Werlhof's disease (thrombocytopenic purpura): what is it, symptoms and treatment
About 40% of all hemorrhagic rashes are associated with thrombocytopenic purpura. Its prevalence is from 1 to 13 people per 100 thousand population depending on the region.
Among all diathesis of a hemorrhagic nature, thrombocytopenic purpura ranks first in prevalence among preschool children, in adults, cider is less common and mainly affects women.
Content
- What is thrombocytopenic purpura?
- Causes of occurrence
- Risk factors
- Symptoms of thrombocytopenic purpura
- Acute thrombocytopenic purpura
- Chronic thrombocytopenic purpura
- Thrombotic form of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of Werlhof's disease
- Conservative therapy
- Surgery
- Traditional medicine
- Diet
- Forecast
- Prophylaxis
- Related Videos
What is thrombocytopenic purpura?
Thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof disease, ITP, primary immune thrombocytopenia) - a disease characterized by a reduced level of platelets in the blood (thrombocytopenia).
The life span of platelets ranges from 7 to 10 days.
In thrombocytopenic purpura, the immune system suppresses its own blood cells, and they die within a few hours. The consequence of this is an increased bleeding time.
Thrombocytopenic purpura is divided into acute, recurrent and chronic forms of the course of the disease.
- Sharp form predominantly children are ill, the disease lasts about 6 months, after recovery, the level of platelets in the blood normalizes, there are no relapses.
- Chronic form lasts more than 6 months, affects adults.
- Recurrent form has a cyclical nature of the course: relapses are replaced by periods of relief. According to the frequency of exacerbations, the disease is divided into frequent, rare, and continuously recurrent.
Depending on the cause of the disease, thrombocytopenic purpura is divided into the following forms:
- isoimmune (alloimmune) thrombocytopenia occurs during intrauterine development, is associated with:
- penetration of antiplatelet antibodies through the placenta from mother to child, a reduced level of platelets is observed in the prenatal period and in the first months after birth;
- antiplatelet antibodies appear after blood transfusion;
- heteroimmune (haptenic) thrombocytopenia occurs as a result of changes in platelet antigens, as a result, the immune system perceives its own blood cells as foreign. Such a reaction sometimes occurs as a result of a viral, bacterial infection, or after taking certain medications. If heteroimmune thrombocytopenia does not disappear within six months, then it is considered autoimmune.
- Autoimmune thrombocytopenia (AITP) is a variety of forms, including idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (Werlhof disease), the cause of which has not been established.
Causes of occurrence

The reasons for the development of thrombocytic purpura remain unclear until the end.
- 45% of cases thrombocytic purpura is idiopathic (Werlhof disease), that is, the causes have not been established.
- 40% of cases this pathology is associated with an infectious disease and occurs 2-3 weeks after recovery. Most often, an infection of a viral origin (measles, chicken pox, rubella, HIV infection, whooping cough, etc.), much less often bacterial (malaria, typhoid fever, etc.)
Also, the occurrence of thrombocytopenic purpura can be facilitated by:
- severe hypothermia;
- trauma;
- excessive insolation (ultraviolet radiation);
- radiation;
- complication after the administration of the vaccine;
- taking certain medications (barbiturates, salicylic acid, antibiotics, estrogens, arsenic, mercury salts);
- disruption of the hematopoietic system;
- neoplasms localized in the bone marrow;
- vascular prosthetics due to mechanical damage to blood cells;
- taking some oral contraceptives.
Read also:Multiple myeloma: what it is, why it occurs, what provokes the disease, symptoms and treatment
Risk factors
Thrombocytopenic purpura can be found in children and adults of all ages, but there are factors that increase the risk of developing this condition:
- belonging to the female sex (in women, thrombocytopenic purpura occurs three times more often than in men);
- a recent infectious disease increases the risk of developing the disease, especially in children;
- heredity (a disease in close relatives increases the risk of thrombocytopenia);
- frequent stress.
Symptoms of thrombocytopenic purpura


Werlhof's disease in its course has three stages:
- hemorrhagic crisis - manifestations are pronounced, in the blood test, a reduced level of platelets is noted;
- clinical remission - the external signs of thrombocytopenia fade away, but the changes characteristic of it in the blood test are still there;
- clinical and hematological remission - the tests return to normal, there are no clinical signs of the disease either.
The first signs of thrombocytopenia appear when the level of platelets in the blood drops below 50 * 109 / l, this happens about after 2-3 weeks after the factor that caused the disease was affected.
Acute thrombocytopenic purpura

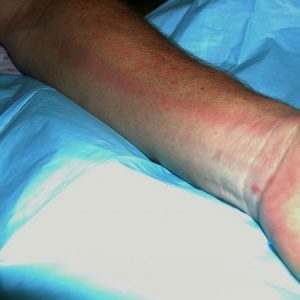
The disease begins suddenly: hemorrhages appear on the skin and mucous membranes (see. photo above), bleeding begins, the general condition worsens, the skin becomes pale, blood pressure decreases.
Body temperature can reach 38 degrees. Lymph nodes become inflamed and painful.
Chronic thrombocytopenic purpura


The main symptom of the disease is rashes. They appear on the skin and mucous membranes, are painful, and vary in size.
Rashes can be of several types:
- petechiae (small dots);
- Vibex (the rash gathers in groups or stripes);
- large spots, including petechiae and stripes.
The color of fresh rashes is purple. Fading "rashes are yellow or green. The rash on the skin can be wet or dry.
In case of wet rashes, bleeding is possible, especially at night.
Typical location: on the chest, abdomen, upper and lower extremities, rarely on the face and neck. At the same time, a rash appears on the mucous membranes.
Some localizations are inaccessible for examination without special equipment: the tympanic membrane, the serous membrane of the brain and other organs.
An important symptom of the disease is bleeding of varying intensity. The most common bleeding:
- nose bleed;
- from the gums and in places of extracted teeth;
- after tonsil surgery;
- when coughing from the respiratory tract;
- from the digestive tract with vomit or urine;
- uterine bleeding.
Bleeding occurs either simultaneously with skin rashes, or after.
Body temperature with chronic thrombocytopenic purpura is not elevated, sometimes there is a rapid heartbeat, in children, lymph nodes increase and become painful.
Read also:Malaria
Thrombotic form of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura.

This form of the disease is the most dangerous of all.
Characterized by an acute, spontaneous onset, malignant course.
Due to the formation of hyaline blood clots, the blood supply to various organs is disrupted.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) of the thrombotic type is characterized by the following symptoms:
- hemorrhagic rash;
- fever;
- acute renal failure (it is she who is the cause of death);
- convulsions, impaired sensitivity;
- jaundice;
- joint pain;
- neurosis, confusion, coma;
- arrhythmia;
- abdominal pain.
Diagnostics
To diagnose Werlhof's disease, a survey and examination of the patient is carried out. To confirm the presence of the disease, laboratory methods for examining blood, urine and spinal cord are used.
In a chronic course, hematological parameters may be within normal limits.
In the course of the survey, a hematologist (a doctor specializing in blood diseases) finds out the presence of a history of factors that contribute to the development of thrombocytopenic purpura: infection with viruses, taking medications, vaccinations, exposure to radiation and etc.
Examination of the patient reveals a characteristic sign of this disease - a hemorrhagic rash on the skin and mucous membranes. Also, the doctor can conduct a series of tests that make it possible to identify hemorrhages in the skin:
- Cuff test used in adults and children from 3 years old. The patient is put on a cuff to measure the pressure, if after 10 minutes punctate hemorrhages are found, the test is considered positive.
- Harness sample only used in adults. When applying a medical tourniquet, hemorrhages appear at the place of pressure.
- "Pinch Method" - after a small pinch, a bruise is formed.
A general blood test reveals abnormalities in the level of hemoglobin (anemia noted with significant blood loss), platelets. Coagulogram of blood shows the rate of blood coagulation, the presence of antiplatelet antibodies, reduced clot retraction or its absence. IN general urine analysis erythrocytes are found.
In severe cases, a biopsy of the red bone marrow is done. When examining a biopsy specimen, a normal or increased content of megakaryocytes, the presence of their immature forms are revealed.
In the case of typical clinical symptoms, treatment can be started immediately, without waiting for the results of laboratory tests.
Treatment of Werlhof's disease
If thrombocytopenic purpura does not cause complications, there are no pronounced bleeding, indicators platelets in the blood of at least 50 * 109 / l, medical tactics consists in observation - no treatment required.
With a decrease in the level of platelets to 30-50 * 109 / l, treatment is necessary for patients at risk for the development of bleeding (arterial hypertension, peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract).
If the platelet count falls below 30 * 109 / l, urgent hospitalization is required.
Conservative therapy

Conservative therapy includes the use of medications, they can suppress autoimmune processes and reduce vascular permeability:
- glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone) give the effect of treatment within 1-2 weeks;
- globulins (Immunoglobulin G), increases platelet count;
- interferons (Interferon A2) are used when glucocorticosteroids are powerless;
- cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Imuran, Vinblastine, Vincristine and Azathioprine);
- vitamins PP and C, calcium salts, aminocaproic acid.
To stop external bleeding, a hemostatic sponge is used, with internal bleeding, drugs are injected to stop the blood.
Read also:Increased blood eosinophils in an adult
In case of severe course, plasmapheresis is used - transfusion of blood components, platelet mass.
Surgery
In some cases, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura does not respond to conservative therapy, then surgery is performed to remove spleen - splenectomy.
A significant improvement is immediately observed, but there is a risk of postoperative complications and the body's resistance to infectious diseases is significantly reduced.
Splenectomy is performed for a number of indications:
- the duration of the disease is more than 1 year, 2-3 periods of exacerbation, the ineffectiveness of glucocorticosteroid therapy;
- contraindications to adrenocorticosteroid intake;
- relapse of thrombocytopenia after a course of drug therapy;
- severe course of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemorrhage in vital organs.
Traditional medicine
For the treatment of platelet purpura, in addition to medications, medicinal plants with hemostatic properties are used. Among them:
- stinging nettle;
- horsetail;
- burnet;
- shepherd's bag;
- viburnum bark;
- oxalis;
- melissa;
- shepherd's bag;
- ginseng;
- goose cinquefoil.
Diet
It is important that the food you eat is lukewarm or cool. Fresh vegetables and fruits are useful, but care must be taken to ensure that they do not cause an allergic reaction.
Prohibited:
- salty foods;
- smoked;
- spices;
- fast food products;
- drinks: carbonated, alcoholic, coffee.
Forecast
In adults, thrombocytopenic purpura ends in full recovery in 75% of cases, in children - in 90% cases. The emergence of serious complications is possible only in the acute period of the disease.
The probability of death in thrombotic variant of thrombocytopenic purpura depends on the extent of the lesion and the degree of damage to the brain, cardiovascular system, kidneys and others organs.
Patients with a history of this pathology need constant medical supervision, the exclusion of medications that negatively affect blood clotting, a revision of lifestyle and nutrition.
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures for thrombocytopenic purpura are aimed at preventing exacerbations. They involve maintaining the level of platelets and hemoglobin in the blood and include:
- exclusion of allergens in food (spicy, fried, alcohol);
- rejection of medications that affect platelet aggregation (ibuprofen, drugs with caffeine, sleeping pills, aspirin);
- abstaining from prolonged exposure to the sun;
- limit vaccination, refuse the anti-influenza vaccine;
- avoiding contact with infectious patients;
- avoiding traumatic sports;
- elimination of rigid diets;
- minimizing stressful situations.
After being discharged from the hospital, the patient is registered at the dispensary at the place of residence - he is observed by a doctor for at least 2 years.
However, a large share of the responsibility for health falls on the shoulders of the patient or his parents, in the event of a child's illness.
Given that thrombocytopenic purpura is common in children, teaching the whole family how to prevent this disease is very important.