What is sigmoidoscopy and how is it done
Intestinal endoscopic research is a very productive area of diagnostic medicine. Requiring no surgical access, long-term complex preparation, being a safe and practically painless procedure, sigmoidoscopy can replace a whole range of complex diagnostic procedures. It is carried out in a variety of cases, with suspicion of various diseases, it is an indispensable method in gastroenterology in general and coloproctology in particular. However, this procedure often instills fear in people: they do not know what sigmoidoscopy is, and how it is done, and they are afraid of this. To allay fears, it is important to understand how and why the research is being conducted.
What is sigmoidoscopy and how is it done
Content
- 1 Anatomical excursion
- 2 Indications
- 3 Contraindications
-
4 Preparation
- 4.1 Video: Intestinal sigmoidoscopy: what is it, preparation
-
5 Equipment used
- 5.1 Video: Equipment for proctology
- 6 How is the procedure carried out
-
7 Complications
- 7.1 Video - Intestinal sigmoidoscopy
Anatomical excursion
It is difficult to understand the essence of the study without at least minimal knowledge of the anatomy of the area under study. So, the human intestine is divided into small and large intestines, each of which, in turn, is also divided into sections. The colon includes the following sections:
- blind;
- ascending colon;
- transverse colon;
- descending colonic;
- sigmoid;
- straight.
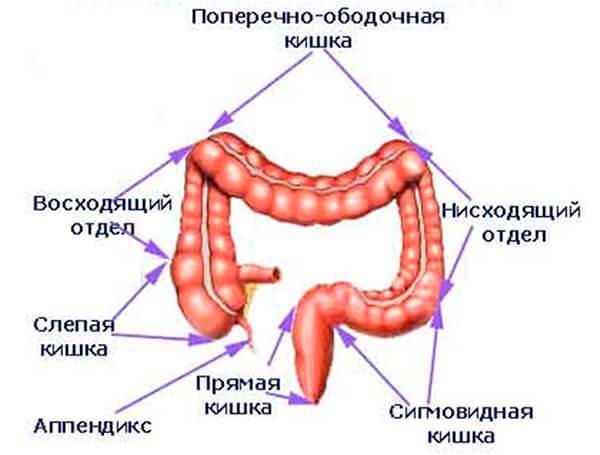
Large intestine
The purpose of sigmoidoscopy is to study the rectum and the lowermost parts of the sigmoid. The rectum is located in a small pelvis, its length ranges from 14 to 18 cm. An extremely important parameter is the structure of the intestinal wall. It consists of four layers:
- muscular membrane;
- muscle plate of the mucous membrane;
- submucosa;
- slime layer.

Rectum
Table. The value of the anatomical features of the rectum for diagnosis.
| Anatomical feature | Diagnostic value |
|---|---|
| As the name suggests, the rectum has no curves, unlike other parts of the intestine. |
This is important for the choice of diagnostic equipment: for sigmoidoscopy, a rigid endoscope is used (although today flexible models have also been developed and introduced). |
| The diameter of the organ is not the same: at the moment of transition from the sigmoid to the straight line, it is about 4 cm, and in the widest part - more than 7 cm. |
This also imposes its limitations on the devices used: the diameter of the endoscope should not be larger than the diameter of the intestine at its narrowest part. |
| The rectum can be conditionally divided into an ampulla (located in the upper part, wide) and an anal canal (about 4 cm long). |
One of the subspecies of sigmoidoscopy is anoscopy. It consists in the study of the anal canal itself. Short anoscopes are used without a claim for a deeper examination. This procedure requires less preparation and is easier to carry out. |
| During sigmoidoscopy, only the mucous membrane is studied, which is the inner wall of the organ. Taking into account the highly developed layers under the mucous membrane, this membrane itself is collected in folds. | This is important, because the folds can hide damage, polyps, ulcers, excessive folding or its absence also speaks of pathology. This area can be explored closely when explored. |
| Anal sinuses are grooves between folds. | This is an area that is often damaged and is the gateway for infectious agents, which are abundant in the intestine. This is how proctitis and other diseases develop. |
| In the area of the anal canal, there are long longitudinal deep folds. There are venous plexuses in the sinuses between them. | Plexus vein dilation or its "prolapse" is called hemorrhoids and cannot always be detected clinically (in the early stages, hemorrhoids do not come out of the intestine). |
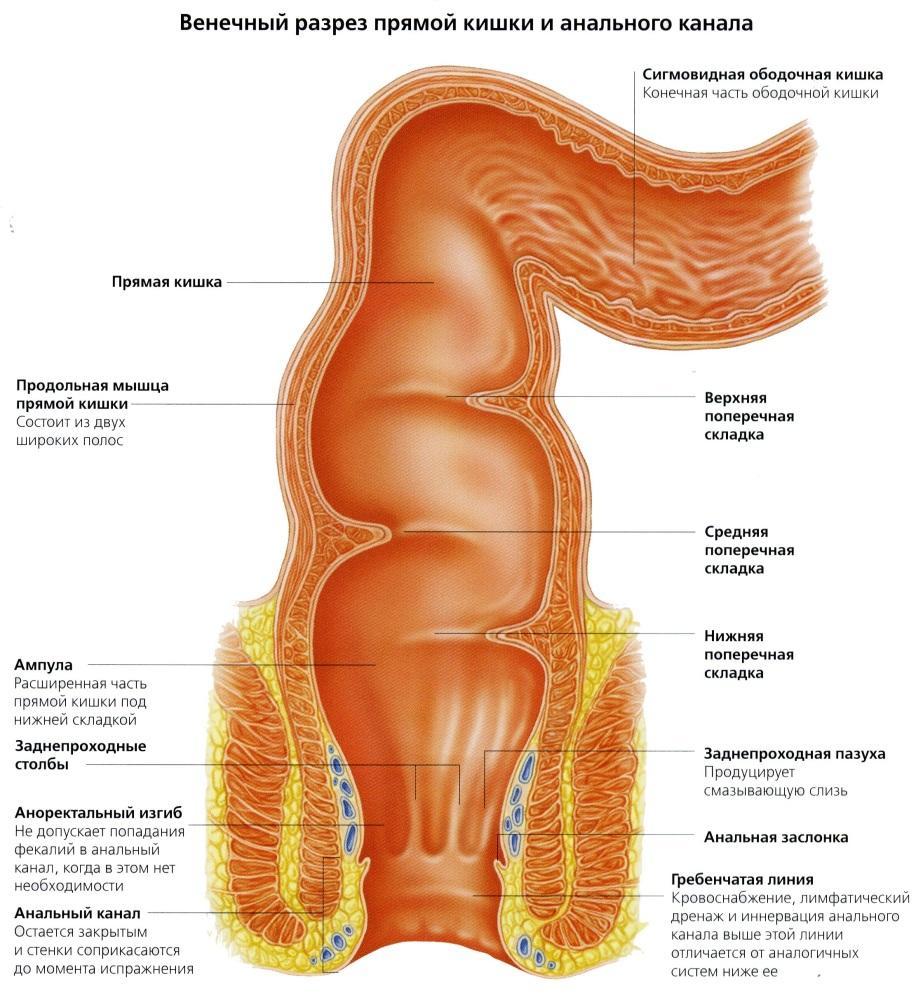
The rectum and anal canal together make up the last part of the gastrointestinal tract. They receive food waste in the form of feces and allow them to leave the body
Thus, every anatomical detail is important for sigmoidoscopy: something helps in carrying out the procedure, something limits it, and something requires increased attention.
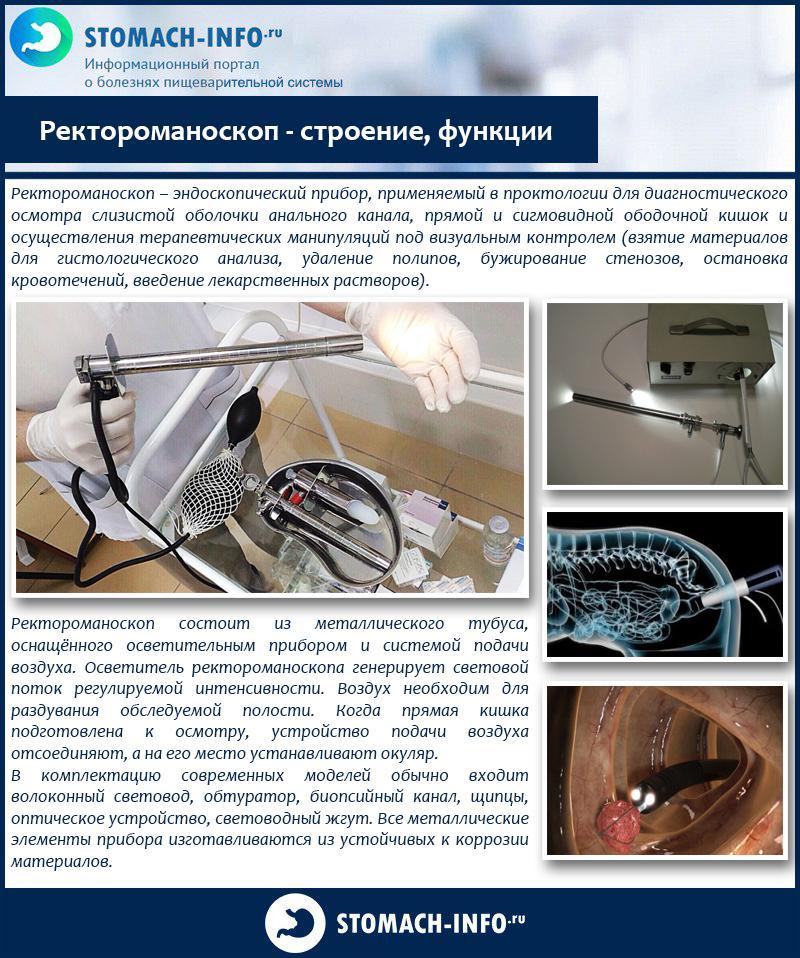
Rectoromanoscope - structure, functions
Indications
Sigmoidoscopy is not done "right and left." Despite the safety, the procedure is not very pleasant for the patient, and many refuse it, even realizing how informative it is. Therefore, there is a clear list of indications for conducting research.
-
The appearance of impurities in the feces. These include pus, mucus, a large amount of undigested fiber, and especially blood. Any suspicion of hematochezia (blood in the stool) is an unquestioning indication for sigmoidoscopy.
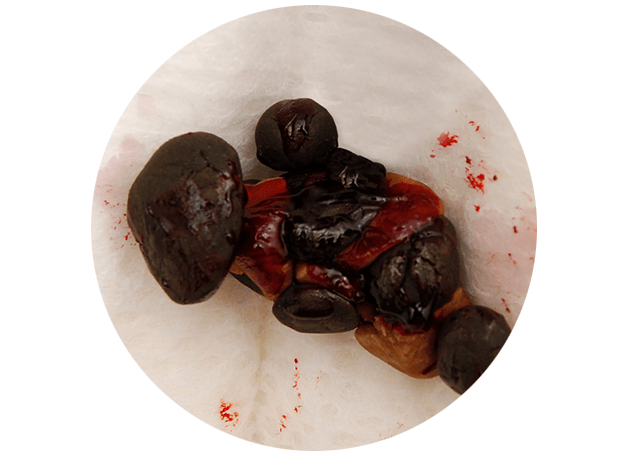

Blood in the stool
- Pain in the rectal area. This can be the lower abdomen, the anus, the perineum. An especially important diagnostic criterion is pain of indeterminate localization, which does not pass for a long time, is not intense, of a pulling and pressing nature.
-
Feeling of fullness in the intestines, weakness, lethargy, unstable stools, discomfort or pain. All these signs together can talk about intestinal cancer.
Bowel cancer symptoms
- Abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, weight loss, intoxication syndrome. These phenomena may indicate the development of inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
-
Anemia. For people under 40, when a decrease in hemoglobin level is detected, EGD is more often shown, but at an older age, the search for a bleeding site begins with the rectum.
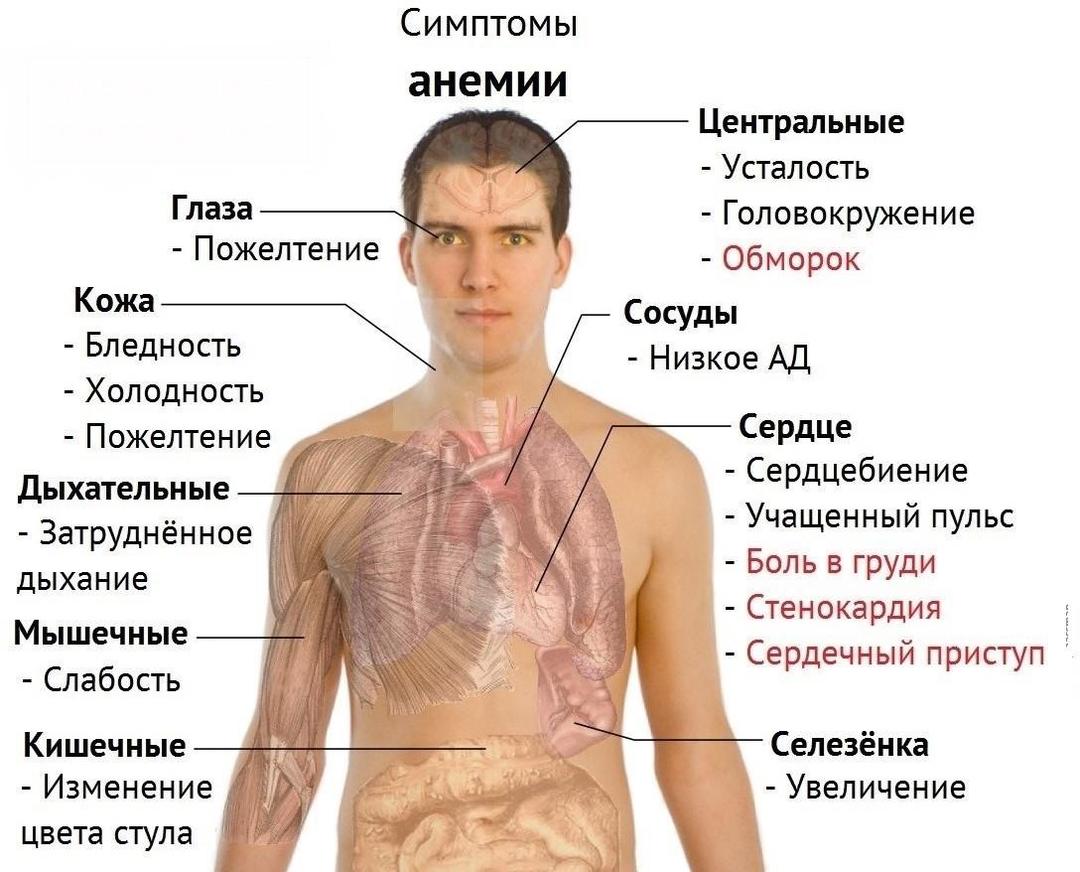
Symptoms of anemia
- Age over 40. In connection with the aggravating situation with respect to coloproctological cancer, people of this age group, the World Health Organization recommends an annual bowel examination.
- Heredity for bowel disease in combination with signs of disruption of the work of this organ.
- The presence of cancer of the pelvic organs. Sigmoidoscopy is performed to determine the presence of metastasis or tumor invasion into the rectum.
On examination by a proctologist
Contraindications
There are no situations in which it is categorically impossible to conduct research. However, there are temporary contraindications, focusing on which, the doctor is forced to postpone the procedure.
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the anus, sphincter, perineum, peri-rectal tissue.
- Complete obstruction of the intestine due to coprolithiasis, tumor, polyp.
- Continued bleeding.
- Chronic diseases of the pelvic organs in the acute stage.
- There is only one absolute contraindication - the patient's refusal from the procedure.

Refusal of the patient from the procedure
Preparation
Doctors of many specialties can prescribe research. First of all, these are, of course, proctologists. However, referrals are given by gastroenterologists, gynecologists, surgeons, hematologists and other specialists. Information about the necessary preparation is provided by the referring doctor, who must also explain how and why the procedure is performed.
The first and most important stage is colon cleansing. Two days before the study, it is recommended to switch to a sparing diet: reduce fiber levels, give up alcohol, fatty foods, fast food, spicy and salty foods. It is not recommended to use products that produce gas - cabbage, black bread, fresh baked goods, fermented milk products. It is worth eating three or four times a day in medium sized servings. The last meal should be taken 18 hours before the examination, tea can be drunk 12 hours before the procedure. In the morning before the examination, it is forbidden to eat.

Preparation for the procedure involves a special diet
Before the procedure, it is recommended give an enema. This requirement is justified: if the intestinal wall is contaminated with feces, the doctor will not be able to thoroughly study the state of the mucous membrane. Therefore, the intestines are washed in the evening, on the eve of the study, and, if possible, an enema is carried out immediately before the diagnostic measure.
Sometimes you are asked to bring a diaper or a sheet with you to the procedure, although many clinics today have disposable underwear. The patient must have with him the results of previous studies, if any, as well as a referral from a doctor.
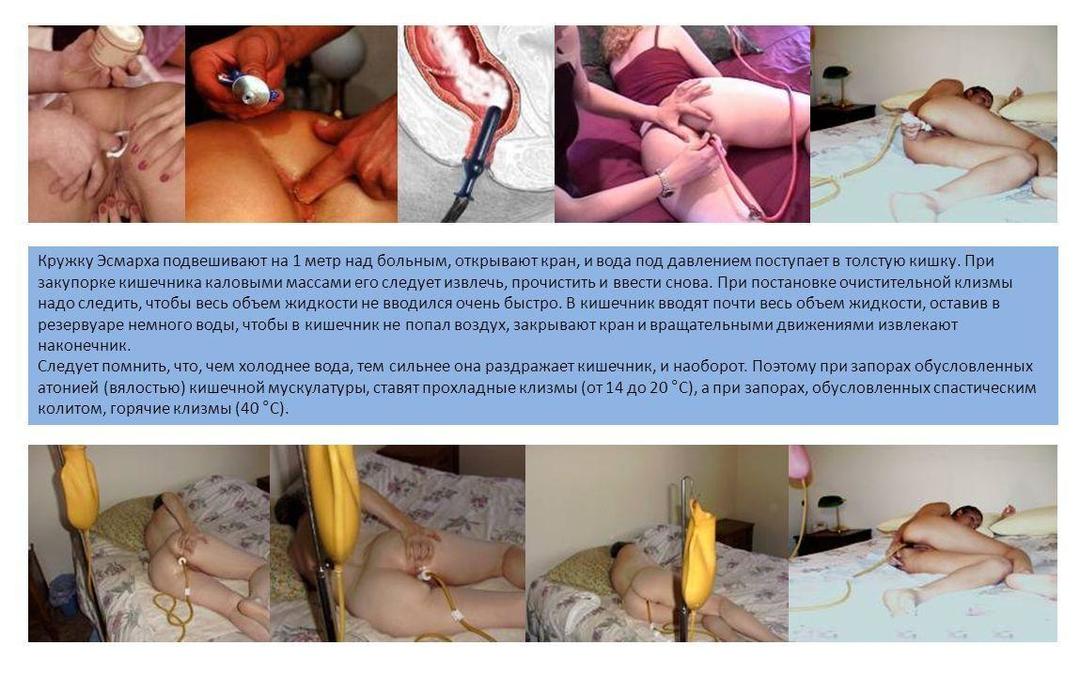
Enema at home - photo
The most important stage of preparation is formation of the correct psychological mood. This is especially true for men. It is important to understand that there is nothing terrible, shameful, or shameful in the procedure. The more calm and relaxed the patient is, the easier and faster the event will take place.
Video: Intestinal sigmoidoscopy: what is it, preparation
Equipment used
For sigmoidoscopy, a rectoscope or anoscope is required. The rectoscope can be rigid (more often) or flexible (new technology from the German company Karl Storz). Rigid rectoscopes look like metal tubes with an eyepiece at one end and a video system at the other. They can be longer for adults or shorter for children. They are also divided into diagnostic and operating rooms (the latter have the ability to introduce a surgical instrument into the intestine). The diameter of the tube can be different - from 10 to 20 mm, the length ranges from 50 to 300 mm. This is a reusable equipment, therefore, after each patient, the device undergoes a complex multi-stage disinfection and sterilization procedure.

Rectoscope with optical fiber and obturator
There are also disposable rectoscopes. They are made of high quality plastic and are disposed of after each procedure.
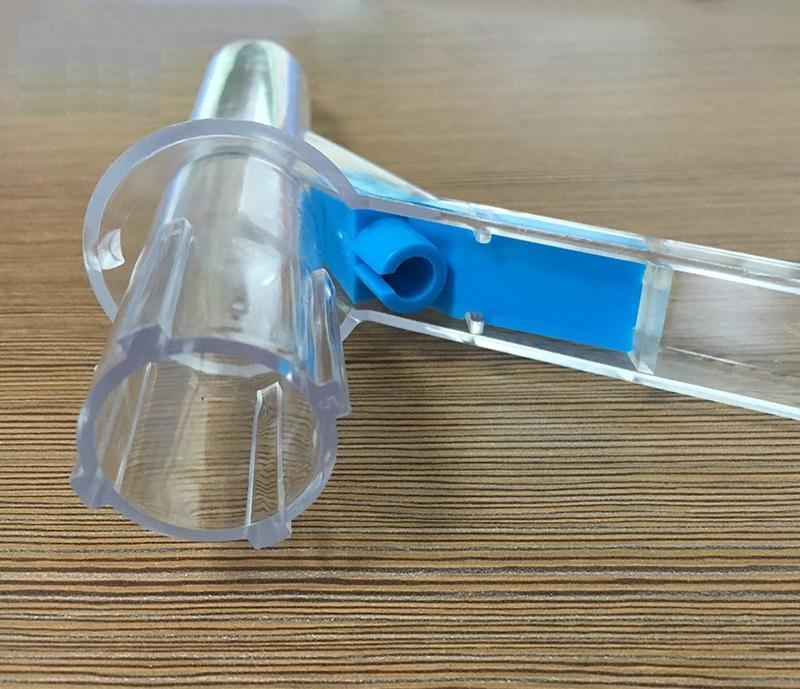

Plastic disposable rectoscope
Since the intestine has no bends, there is no need to change the trajectory of the device, therefore it is completely solid, without the possibility of bending it in any way. Usually a blower is connected to the rectoscope - a "pear", similar to the one that injects air into the tonometer cuff. This is done in order to be able to straighten the folds of the mucous membrane with air and carefully examine all its areas.

Rectoscope with optical fiber and obturator, with biopsy channel
Flexible rectoscopes are an innovation. Not all healthcare facilities have them. Their use is more comfortable for people, since they cause less discomfort in the anus. In addition, the device is smaller in diameter, flexible and soft, therefore it is almost not felt in the intestine.
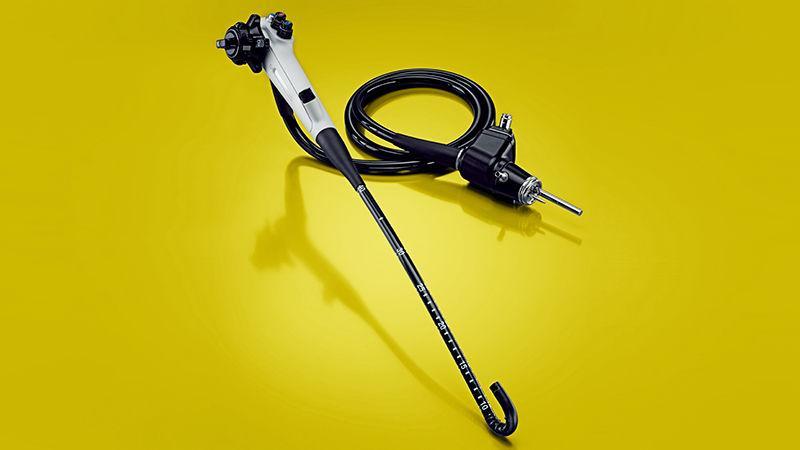

Flexible rectoscope
In addition to a direct visual assessment of the state of the mucous membrane, rectoscopes allow:
- take material for research (biopsy);
- photograph and record on video everything that the doctor sees inside the intestine;
- carry out surgical manipulations (from stopping bleeding and removing a polyp to extensive proctological operations - depending on the type of rectoscope).
If the problem is in the anal canal and the large rectoscope cannot see the damage, the doctor may take an anoscope. This is the same metal tube, only of a much shorter length. It allows you to study the anus, the anal canal in more detail.
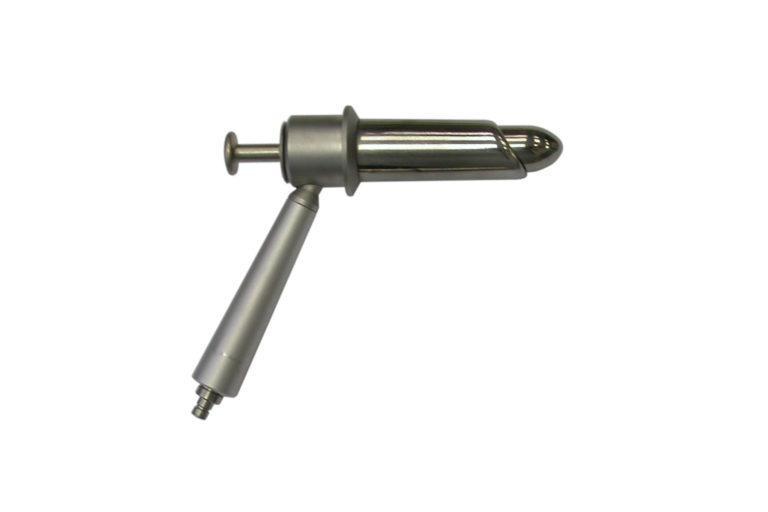

Anoscope
Video: Equipment for proctology
How is the procedure carried out
First of all, as soon as the patient enters the doctor's office, they explain to him what they will do, how and why, as well as what risks this manipulation entails. If a person agrees to the study, he must sign an informed voluntary consent, only after that the doctor has the right to touch the patient.
Remove clothing below the waist, including underwear, and sit on the couch. When using a rigid rectoscope, the patient should take a knee-elbow position, and when performing sigmoidoscopy with flexible equipment, you can lie on the left side and tighten your knees. Before introducing the equipment into the rectum, the doctor must conduct a digital rectal examination. It is needed in order to assess the muscle tone of the rectum, to identify the presence of edema, changes in the walls of the organ, and soreness.

Digital rectal examination
After conducting a finger examination, the doctor changes gloves, liberally treats the device with medical petroleum jelly and gently inserts it into the intestine. With the proper competence of the specialist and the absence of resistance from the patient (a sharp change in body position, muscle tension, etc.) the procedure does not cause much discomfort and certainly does not carry pain sensations. The manipulation lasts on average from 10 to 30 minutes - depending on the individual characteristics of the person, the complexity of the situation, the goals of the diagnosis.
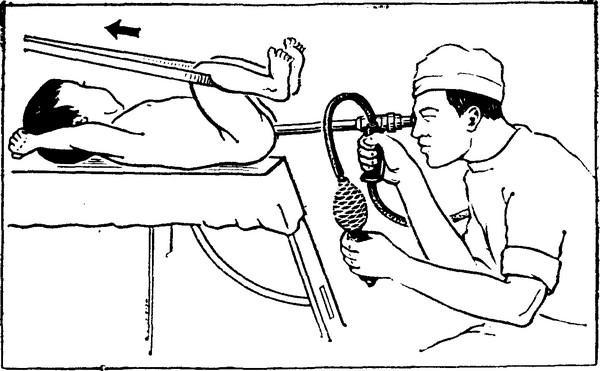
Intestinal sigmoidoscopy
The recovery period after the procedure is not required. There may be a mild burning sensation in the anus, but it goes away within a few hours.
Complications
During the procedure, complications are very rare. However, there are such negative consequences as damage to the intestinal wall (with insufficient competence of the doctor, a sharp change in body position on the part of the patient), bleeding. If such complications develop, the patient will need emergency surgery.

Rectoscopy in the knee-elbow position
Thus, sigmoidoscopy is a safe, simple and very informative procedure. It is mandatory before colon surgery, as a preparatory method before colonoscopy, with suspicion of pathology of the straight or end section of the sigmoid intestines. It is not worth giving up on it, despite the seeming amount of unpleasant sensations.