Alveolitis: what is it, causes, symptoms, treatment, diagnosis, forms, complications, prevention
Complications after tooth extraction become an obstacle to the formation of a blood clot or accelerate its disintegration. The result is the exposure of the bone tissue of the hole, the impact on it of unfavorable factors. One of these complications is alveolitis after tooth extraction. To reduce the likelihood of a problem occurring, it is recommended to follow the preventive recommendations.
Content
- 1 Alveolitis reasons
-
2 Alveolitis symptoms
- 2.1 Acute form
- 2.2 Chronic form
- 3 Diagnostics of the alveolitis
-
4 Treatment
- 4.1 Possible complications of alveolitis
- 5 Preventive actions
Alveolitis reasons
Filling the alveoli with a blood clot is the norm. It contains fibrillar protein, blood cell elements. Thanks to this clot, the penetration of bacteria and injury to the wound surface will not occur. Some predisposing factors can provoke its displacement or deformation. After that, an infection enters the wound, and alveolitis of the tooth socket develops.
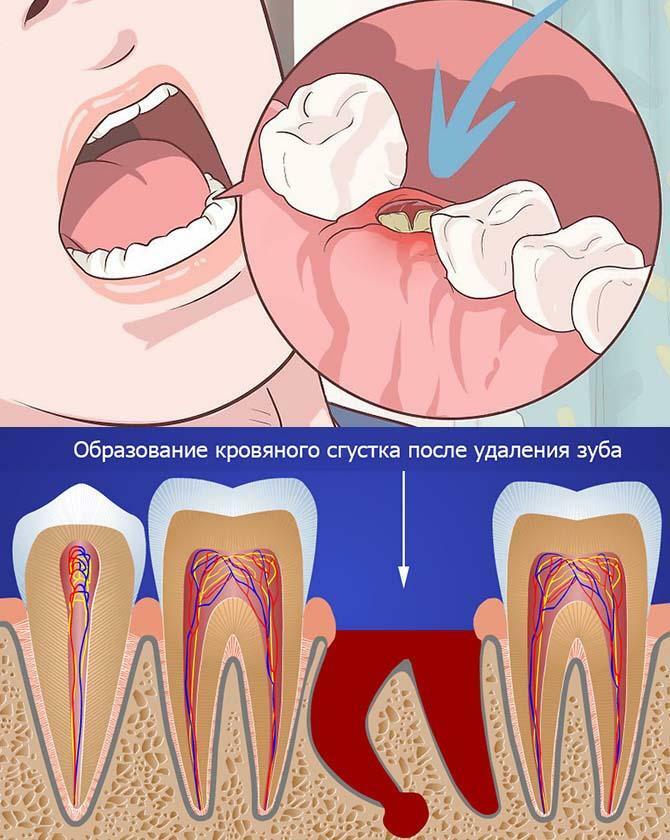
The main causes of the inflammatory process:
- Complex surgery. Difficult / traumatic removal is the cause of postoperative bone inflammation.
- Extraction of the figure of eight. The periodontal bone tissue has a dense structure and less vascularization. As a result, a dry socket is formed. In addition, wisdom teeth are distinguished by a complex anatomical structure of the roots, which contributes to more traumatic removal.
- Age. In older people, the metabolism, the regenerative capacity of the body slows down, the immune system deteriorates, which increases the risk of developing alveolitis after tooth extraction.
- Anesthesia. According to some studies, with excessive use of a drug that has a high concentration of a vasoconstrictor, ischemia may appear, the hole is difficult to fill with blood.
- Accompanying illnesses. Some pathologies disrupt the regenerative processes of tissues in the body. In people with immune diseases, diabetes mellitus, the risk of alveolitis after removal increases 5 times.
- Taking oral contraceptives. This is the only medication that can cause alveolitis. Due to estrogen, the fibrinolytic process intensifies, as a result of which the blood clot breaks down.
- Pathogenic microorganisms. Poor oral hygiene and the presence of infectious processes can provoke the development of alveolitis.
The reasons for the development of alveolitis include poor blood clotting, violation of medical recommendations after tooth extraction, when a person rinses his mouth, drinks through a straw, eats solid food, smokes.
Alveolitis does not appear in children, since milk teeth have a physiological specificity. They have a short root system, due to which the removal of a unit of the dentition does not provoke injury to the surrounding tissues. A shallow hole is formed. Alveolitis affects adults and older children.
Alveolitis symptoms
The inflammatory process in the hole is acute and chronic. Each species has its own symptoms.
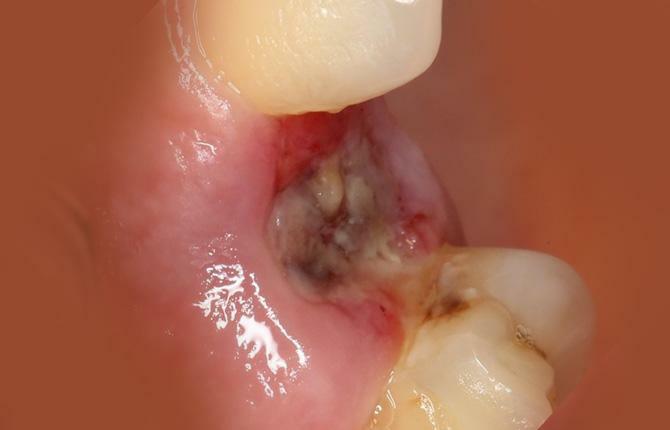
Acute form
The period lasts up to 2 weeks. There are the following forms:
- Serous. Symptoms of alveolitis appear on the second or third day after tooth extraction and last about 5-7 days. Aching painful sensations appear, which intensify when chewing. There were no changes in general well-being.
- Purulent. 2 days after removal, the painful syndrome changes. The pain is intense, constant. It can radiate to the area of the ear, jaw, occipital or temporal lobes, the adjacent tooth. There is an increase in body temperature, an increase in the submandibular lymph nodes. It smells unpleasant from the mouth. The cause of the unpleasant odor is the decomposition of a blood clot.
- Purulent-necrotic. This form of alveolitis is characterized by continuous pulsating painful sensations, the localization of which is half of the face on the side where the tooth was removed. The person becomes weakened, the body temperature rises, the head hurts. The well acquires a green tint, a pronounced unpleasant odor.
Chronic form
Acute inflammation begins to disappear after 2 weeks. Intense pain subsides, the smell from the mouth stops. The walls of the hole are cleaned. The chronic form of alveolitis after tooth extraction is characterized by the growth of granulation tissues. If you press on them, pus is released. The mucous membranes swell and become bluish.
Diagnostics of the alveolitis
If the first symptoms of the inflammatory process appear, it is recommended not to postpone the visit to the doctor. In a dental clinic, a person is examined, on the basis of which an accurate diagnosis will be made. To identify alveolitis after tooth extraction, in most cases, the doctor only needs to conduct a visual examination and listen to complaints.
If necessary, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed (X-ray, orthopantomogram, CT). Using these methods, foreign bodies in the hole, bone fragments, etc. are detected. In addition, such a diagnosis will make it possible to differentiate alveolitis from another maxillofacial pathology that has similar symptoms.
Treatment
If you do not start the treatment of the inflammatory process in a timely manner, a person will face serious complications. How to treat alveolitis is determined by a qualified dentist after examination and diagnosis.
Treatment measures are as follows:
- An anesthetic drug is injected into the affected area.
- The tooth socket is washed with antiseptic preparations (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, etc.). Pus, saliva, food are removed.
- With a special surgical instrument, the doctor cleans the alveolus, removes the disintegrated blood clot, tooth fragments, and existing granulations.
- The wound is re-disinfected.
- An antiseptic compress with Levomekol, Oflokain, etc., and a medicinal bandage are applied.
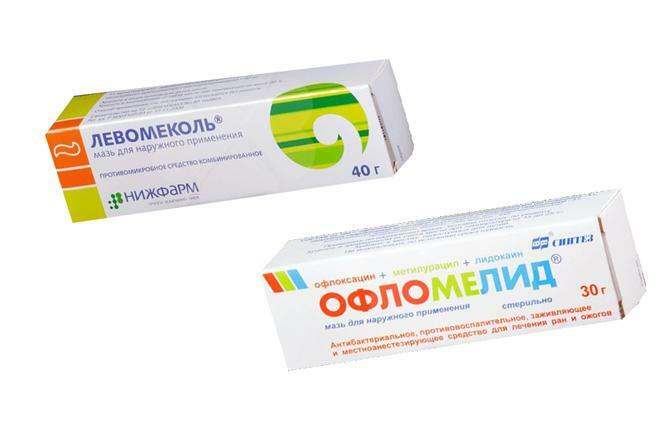
After the procedure, medication is prescribed. It consists in taking antibiotics, antiallergenic drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics. Physiotherapy can complement drug therapy.
Possible complications of alveolitis
In the absence of qualified treatment for alveolitis, the likelihood of developing:
- Cellulitis. An inflammatory process, the localization of which is subcutaneous, submucous and interstitial tissue. There is a sharp pain, the person cannot chew, swallow, talk. Facial asymmetry is observed, body temperature is increased. The appearance of meningitis is possible.
- Abscess. Tissues disintegrate, there is pain, fever.
- Osteomyelitis. Infectious inflammatory process in the jaw bones. The person does not feel well, the head and jaw hurt, the temperature rises.
- Blood infections.
To avoid the appearance of these complications, it is necessary to contact the dental clinic in a timely manner and not self-medicate alveolitis.
Preventive actions
To reduce the risk of dangerous complications in alveolitis, it is necessary to carefully observe preventive measures after tooth extraction, as well as to properly care for the wound. Prevention of alveolitis after removal is as follows:
- For 24 hours after removal, do not do something that requires effort or tension.
- Do not touch the hole with your tongue or other object (match, finger, etc.) for at least 8 hours.
- In the next day after removal, eat only liquid and soft foods. Do not chew on the side where the tooth was extracted.
- Do not drink or eat hot food for at least 24 hours. This can provoke the dissolution of the forming blood clot.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol for a few days. During smoking, a vacuum is formed in the oral cavity, due to which the blood clot can be displaced, a dry socket is formed, and healing slows down.
- In the next day, do not brush teeth that are close to the wound. For several days, brush your teeth with a soft brush.
- Do not go to the sauna, bath.
- Carefully observe hygiene measures, take care of the removal site.
- Stop using the rinse aid during the day. It can irritate the wound.
To avoid the development of alveolitis after tooth extraction, you must conscientiously observe all preventive recommendations, and when the first signs of alveolitis appear, immediately visit dental clinic. The earlier treatment begins, the lower the risk of dangerous health complications.
Have you had your teeth removed? Have you faced any complications after that? If so, what treatment worked?
Why does alveolitis occur after tooth extraction? Explains the dental surgeon:
We also suggest that you familiarize yourself with our article: Causes of a sour taste in the mouth.