Impetigo: what is it, causes, symptoms, treatment, complications
Content
- What is impetigo?
- Classification
- Causes of impetigo
- Impetigo symptoms
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Impetigo treatment
- Folk remedies for the treatment of impetigo
- How can i prevent impetigo?
- Precautionary measures
- What do you need to know?
What is impetigo?
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria. It is usually caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, but it can also be caused by Streptococcus bacteria. The disease is most common in children between the ages of two and six. The disease usually begins when bacteria invade the skin, such as from cuts, scrapes, or insect bites.
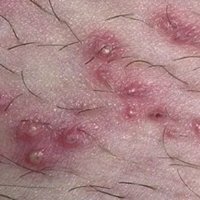
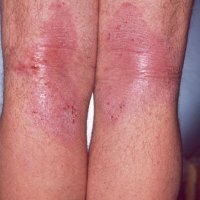
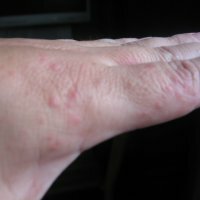
Symptoms begin with red or pimple-like sores surrounded by red skin. These sores can occur anywhere, but they usually appear on the face, arms, and legs. The sores fill with pus, then rupture after a few days and form a thick crust. They often itch, but if you scratch them, ulcers can spread.
Impetigo can be spread by contact with sores or nasal discharge from an infected person. Impetigo is treated with antibiotics. With therapy, the disease usually resolves within two to three weeks.
Classification
The classification of impetigo distinguishes between non-bullous, bullous impetigo and ecthyma.
- Non-bullous or contagious impetigo (Most common): Usually starts with red sores around the nose and mouth. Red bubbles appear on the surface of the skin of the face, they burst, releasing fluid, after which a thick yellow crust forms. The most common form of impetigo in children;
- Bullous impetigo (less common): most common in children under 2 years of age, lesions are concentrated on the neck, buttocks, back. The blisters are much larger, filled with a transparent liquid, which becomes cloudy before the film breaks through;
- Ektim (most serious form of the disease): An ulcerative form of impetigo, in which the lesion extends through the epidermis (the surface layer of the skin) deep into the dermis (the deep layer of the skin). The skin becomes covered with purulent blisters, the formation of ulcers and scars is possible.
Causes of impetigo

Impetigo results from an infection of the skin with one of two types of bacteria - staphylococcus and streptococcus.
Any open wounds, burns, insect bites are potentially dangerous. The risk increases during the period of colds, during the season of allergies - a moist environment is required for the penetration of bacteria, which is facilitated by a runny nose and a wet cough. A child can become infected when attending kindergarten, school, participating in sports, staying in play centers. At risk:
- patients with diabetes;
- eczema;
- herpes;
- chickenpox.
Adults and people with diabetes or a weakened immune system are more likely to develop ecthyma.
Impetigo symptoms

The first sign of impetigo is tiny red blisters around the nose and mouth. photo above). As impetigo develops, small pimples rapidly increase in size. Although symptoms vary slightly from type to type, they are similar and may be accompanied by:
- skin lesions;
- rashes;
- red sores (easily appear and leave a yellow crust on the surface of the dermis);
- blisters filled with fluid;
- itchy rash;
- swollen lymph nodes.
Read also:Lichen planus in humans: causes, symptoms (photo), diagnosis and treatment
With non-bullous (type 1), general symptoms are characteristic, described above.
With bullous impetigo, there is:
- weakness;
- diarrhea;
- fever;
- nausea.
Ecthyma disease (type 3) is characterized by:
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- the formation of ulcers.
These symptoms are more common in people with diabetes and HIV carriers.
Complications
Impetigo is generally not dangerous. And ulcers in milder forms of infection usually heal without scarring.
Rarely, complications of impetigo include:
- Cellulite This potentially serious infection affects the tissues underlying the skin and can eventually spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream. Cellulite can quickly become life-threatening if left untreated.
- Kidney problems. One type of bacteria that causes impetigo can also damage the kidneys and cause glomerulonephritiswhich can cause hematuria (blood in urine) and high blood pressure.
- Scarring. Ulcers associated with ecthyma can leave scars.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of impetigo is not difficult, visual examination allows to identify the disease, and to confirm the diagnosis - analysis of discharge from abscesses. The information obtained from the tests will help the doctor decide if you need antibiotics and what type of antibiotics is best to prescribe.
Impetigo treatment

Treatment for impetigo depends on the severity of the symptoms as well as the type of bacteria causing the disease. For severe illness, doctors prescribe antibiotic treatment.
To destroy the pathogen bacteria, the following antibiotic and antiseptic ointments, creams and anti-inflammatory drugs are used:
- Carbapenems (drugs: Meropenem Jodas and Invanz).
- Penicillins (Amoxicillin);
- Fluoroquinolones (Avelox);
- Amphenicols (drugs: Cephalosporin, Levomycetin sodium succinate and Levomycetin-UBF).
Folk remedies for the treatment of impetigo
Grapefruit extract. Effective against candidal fungal infections, Staphylococcus aureus (one of the causative agents of impetigo). The antibacterial effect is most fully manifested when the extract is combined with geranium oil.
Ginger. Accelerates wound healing, fights bacteria, reduces inflammation. Ginger is best consumed fresh (in salads, cocktails, using for making tea).

The following drink will strengthen the immune system: pass through a juicer carrots (6 pieces of medium size), ginger (1-2 centimeters of fresh peeled root is enough), orange and cucumber (1 piece each). Stir and drink immediately after preparation.
Apple vinegar. Promotes detoxification, disinfects the skin, relieves inflammation (applied topically).
Turmeric. Curcumin has potent antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus.
Read also:Baldness: causes, treatment
Ointment to relieve itching and inflammation: Mix coconut oil (10 ml) with a teaspoon of ground turmeric. Apply to pustules, cover with a bandage. Change the bandage twice a day, renewing the ointment layer, until recovery.
Lauric acid. Lauric acid destroys many pathogens (including bacteria, viruses, fungi) and promotes detoxification. The product is used as a lotion and can be combined with melaleuca oil to increase its effectiveness.
Honey. Application to ulcers requires caution and control - an allergic reaction and worsening of the condition are possible. Therefore, honey in the treatment of impetigo is best used to maintain immunity internally. The product stops the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria, fights viruses, fungal infection.
Goldenroot (hydrastis). Used in treatment skin diseases, effective against staphylococcus.

An antibacterial tonic can be prepared from hydrastis: a tablespoon of crushed raw materials, pour a glass of boiling water. Insist for 20-25 minutes, strain, store in a cold place. The solution will relieve itching, help remove dry crusts painlessly.
Melaleuca oil. Used in the treatment of impetigo, ringworm, eczema, psoriasis, acne. Oil extract (5%) can compete with prescription antibiotics. Lubricate the rash, combining with coconut or olive oil, so as not to burn the skin (a drop of melaleuca oil is enough for a tablespoon of the base oil).
Green tea. The antibacterial properties of the drink have been known for a long time. But to activate the immune system while fighting a bacterial infection (especially streptococcal impetigo) will help not only tea, but also soup prepared in a traditional way.
Green tea is part of an unusual soup (the dish is recommended as a fortifying, anti-inflammatory agent).
Ingredients:
- 2 liters of chicken broth;
- 1 chicken breast, sliced
- 2 tablespoons of coconut oil;
- Bay leaf
- 6-7 green tea bags;
- red onion head;
- 2 carrots;
- 1-2 cloves of finely chopped garlic;
- 200 g celery stalks;
- salt (sea salt can be used);
- black pepper.
Preparation: Boil the broth, turn off the heat, place tea bags in a saucepan (for 10-15 minutes). Put the pan on the fire again, dip the chicken breast into the liquid, cook for 15 minutes. Add onions, carrots, celery, boil until the meat is tender. Before turning off the heat, add the rest of the ingredients and serve hot.
How can i prevent impetigo?
- Compliance with hygiene. Despite the fact that the disease is highly contagious, simple hand washing will protect against infection. A natural antibacterial agent can be made from the following ingredients: 100 g Castile soap, vitamin E (in liquid form - a teaspoon), 100 ml of water, 10 drops of mint, 30 drops of melaleuca oil and 1 spoon coconut. Mix the ingredients thoroughly, place in a container with a dispenser.
- Clipped nails. Dirt, bacteria, viruses, fungi most often live under the nails. Even with thorough hand washing, babies do not always pay attention to this area. Therefore, it is better for children to cut their nails short.
- Food that strengthens the immune system. It is important to get enough substances with food to help resist inflammation, toxins, bacteria. The diet should contain: probiotics (kefir, kombucha, yogurt, soft cheeses, pickled vegetables), garlic, lemon, honey, ginger, citrus fruits, berries, cabbage, apples, sea fish, radish, rosehip drink.
Read also:Weeping lichen in humans: causes, photo signs and treatment
Precautionary measures
Bacteria are easily transmitted by tactile contact, therefore, during the active stage of the disease (until the crusts open and begin to dry out), the patient must be isolated.
Patients with diabetes need to carefully monitor the changes in the affected areas in order to understand how effective the therapy is and not to start the disease.
With weakened immunity, septic complications are not excluded. It is important to control the patient's condition, the appearance of the wounds; with progressive inflammation, urgent medical attention will be needed. The disease is fraught with the development of nephritis, myocarditis, abscess and phlegmon.
Staphylococcal and streptococcal impetigo respond well to treatment - after a week the person fully recovers.
Help your body fight off bacterial infection by strengthening your immune system using the guidelines above.
What do you need to know?
- The most common strains of bacteria that cause impetigo include group A beta-hemolytic streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Impetigo is spread by direct contact with infected lesions. If a child scratches an infected area and then touches another part of their body, the lesions can spread. The infection can also spread if someone touches an infected person's clothes, towels, or sheets.
- Children usually stop being contagious after taking antibiotics for 24 to 48 hours, the rash goes away, and you see signs of improvement.
- S. aureus usually live on or colonize the skin of children and adults. It can be found especially often in the nose, so it can spread easily when children pick their noses.
- Keep bites, burns, and scrapes clean and covered, and apply antibiotics to them three times a day to prevent staphylococcal bacteria.
- To get rid of staphylococcal colonization, it is sometimes possible to treat all family members with mupirocin nasal gel twice a day for five to seven days, take daily baths with Hibiclens (an antiseptic, antimicrobial skin cleanser) and wash frequently arms.