Parkinson's disease: causes, signs, stages, how to treat Parkinson's disease?
What it is?
Parkinson disease or idiopathic parkinsonism syndrome, trembling paralysis - slowly progressive chronic neurological disease.
It arises as a result of progressive damage to the nervous system (NS), characterized by bradykinesia (slowing down of voluntary movements), muscle stiffness (increased muscle tone, manifested by resistance when trying to make a movement) and tremors at rest

.
James Parkinson described the condition in 1817 while observing Londoners walking down the street. He was able to determine that parkinsonism, as shaking palsy would later be called, refers to diseases of the central nervous system.
Content
- Etiology (causes) of the disease
- What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
- How many stages of the disease are there in Parkinson's?
- Parkinson's disease classification
- Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease
- Parkinson's disease treatment
- Antiparkinsonian drugs
- Surgery
- Physiotherapy and massage
- Nutrition and diet for Parkinsonism
- Traditional medicine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
- What is the prognosis for Parkinson's disease?
- Disease prevention
- Related Videos
Etiology (causes) of the disease
There is no definitive opinion on the causes of Parkinson's disease. Doctors identify several factors that can be the reasons for the appearance of degenerative changes in the brain (GM):
- age (the decrease in neurons during aging plays an important role;
- burdened family history (genetic predisposition is a significant cause of parkinsonism);
- toxic substances (it is believed that some toxins can cause damage to brain neurons and trigger the development of Parkinson's disease);
Other possible reasons:
- infections of viral etiology;
- neuroinfection;
- atherosclerosis of the GM vessels;
- traumatic brain injury;
- the use of certain medications (for example, antipsychotics);
- GM tumors, which can be provoking factors for the development of parkinsonism.
What are the symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
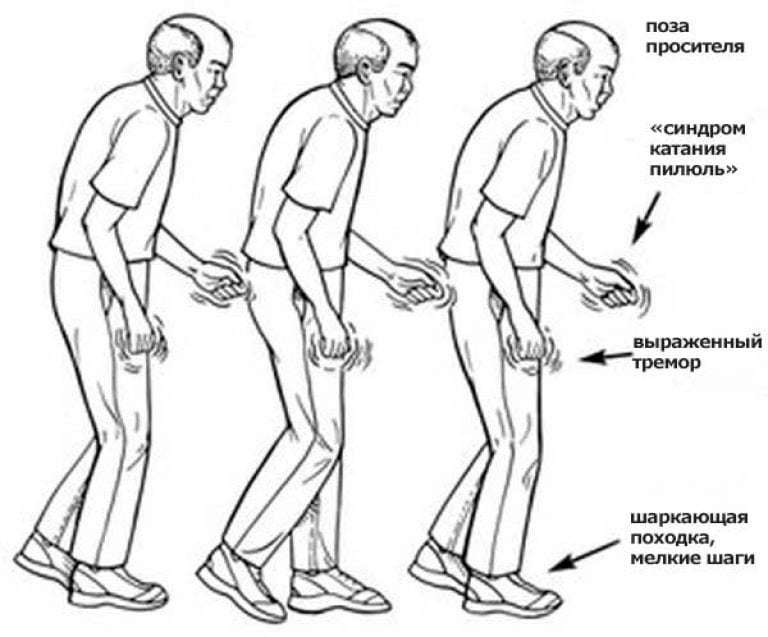
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease can progress over a long period of time, however, one way or another, they lead to disability and self-care skills. The first manifestations of the disease are:
- general weakness, apathy, subjective feeling of ill health;
- the gait becomes unstable, the patient walks short and hesitant steps;
- there is a change in the timbre of the voice and the pronunciation of sounds is disturbed; the patient is inclined not to bring the thought to the end during reasoning;
- there is a change in handwriting, which becomes "shaky";
- the patient is inclined to fall into depression, frequent mood swings occur;
- the patient becomes mostly emotionless ("masked face");
- painful muscle tension is observed, due to an increase in their tone (muscle rigidity);
- unilateral tremor with subsequent transition to both sides;
With the further development of the disease, the symptoms of the disease become more pronounced:
- severe stiffness is characterized by painful muscle tension that is unable to work in concert due to which the patient feels constant weakness and during exercise there is a rapid fatigue;
- "Mask-like face" - the patient does not use the facial muscles in any way, the face becomes impenetrable with a constant expression;
- there is a constant semi-bent position of the upper and lower extremities. This disease is characterized by the "cogwheel phenomenon" - when you try to straighten an arm or leg, the movement becomes intermittent.
- the patient has a specific type of tremor - the fingers move, as if counting coins. The tremor is observed on the hands, feet and lower jaw even during rest, but disappears when the patient is asleep;
- there is a decrease in the speed of movements (bradykinesia), which is why patients spend a lot of time on ordinary daily activities;
- the patient begins to slouch - "the pose of the supplicant";
- pain syndrome extends to the entire musculature of the body. Pain occurs due to continuous spasm of muscle fibers;
- the patient begins to walk uncertainly, often loses balance and falls;
- the inability to stay in one position;
- the process of urination and defecation (constipation) is disrupted due to spasm of the bladder and intestines;
- the patient will fall into severe depression, become fearful, insecure, afraid of public places, cognitive impairments are observed;
- the voice changes (becomes nasal, unintelligible). The patient repeats the same words;
- sweating is disturbed (increased sweat production);
- sufferers often suffer from insomnia and nightmares.
How many stages of the disease are there in Parkinson's?

Parkinson's disease in its development has three stages, which are differentiated by the severity of clinical symptoms:
- The initial stage of the disease - this stage is partially compensated. There are minor disorders of the locomotor system, a socially patient can fully exist independently;
- Expanded stage - clinical symptoms are acutely expressed, the patient needs drug treatment;
- Late stage of the disease - the patient is disoriented in the social sphere, unable to perform normal household work; drug treatment has practically no effect.
Read also:Dementia in the elderly
There is also a newer and more practical Hen-Yar classification:
- Zero stage - the manifestation of the disease has not yet occurred.
- First stage - there is an unexpressed one-sided hand tremor. The patient feels weakness, increased fatigue. Habitual activities (dressing, for example) begin to take a little longer.
- Second stage characterized by the prevalence of the process on two sides: mild tremor, rigidity of the muscles of the trunk. The face becomes "mask-like" due to the defeat of the facial muscles. Dysphagia (impaired swallowing), speech impairment may occur. The patient may shake his head slightly.
- Third stage - the manifestation of symptoms increases, but the patient is able to serve himself. The gait becomes mincing and shuffling. The patient is completely constrained in movements (his hands are tightly pressed to the body).
- Fourth stage - pronounced hypokinesia and tremor lead to the fact that the patient is not able to carry out hygienic activities in relation to oneself, becomes completely incapable of physical activities. The patient can easily lose balance, so he often uses support.
- Fifth stage - due to progressive symptoms, the patient is unable to move independently, only bed rest is indicated. Wheelchairs can be used. Due to severe dysphagia, the patient loses mass, exhaustion occurs.
Parkinson's disease classification
There are several types of this disease.
If the development of the disease occurred for no reason, with no prerequisites, then the neurologist will diagnose primary parkinsonism or idiopathic parkinsonism syndrome.
Secondary parkinsonism occurs against the background of taking medications that cause similar symptoms, intoxication, diseases affecting the brain (potentzaphalytic parkinsonism), cerebral disorders blood circulation.
Parkinsonism Plus - a group of independent degenerative diseases, the clinical manifestation of which resembles primary parkinsonism. This is:
- multisystem atrophy;
- cortico-basal degeneration;
- progressive supranuclear palsy.
These diseases are not amenable to correction with antiparkinsonian drugs.
According to the presence or absence of any symptoms of the disease, Parkinson's disease is classified into:
- disease with severe tremor;
- diseases without tremor;
- mixed form;
- atypical form of the disease.
Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease
In order to diagnose a patient with Parkinson's disease, a neurologist must collect a thorough history, conduct an examination and evaluate the results of laboratory and instrumental research methods.
During the survey, a specialist should find out the answers to such questions:
- In which region does this patient live?
- Did any of your relatives suffer from tremors?
- When did the patient first notice their symptoms?
- Have any traumatic brain injuries or diseases affecting the brain tissue?
- What disorders of the locomotor system does the patient notice?
- Is sweating impaired?
- Does the patient have insomnia, how often does the mood change?
- Did you take any medications? If so, which ones and in what dose?
- Has the patient's handwriting changed since the first symptom appeared?
Examining a patient, a neurologist should pay attention to the patient's gait, his motor activity, tremors, emotions.
Laboratory tests will not give us a specific picture of the disease. This method is used to exclude diseases similar in symptoms to Parkinson's. The level is determined:
- glucose;
- creatinine and urea;
- cholesterol;
- enzymes (enzymes) of the liver;
- thyroid hormones.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing tremor paralysis:
- Electroencephalography, by which the electrical activity of the brain is determined. With Parkinson's, this indicator decreases in relation to the norm.
- Electromyography shows the rhythm of the tremor.
- Positron emission tomography involves the use of a radioactive drug in order to determine its degree of accumulation in the substantia nigra and striatum. This indicator decreases with Parkinson's.
- Single Photon Emission CT (SPECT or SPECT), which measures dopamine levels.
- MRI is not a diagnostically important study in Parkinson's disease, however, in the later stages, it can reveal atrophy of the structures of the extrapyramidal system. Moreover, for the differential diagnosis of Parkinson's with brain tumors, Alzheimer's disease and hydrocephalus MRI has an advantage over other instrumental research methods.
Read also:Intracranial pressure in adults: symptoms and treatment
There are also additional tests available to diagnose Parkinson's disease. They are not specific, however, in combination with the rest of the data, I can help a neurologist with the formulation of a diagnosis. For example, a patient needs to stretch out his arms and quickly clench his fingers into a fist several times, and then unclench. In the presence of a disease, these movements will not be performed symmetrically.
Parkinson's disease treatment
With Parkinson's, medication is used to eliminate the cause of the disease - an attempt stop the death of dopamine receptors, as well as in order to reduce interfering with normal life symptoms.
Antiparkinsonian drugs
Antiparkinsonian drugs are:
- Levodopa.

This drug is a precursor to dopamine. Converting into dopamine directly in the central nervous system, Levodopa compensates for the reduced level of this substances and removes the symptoms of Parkinson's disease: tremor, rigidity, hypokinesia, dysphagia and salivation.
In this case, Levodopa has many side effects:
- dyspeptic disorders (diarrhea or constipation, nausea, vomiting);
- decreased appetite;
- the formation of erosions on the mucous membrane of the stomach;
- gastralgia (stomach pain);
- bleeding, if there is a history of the patient stomach ulcer;
- dizziness, insomnia or increased drowsiness, unreasonable feeling of anxiety (panic attacks), depression, ataxia;
- convulsions;
- orthostatic collapse, decreased blood pressure;
- interruptions in the activity of the heart;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- a decrease in the level of leukocytes and platelets in the blood;
- an increase in the volume of urine excreted per day.
To reduce the side effects of Levodopa, Carbidopa is used.
The next group of drugs that are used to treat Parkinson's disease are dopamine receptor agonists (stimulants). This is:
- derivatives of ergot alkaloids (Bromocriptine and Pergolide);
- Pramipexole, Ropinirole.
Other less used antiparkinsonian medicines:
- selective MAO inhibitors (Selegiline);
- catechol-ortho-methyltransferase inhibitors (Tolcapon and Entacapon);
- stimulants of dopaminergic transmission in the central nervous system (Amantadine, Memantine, Piribedil).
Surgery
There are also methods of surgical treatment for Parkinson's disease. Exist stereotactic surgery, which implies destructive operations - thalamotomy (destruction of individual parts of the thalamus) and pallidotomy (destruction of one of the parts of the globus pallidus); applied electrical stimulation of the deep parts of the brain - high-frequency irritation of the subthalamic nucleus (the operation is complex and has many contraindications, however, with the correct procedure, patients will be able to return to their normal lifestyle); gene therapy using stem cells is currently under development.
Physiotherapy and massage
It is also recommended for patients with parkinsonism physiotherapy.
In the initial stages of the disease, these are:
- walking;
- swinging the upper limbs;
- walking;
- golf, badminton;
With the progression of symptoms of Parkinson's disease, it is recommended:
- breathing exercises;
- squats;
- walking;
- posture exercises;
- stretching exercises.
As a therapy for Parkinson's disease, massage:
- stroking - performed primarily to relax the muscles and prepare for further manipulations;
- rubbing - using this method improves blood circulation and lymph flow, relieves tension and stiffness of the muscles;
- kneading;
- movement - it can be active, passive movements, with resistance;
- blows and beating;
- patting;
- vibration.
Massage is an important part of the treatment of parkinsonism, because it helps to restore the functioning of the locomotor system, and also has a positive effect on the central nervous system. The recommended frequency of massage is every day or every other day.
Nutrition and diet for Parkinsonism

Patients with Parkinson's should remember that it is necessary to eat after two hours from taking medications in order to could penetrate the small intestine without obstacles and from there, in the maximum possible concentration, be absorbed into the blood in order to exert their action.
Nutrition should be correct and balanced with the obligatory intake of the proper amount of protein.
With this disease, patients often suffer from constipation, which is a negative effect of taking medications. Therefore, it is necessary to increase the amount of consumed fruits and vegetables.
Also, the patient should remember about normal fluid intake. You need to drink 6-8 glasses of water a day.
Dysphagia is a major problem with Parkinson's disease during meals. To facilitate this process, you need:
- chew food thoroughly;
- do not put the next portion of food if the previous one was not chewed and swallowed enough;
- when swallowing, it is recommended to tilt the body forward;
- you need to sit upright;
- portions should be small, but meals should be in the amount of five to six;
- it is recommended to drink water during meals;
- food must be liquid or creamy;
- you can not eat dry foods (crackers, cookies);
- vegetables must be thoroughly cooked, fruits must be peeled;
Read also:Dyscirculatory encephalopathy of 1, 2 and 3 degrees, what is it, symptoms and methods of treatment
Traditional medicine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease

Treating Parkinson's syndrome at home with folk remedies has a minimal number of side effects, which is undoubtedly a plus.
The following are several recipes for decoctions, tinctures for this disease.
Recipe # 1.
300 grams of dried sage should be placed in a gauze bag and placed in a bucket. Next, you need to pour boiling water over the edge of the bucket and let it brew overnight.
Then in the morning you need to take a bath of hot water, pour the resulting liquid into it and completely immerse your body in it (along with the back of your head).
Such bathrooms should be taken every other day 5 times.
Recipe # 2.
Would need:
- 4 rose hips;
- Bay leaf;
- dill and parsley;
- green apple peel,
- 1 hour l. black tea.
All components must be finely chopped, mixed and filled with 1 liter of boiling water. Let it brew for two hours. Drinking the resulting medicine is worth instead of tea every day. This recipe has no restrictions on its use, so this tea can be consumed until the symptoms of Parkinson's disease disappear.
Recipe # 3.
Chrysanthemum flowers can be brewed like herbal tea and drunk without restriction. After two months of regular use of the tea, hand tremors disappear.
Recipe # 4.
At 1 st. l. knotweed (bird knotweed), two glasses of boiling water are poured, after which the tea is infused for several hours. It should be taken half a glass at a time 5 times a day.
Recipe # 5.
Brew linden leaves like regular tea and drink in the morning. After a month of use, take a break for the same duration. The total duration of the course is 6 months.
What is the prognosis for Parkinson's disease?
Unfortunately, this disease is a degenerative disease that is prone to progression. Medicine has not yet reached such a level of development to restore the destroyed structures of the brain. Therefore, the prognosis is unfavorable.
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease can progress in each patient at a different rate, over the course of 20 or 5 years.
However, a timely visit to a doctor, strict adherence to his prescriptions and the fulfillment of all appointments will be able to reduce negative symptoms in Parkinson's disease, as well as extend the duration of work and life.
Disease prevention
In order to avoid parkinsonism, it is necessary to know the causes of degenerative processes. and factors that increase the risk of the disease, as well as points that will help avoid a terrible diagnosis:
- Try not to work in enterprises whose activities are related to toxic substances;
- It is necessary to maintain your immunity: a contrast shower, hardening, vaccinations;
- If the body suffers from vascular or endocrine pathologies, then adherence to the prescribed treatment will prevent parkinsonism;
- In case of traumatic work, it is necessary to observe safety measures; if possible, limit traumatic sports in life;
- Monitor the daily intake of vitamins of group B, C, E, folic acid;
- Healthy balanced diet;
- Regular physical activity (walking in the fresh air, brisk and slow walking);
- It is necessary to know and apply in practice methods of stress prevention (meditation, relaxation, micro pauses at work, breathing exercises, planning your day, communicating with loved ones, full sleep);
- Passing a genetic examination if there are cases of Parkinson's disease among relatives;
- Women should carefully monitor hormonal levels (control of estrogen levels).
For any manifestation of symptoms of Parkinson's disease, it is necessary to immediately consult a neurologist in order to start therapy as early as possible.