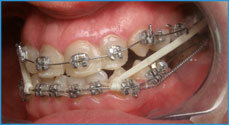
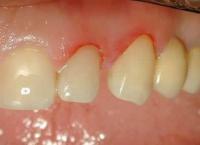
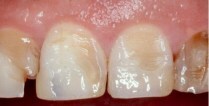
Periodontal disease: what is it, causes of the disease, symptoms, treatment, diagnosis, types and degrees, forms, prevention
Periodontal disease is an atrophic lesion of the deep periodontal tissue. It is characterized by a violation of the ligamentous apparatus, a decrease in the stability of the dentition. Differs in a progressive course with subsequent exposure of the neck of the teeth.
Content
- 1 What is periodontal disease
- 2 Causes of the disease
- 3 Types and symptoms
- 4 Diagnosis of periodontal disease
-
5 Periodontal disease treatment
- 5.1 Drug therapy
- 6 Prevention of periodontal disease
What is periodontal disease
It is based on the process of sclerosis of the vascular walls, which leads to a lack of oxygen, nutrients, and a violation of mineral metabolism. Dystrophic changes occur in the bone and soft tissue surrounding the tooth, as well as periodontal fibers.
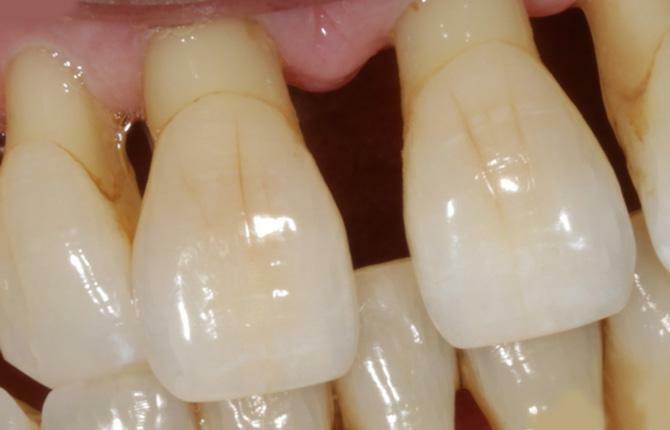
The word "periodontal disease" is not used quite correctly, calling so any pathology of the gums. In fact, it is an uncommon disease. It is found in 3-10% of patients who seek help. Most are diagnosed with chronic periodontitis.
Periodontal disease of the teeth is manifested by a decrease in the height of the gums and exposure of the roots of the teeth, without the presence of an inflammatory process. In turn, with periodontitis, bleeding occurs, pain when brushing teeth, which indicates inflammation of the gums.
Causes of the disease
The unconditional reason for the appearance of periodontal disease is dental plaque. As a result of the vital activity of microorganisms, the gums become loose, the connection between the tooth and the gum is destroyed. Plaque penetrates deeply, hardens and affects the enamel.
The roots become bare with age, the teeth become mobile. In addition to aesthetic problems, older people with periodontal disease experience discomfort, cannot chew normally. Oral care becomes a problem, which further exacerbates the situation. There are other factors that increase your risk of periodontal disease:
- endocrine diseases;
- hypovitaminosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- disorders of the nervous system;
- disruption of the digestive tract.
The cause of dystrophic changes is anomalies in the structure of the masticatory apparatus - this is a violation of the bite, an incorrect location of the dentition. And also fillings, caries, tooth loss as a result of improper care or untimely treatment.
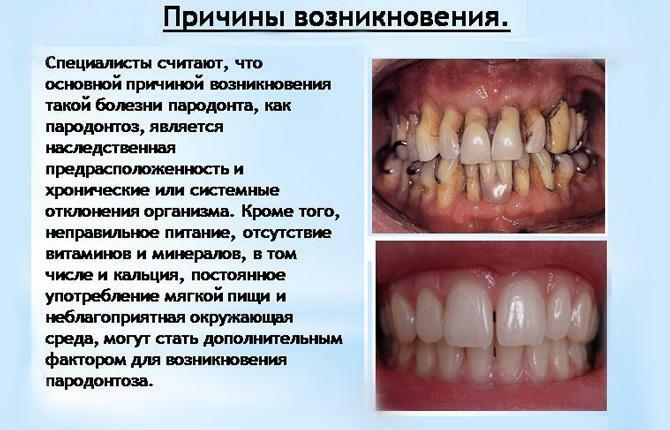
The diet of most people is dominated by mechanically and thermally processed food. There are not enough raw vegetables and fruits. As a result, there is no physiological cleaning of the gums and teeth.
Types and symptoms
Periodontal disease is acute and chronic. The first type is rare, mainly in older people against the background of common diseases. Sometimes it is due to a hereditary predisposition. A chronic illness can last for decades. Therefore, the likelihood of prolonging the disease to a serious condition and not noticing the signs is minimal.
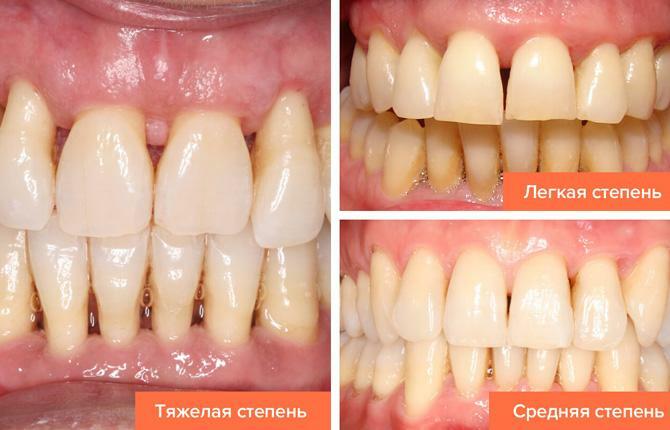
Local periodontal disease is characterized by affection of one to three teeth. The generalized form is a disease of the entire lower or upper jaw at once. In case of untimely diagnosis and treatment, the local form is transformed into a generalized one. Periodontal disease is classified by severity:
- The mild degree is characterized by slight itching, burning, the gums seem to pulsate. The teeth are exposed up to 2 mm, and mineral deposits are visible on them. From the mouth appears bad smell.
- With an average degree of periodontal disease, signs of discomfort increase - pain in the gums, reaction to cold, hot, sour. The necks of the teeth are bare by 3-4 mm. The distance between them increases, slight loosening is noted.
- In severe cases, the roots are strongly exposed, the teeth are loose, and some can be easily extracted. Gums are dense, whitened. Chronic sensitivity is noted, even when talking, which significantly impairs the quality of life.
With periodontal disease, a person reacts sharply to all types of stimuli. In this regard, nervousness, the risk of stressful situations increase, the psychoemotional state is disturbed. When the connection of the tooth with the gum is broken, plaques form on the exposed roots. The jawbone and septa atrophy, resulting in tooth shakiness.
And although periodontal disease is not infectious, with a neglected form and the addition of pathogenic bacterial flora, a purulent process occurs. In this situation, the main role is played by the accumulation of food debris in pockets, the lack of proper hygienic care.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease
For the choice of treatment tactics, it is important to determine the degree of damage, to find the cause that led to the malnutrition of the gums. The survey consists of the following activities:
- questioning the patient about complaints;
- collection of anamnesis;
- examination of the oral cavity and assessment of the condition;
- x-ray;
- study of tissue blood filling - rheography;
- determination of the degree of oxygen deficiency;
- measurement of bone density.
If the blood supply is disturbed, the polarography method is used. With its help, the level of tissue oxygenation is determined. Functional studies can predict the effectiveness of the treatment of periodontal disease. The main criteria for making a diagnosis are the presence of sclerosed bone foci in the image and the absence of pockets.
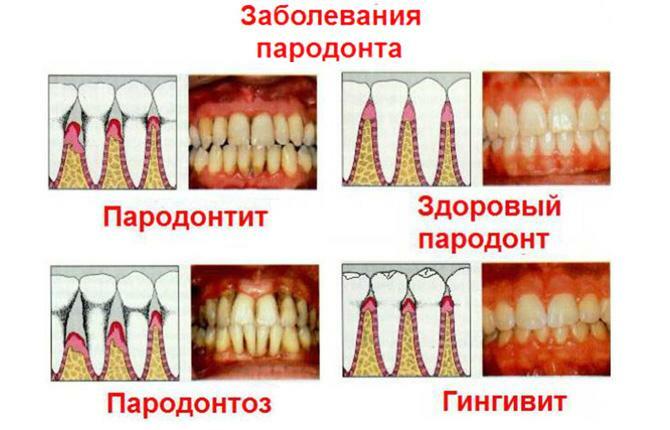
Differential diagnosis with catarrhal gingivitis is required. Sometimes, on x-ray examination, there are clear signs of periodontal disease, and a visual examination shows an inflammatory process of the gums. This often happens when soft plaque builds up due to poor oral care.
Periodontal disease treatment
The goal of therapy is to normalize metabolism, provide tissues with useful substances. Individual characteristics of a person, age and existing systemic diseases are taken into account. Complex therapy includes regular oral cavity sanitation, adjustment of hygiene procedures and means.
In the presence of local problems, professional oral hygiene and ultrasonic cleaning are necessary. If necessary, the dentist corrects the bite, selects a means to reduce sensitivity, and installs prostheses instead of missing teeth.
Sometimes teeth are reshaped to improve contact between the upper and lower rows. When mobility or fan-shaped divergence appears, the splinting method is used.
Massage and physiotherapy are used to improve local blood circulation:
- mechanical stimulation of tissues;
- electrophoresis with heparin;
- phonophoresis with vitamin formulations;
- diadynamic;
- magnetotherapy;
- hardware vacuum massage;
- exposure to ultraviolet infrared or laser radiation.
Drug therapy
Medicines for periodontal disease are aimed at stimulating blood circulation, reducing hypoxia. The doctor selects drugs individually for each patient. These are products containing amino acids, proteins, antioxidants. Vitamins and microelements contribute to the acceleration of metabolism:
- folic acid to improve metabolic processes;
- zinc and calcium stimulate bone regeneration;
- selenium has an immunomodulatory effect;
- vitamin complex.
If periodontal disease develops with diabetes mellitus or gastrointestinal disease, vitamins of group "B" are shown. With a complicated inflammatory process, antibacterial drugs are added.

To protect against destruction of periodontal tissues, special plates are used. They are made from natural materials, contain gelatin, collagen, sodium alginate. They have a tonic effect.
Medicinal components increase vascular tone, speed up metabolism. They are attached to the gums by pressing in between the teeth. The plate lasts for 6-10 hours. The residues are rinsed out.
Since periodontal disease often has a long chronic course, the question arises of how to treat periodontal disease at home. This treatment includes normal dental care using special toothpastes and a finger massage for the gums with gel.
It is performed daily in the morning after a hygiene procedure. A finger is carried out in a circular motion, starting from the front teeth, moving to the molars. The procedure lasts from 3 to 5 minutes on each side of the jaw. You can use the gel:
- Metrogyl Denta;
- Holisal;
- Kamistad.
Manipulation is not carried out for gum disease and bleeding.
For hygienic care for periodontal disease, the doctor can suggest a suitable remedy. Apart from abrasive substances, medicinal toothpastes contain antiseptics, oils and plant extracts, trace elements and vitamins. These are such care products as:
- Lacalut Active;
- Parodontax;
- PresiDENT;
- Forest balm.
Prevention of periodontal disease
An important factor is regular dental check-ups, proper oral care. It is recommended to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day, and if possible after each meal. For care, you need to choose a quality toothbrush and toothpaste. Interdental spaces are cleaned with a toothpick, floss, sugar-free chewing gum.
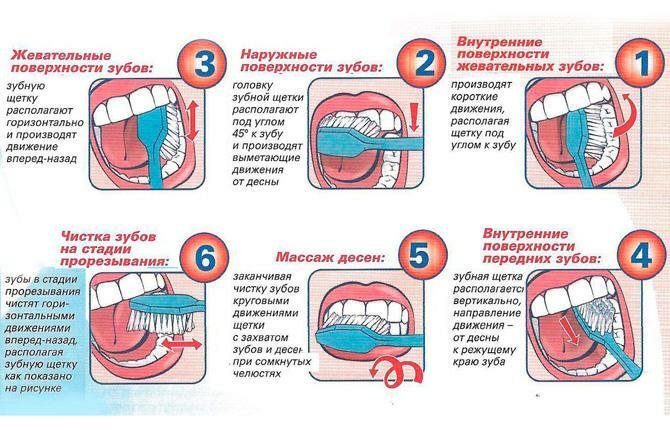
How to brush your teeth properly
To prevent periodontal disease, folk remedies are widely used - these are herbal decoctions, infusions and alcoholic tinctures for rinsing and treating the gums. Most often used for these purposes:
- propolis;
- oak bark;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- sage.
In order to prevent the development of degenerative changes in bone structures, the following conditions are necessary:
- elimination of dentition anomalies in childhood;
- correction of common diseases;
- vitamin therapy;
- balanced diet;
- to give up smoking;
- thorough oral hygiene.
If there is a risk of developing periodontal disease, you need to visit the dentist 2 times a year and carry out professional teeth cleaning.
You should not look for a miracle cure for periodontal disease, it does not exist. The disease cannot be attributed only to systemic disorders of the body. In each specific situation, there is a root cause that, with age, will lead to exposure of roots and loss of teeth.
Tell us in the comments how you prevent gum disease. Share a useful article with your friends on social networks and save it to bookmarks.
The video will discuss the causes of oral diseases (unknown facts), how to treat periodontal disease:
Alveolitis after tooth extraction - how the disease threatens can be learned from our article.
Sources:
- https://32zuba.guru/parodontoz/klassifikatsiya
- https://zubzdorov.online/bolezni/parodontologiya/parodontoz
- https://www.nrmed.ru/rus/dlya-vzroslykh/stomatologiya/parodontoz
- https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_stomatology
- https://24stoma.ru/parodontoz-lechenie.html