, or by blood diseases, or by serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Breakthrough bleeding
Such uterine bleeding is also called iatrogenic. They are diagnosed after exceeding the dosage and course of taking certain medications, frequent use of hormonal contraceptives, as well as after an operation to install a spiral and after other surgical procedures on organs reproductive system.
When taking hormonal drugs, there are usually scanty bleedingmeaning that the body is adapting to synthetic hormones. In this situation, it is recommended to consult with your doctor about changing the dosage of the medication.
In most cases, with breakthrough bleeding, gynecologists advise patients to increase the dosage of the hormonal agent for a certain time. If after this measure the amount of released blood does not decrease, but increases, then an urgent medical examination is needed. In this case, the cause of the pathological condition may be a serious disease of the reproductive system.
Read also:It hurts to go to the toilet like a little woman: causes and treatment
If uterine bleeding occurs after the installation of the spiral, then the contraceptive device, most likely, injured the walls of the uterus. In this situation, you should immediately remove the spiral and wait for the healing of the uterine walls.
Bleeding due to pregnancy and childbirth

In the first months of pregnancy, bleeding from the uterus is a sign of either a threat of spontaneous abortion or an ectopic fetus. With these pathological conditions, severe pain in the lower abdomen is noted.
A pregnant woman who has started uterine bleeding should see a doctor immediately.
When a spontaneous abortion begins, the fetus can be saved if the correct treatment is started on time. In the last stages of miscarriage, pregnancy will have to say goodbye, in this case, scraping is prescribed.
In an ectopic pregnancy, the fetus develops in the fallopian tube or cervix. Menstruation is delayed, some pregnancy symptoms are noted, but the embryo is not found in the uterus. When the fetus reaches a certain stage of development, bleeding occurs. In this situation, a woman needs urgent medical attention.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, uterine bleeding is fatal to both the mother and the developing baby in the womb.
The causes of the pathological condition in the late gestation period are previa or placental abruption, rupture of the uterine walls. In these cases, the woman urgently needs medical assistance, usually a cesarean section is performed. Patients who are at high risk of the above pathologies should be kept in preservation.
Uterine bleeding can also occur during childbirth. In this case, the following pathological conditions may be its causes:
- placenta previa;
- violation of blood clotting;
- low contractility of the uterus;
- placental abruption;
- afterbirth stuck in the uterus.
If bleeding from the uterus occurs a few days after childbirth, then you need to immediately call an ambulance. The young mother will need urgent hospitalization.
First emergency aid before the arrival of doctors
Excessive bleeding from the vagina should be stopped or at least reduced before the arrival of doctors. It is a matter of a woman's life and death. In most cases, with competent first aid, bleeding stops, but in 15% of cases, the pathological process ends fatally.
Every woman should know how to help herself before the arrival of doctors, what can and cannot be done.
A sick woman, while waiting for doctors at home, should do the following:
- lie on your back, remove the pillow from under your head;
- put a high roller made of towels or blankets under the shins;
- Putting a bottle of cold water or an ice-filled heating pad on your stomach
- drink cold still water.
With uterine bleeding, it is strictly prohibited:
- be in a standing and sitting position;
- lie with your legs pressed to your stomach;
- take a hot bath;
- do douching;
- put a heating pad on your stomach;
- drink hot drinks;
- take any medication.
Read also:Vulvodynia
Drug therapy
Treatment of diseases that caused bleeding from the uterus is carried out in stationary conditions. In addition, the doctor prescribes medications for the patient to help stop the bleeding.
Hemostatic medications are taken only on the recommendation of a medical specialist; taking medications at their own discretion is strictly prohibited.
Below is a list of the medicines most commonly used to stop bleeding.
- Etamsilat. This drug stimulates the synthesis of thromboplastin, changes the permeability of blood vessels. Blood clotting increases, as a result, bleeding is weakened. The medication is intended for intramuscular injection.
- Oxytocin. A hormonal drug often used during labor to improve uterine contractility. As a result of the contraction of the uterine muscles, bleeding stops. A drug oxytocin prescribed for intravenous administration with added glucose, has a large list of contraindications.
- Aminocaproic acid. This drug prevents blood clots from dissolving under the influence of certain factors, thereby reducing bleeding. The medicine is either taken orally or given intravenously. Treatment with aminocaproic acid of uterine bleeding is carried out under close medical supervision.
- Vikasol. The drug is based on vitamin K. With a deficiency of this vitamin in the body, blood clotting worsens. The medication is prescribed to patients who have a tendency to uterine bleeding. However, vitamin K begins to act only 10 to 12 hours after it enters the body, therefore, it is inappropriate to use the drug to stop blood in emergency cases.
- Calcium gluconate. The drug is prescribed for calcium deficiency in the body. Deficiency increases the permeability of the vascular walls, impairs blood clotting. This drug is also not suitable for use in emergencies, but is used to strengthen blood vessels in patients prone to bleeding.
Treatment with folk remedies
To stop and prevent uterine bleeding, you can use decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants. Listed below are the most popular and effective folk remedies for stopping blood.
- Infusion of yarrow. You need to take 2 teaspoons of dried plant materials, pour a glass of boiling water. The solution is infused for about an hour, then filtered. The infusion is taken in a quarter of a glass 4 times a day before meals.
- Nettle decoction. Take a tablespoon of dried nettle leaves, pour a glass of boiling water. The solution is boiled over low heat for 10 minutes, then filtered. The finished broth is taken in a tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
- Infusion of shepherd's purse. A tablespoon of dried plant materials is taken, poured into a glass of boiling water. The container with the solution is wrapped in a warm towel, left for an hour to infuse. The finished infusion is filtered, taken in a tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
It must be remembered that folk remedies cannot be a full substitute for medicines, they are used only as an addition to the main therapy.
Before using herbal remedies, you should definitely consult with a medical specialist in order to exclude intolerance to the medicinal plant and other contraindications.