Cleft lip and cleft palate in children: photos, reasons, how they are treated
Content
- What are cleft lip and cleft palate?
- Disease photography
- Causes of occurrence
- Disease manifestations
- Types of defects
- Cleft palate classification (cleft palate)
- Diagnostics
- Pathology treatment
- Photo of children before and after surgery
- Prophylaxis
- Forecast
- Related Videos
What are cleft lip and cleft palate?
Cleft palate (cleft palate, cleft lip, honey. name - cheiloschisis, (cheiloschisis)) - refer to congenital malformations of the maxillary region of the face. There are some differences between these pathologies.
The cleft lip, or cheiloschisis, (which translates as "cleft") looks like a cleft in the upper lip, which is sometimes large and affects the nasal cavity.
The cleft palate is an open hard and / or soft palate (cleft palate), as a result of which there is a communication between two cavities - the oral and nasal.
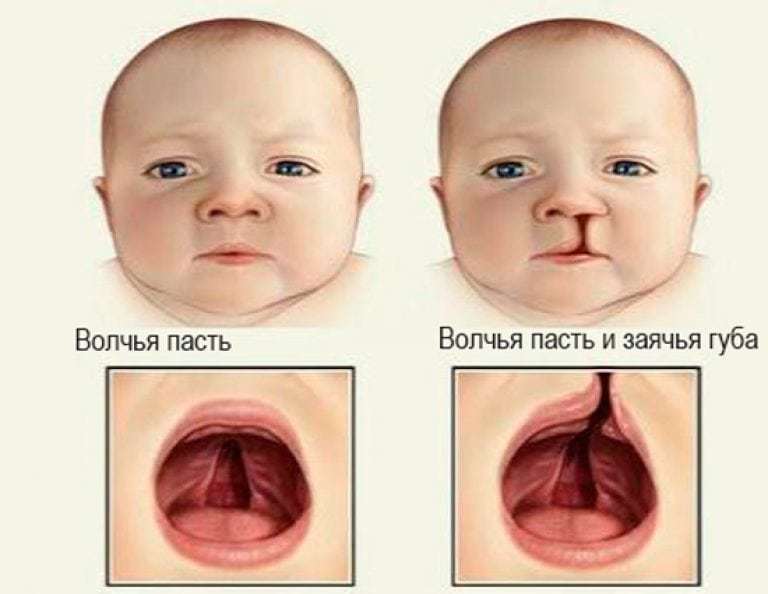
In some cases, a child may have both developmental defects. The approximate ratio of children born with such a pathology and healthy babies is 1: 2500.
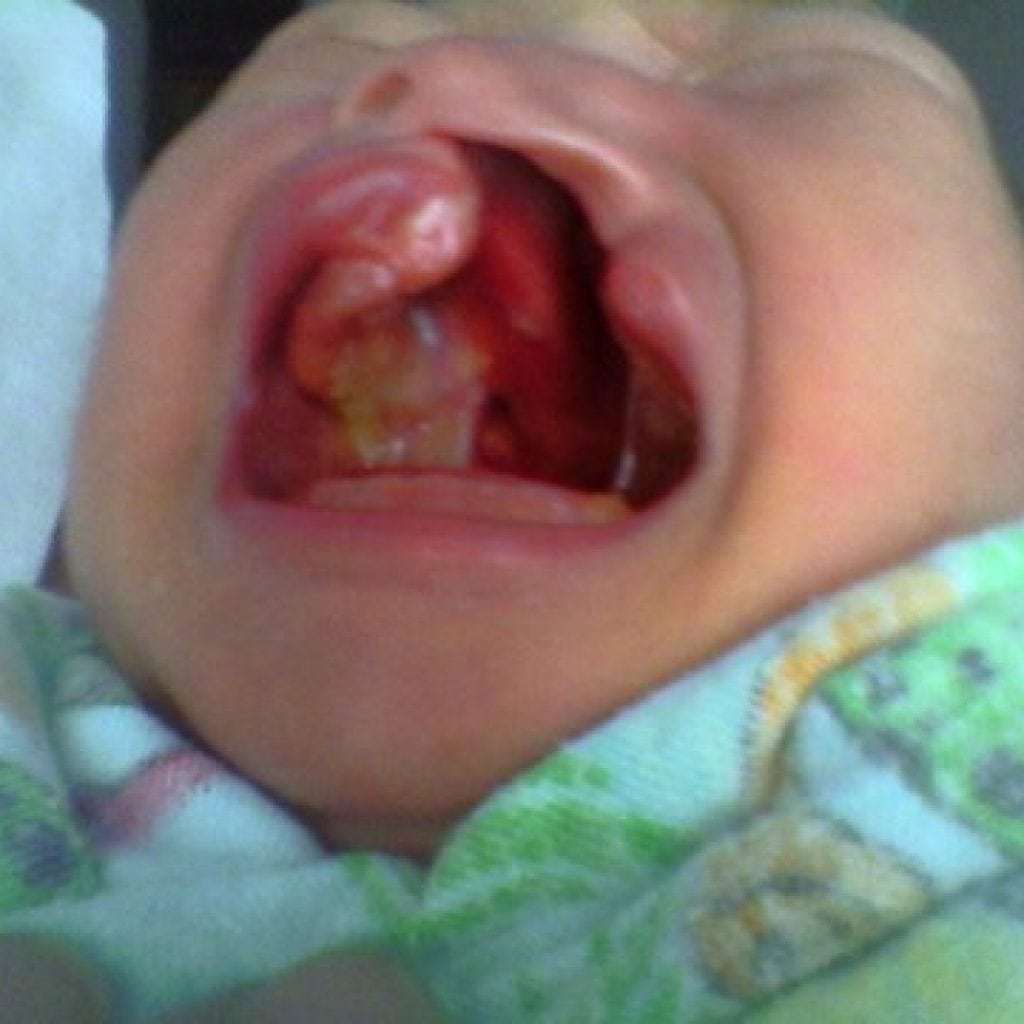
Disease photography
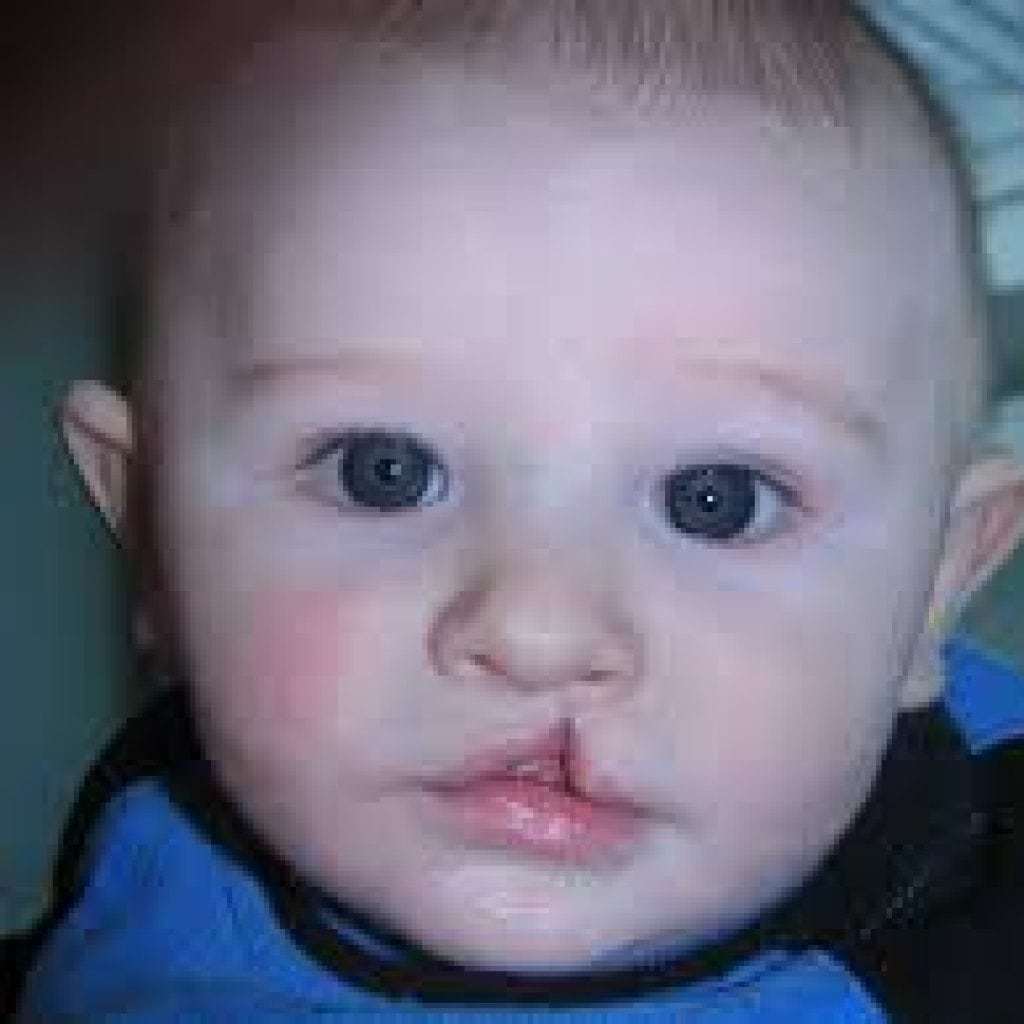
Causes of occurrence
Soft and hard tissues of the maxillofacial area are formed by the end of the 8th week of pregnancy. The correct laying of these structures is influenced by both hereditary and external factors.
Also, the development of the defect can be influenced by "breakage" of chromosomes. Regardless of the type of defect - cleft palate or cleft lip, the reasons for their occurrence are the same.
The share of hereditary factors in the occurrence of cheiloschisis or cleft palate accounts for about 25%.
This issue has not yet been fully understood. Geneticists come to the conclusion that the cause of the development of these pathologies is the action of several genes at once. This is also indicated by the fact that the risk of developing a cleft palate and cleft lip in future generations is only 7%.
Chromosome abnormalities account for only 15%. In this case, the newborn also has other multiple severe malformations combined into whole syndromes.
The remaining 40% are attributable to external pathogenic factors that affected the fetus in the first 2 months of pregnancy. Some factors come directly from the mother's lifestyle and can be easily adjusted:
- smoking during pregnancy, which increases the risk of developing an anomaly by 2 times;
- narcotic substances cause a cleft lip or cleft palate in children 10 times more often;
- excessive use of alcohol and its surrogates;
- the use of some groups of antiepileptic drugs and antibiotics;
- lack of vitamin B9 (folic acid), which must be taken by every pregnant girl, starting from the first weeks of gestation.
There is a group of internal risk factors that, unfortunately, the pregnant woman cannot influence (unmodifiable)
- the age of a pregnant woman is over 35-40 years;
- fetal hypoxia in early pregnancy;
- partial chorionic detachment, which causes the tiny fetus to be undernourished and inhibits its development.
Read also:Streptoderma in children: symptoms, home treatment
And finally, external environmental factors:
- chronic intoxication with pesticides, benzene, mercury or lead.
This can happen if the expectant mother lives near industrial plants or works in a hazardous production.
Disease manifestations
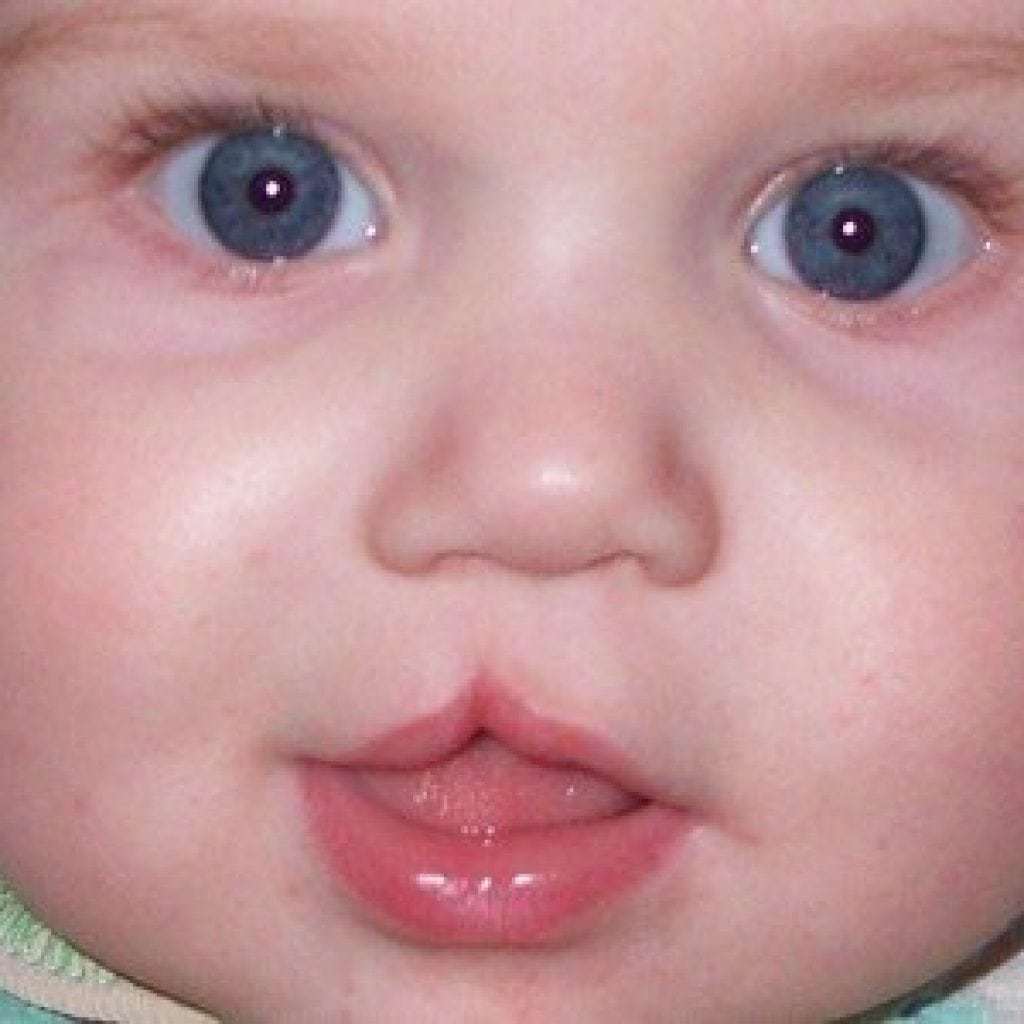
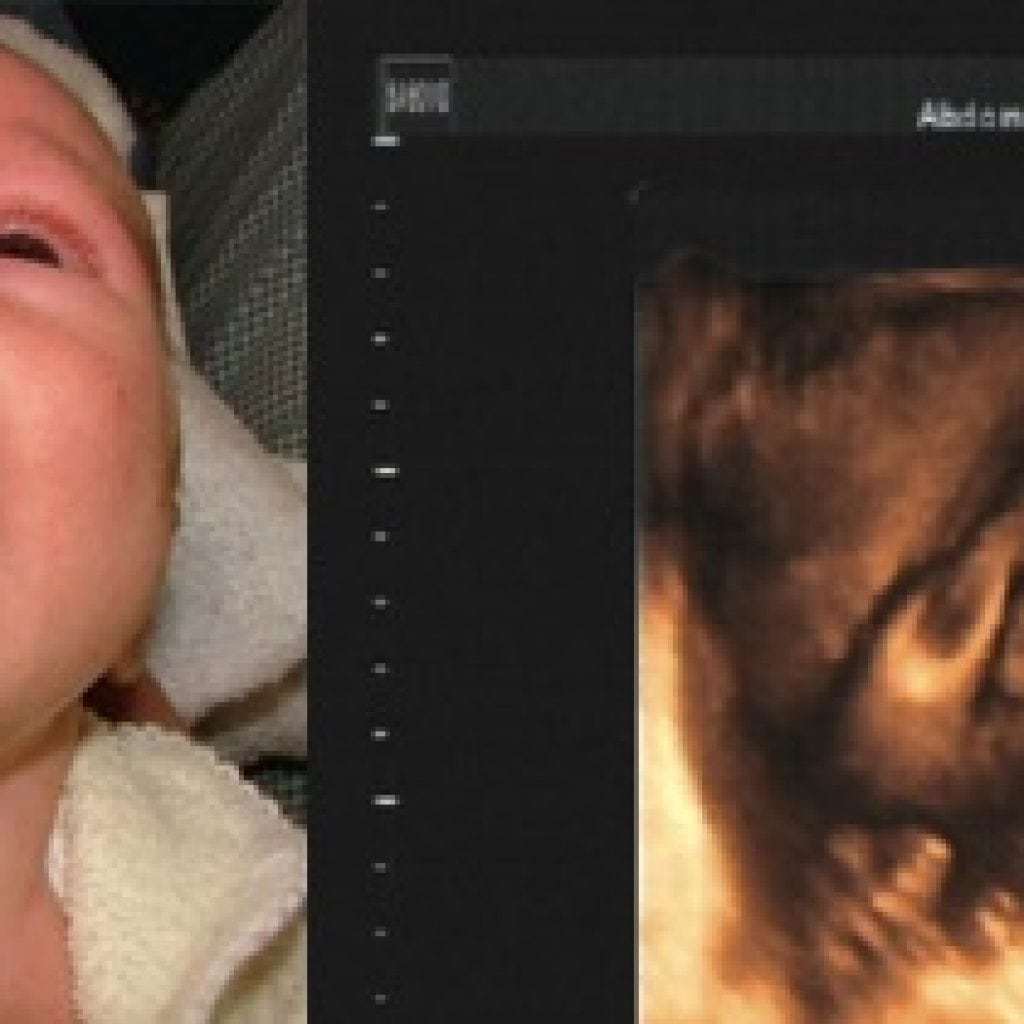
Despite the causes of the disease, the external manifestations are quite typical. Already during the first ultrasound, the expectant mother will be told about the presence and severity of the defect in the baby. So when such a child is born, a team of doctors will provide him with all the necessary assistance.
- Heiloschisis looks like a vertical "gap" in the tissue of the upper lip (see. photo above). It can be barely noticeable, or it can be extended to the nostril. The defeat can be localized on one side or both at once. Babies may have trouble sucking, so feeding bottles are used. Sometimes doctors have to resort to tube feeding.
In the future, children may have problems with teeth (wrong bite, missing some teeth) and speech (nasal voice and problems with pronunciation).
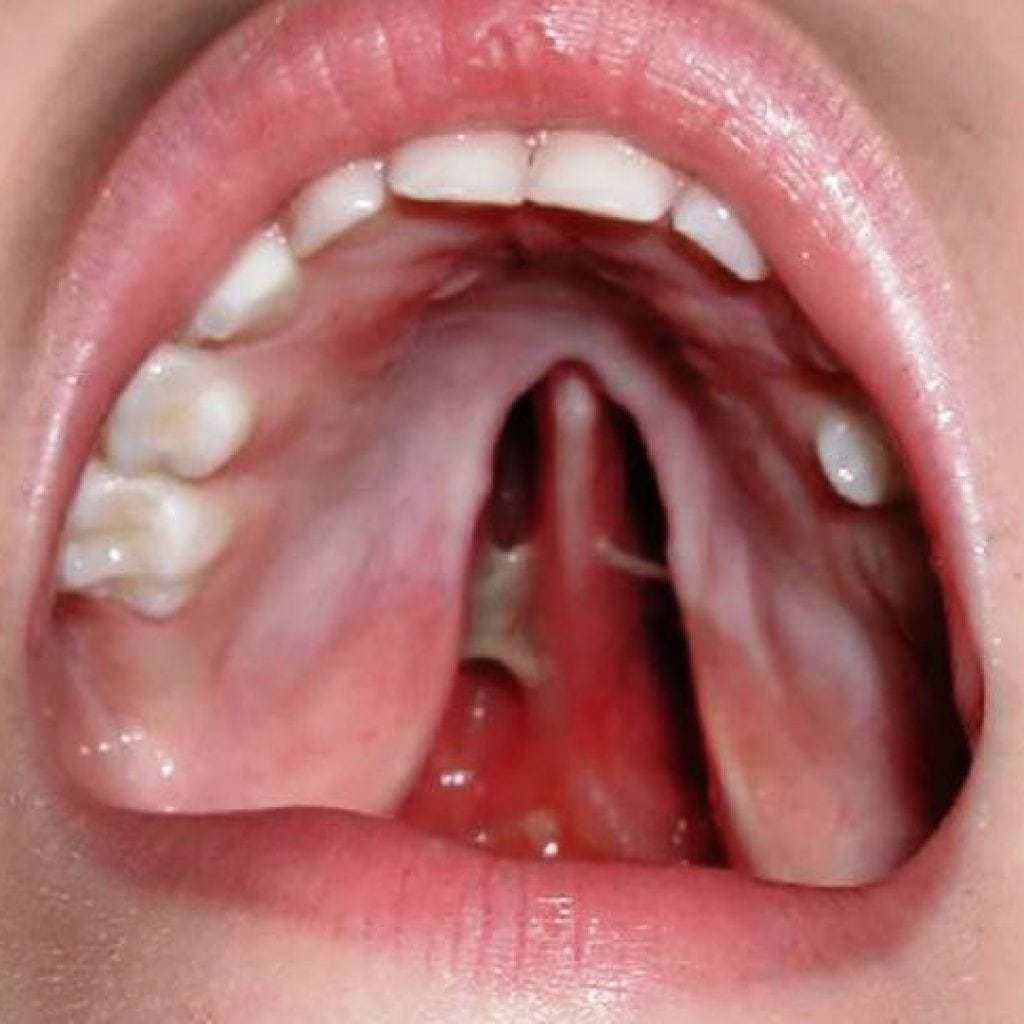
- A cleft palate in children may be invisible during an external examination of a newborn. However, looking into the oral cavity, you can see a vertical opening in the tissues of the upper palate. Such babies already from the first seconds of life experience problems with breathing and sucking and receive all the necessary help.
In addition to the problems that are characteristic of cheiloschisis, children with cleft palates may develop ear infections (otitis media) and facial sinuses (sinusitis). This is due to the throwing of inhaled air or fluids from the nasal cavity into the middle ear.
Types of defects
Two large groups of anatomical defects are classified based on different characteristics.
Heiloschisis classification:
- By localization:
- Upper lip defect;
- Lower lip defect (extremely rare);
- Upper and lower lip defect.
- On the side of defeat
- Unilateral cleavage (most often on the left);
- Bilateral cleavage, symmetrical and asymmetrical.
- By severity
- Complete non-union that extends to the nostril;
- Partial non-union, including microforms of the cleft lip, which can be barely noticeable and do not interfere with the baby's normal nutrition and breathing.
- By severity
- Mild severity (isolated defect of the soft tissues of the lip);
- Moderate and severe (combination with maxillary bone defects of varying severity).
Cleft palate classification (cleft palate)
The principles of classification of the median cleft of the upper palate are slightly different.
- Outwardly:
- Obvious cleft (diagnosis is straightforward);
- Hidden cleft, in which there is only a deep muscle defect, and the mucous membrane remains intact. On examination of such a newborn, the oral cavity appears normal.
- By severity:
- Incomplete (cleavage of only the soft palate);
- Complete (cleft of the soft and hard palate);
- Through (the defect affects not only the palate, but also the bone structure of the upper jaw - the alveolar process).
- Through defects are divided into:
- One-sided;
- Bilateral.
Read also:Symptoms and treatment of laryngitis in children
Also, both pathologies can be divided into complicated (otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia) and uncomplicated.
The combination of cleft lip and cleft palate belongs to a separate classification category.
Diagnostics
Adequate diagnosis of cleft palate or lip is not difficult. As already noted, the diagnosis "cleft palate" and "cleft lip" become apparent on ultrasound in the 1st or 2nd trimesters of pregnancy.
External examination of the newborn allows you to make an accurate diagnosis. However, for a more complete examination, it is sometimes required to resort to certain research methods:
- radiography maxillofacial area for assessing bone defects;
- audiometry or hearing test. It is assessed either with the help of special equipment or by careful observation of the baby (his reaction to auditory stimuli). It is necessary for large clefts with a high risk of hearing loss up to deafness;
- olfactory research (the child's facial expressions and behavioral reactions to some categories of pungent odors are assessed);
- general blood analysis is mandatory for all newborn babies, however, in babies with a defect, special attention should be paid to it. An increase in the level of white blood cells - leukocytes, specific inflammatory proteins (C-reactive protein, ceruloplasmin) and acceleration erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) indicate the addition of an infection, which in weakened babies can be quite difficult to pass.
Pathology treatment
The main method of treating these pathologies is surgical.
Cleft lip surgery is called cheiloplasty. Most often, it is performed closer to 6 months of age, however, in some cases, the baby may need urgent surgery (within the first month of life).
This is usually associated with extensive defects.
Depending on the affected tissue, perform:
- Isolated cheiloplasty - stitching of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscle layer and mucous membrane of the lips;
- Rhinocheiloplasty (lat. "Rino" - nose) - additional correction of the cartilage of the nose;
- Rhinognatocheiloplasty - the formation of the muscular frame of the mouth area.
Unfortunately, one surgical intervention cannot be dispensed with. In the first 3 years life, the baby will have to lie on the operating table 3-4 times.
The success of the treatment of heiloschisis is colossal. In most cases, the child is left with only a slight asymmetry of the lips and a barely visible scar. And already in adulthood, a person can turn to a beautician who will help eliminate minor defects.
Read also:Children's stomatitis: how it can be cured at home
Treatment for cleft palate is called uranoplasty. The timing of this operation differs from cheiloplasty - age is optimal. 3-4 years old. Earlier surgery can damage the growth of the upper jaw.
With extensive through crevices, the operation is postponed up to 5-6 years old. However, by the beginning of the school period, most children receive all the necessary assistance and are no different from their peers.
To ensure that parents do not have fears for the life and health of the child before surgical treatment, the baby wears a special device - an obturator, which creates an internal barrier between the nasal and oral cavity. With it, the child will be able to eat normally, breathe and talk.
Surgery is only one of the stages of treatment. The child will definitely need the help of a speech therapist who will form the correct speech. And the problems with occlusion and abnormal growth of teeth will be solved by the orthodontist by installing braces.
Unfortunately, some children may have problems in the emotional, volitional and social spheres. Therefore, the help of a child psychologist will come in handy. The kid will feel confident and will not have problems communicating with peers.
Photo of children before and after surgery
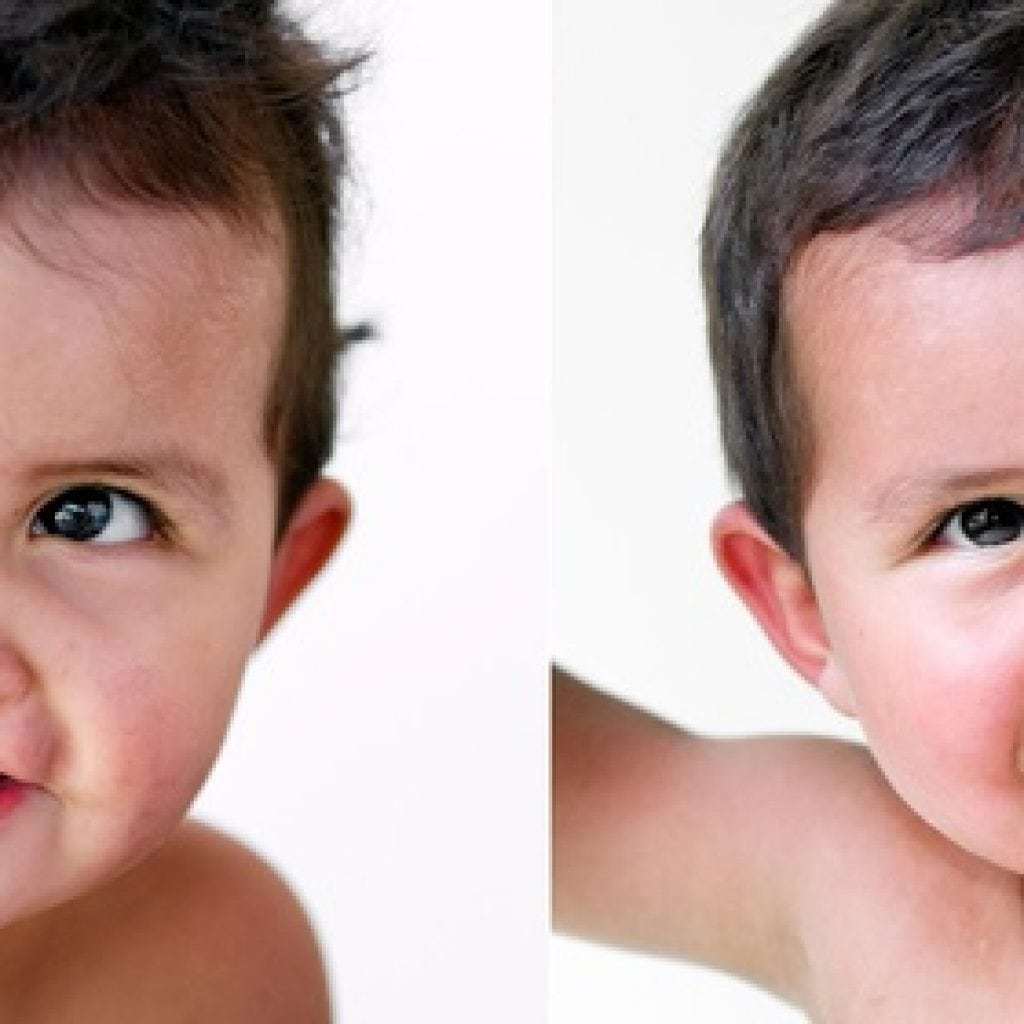
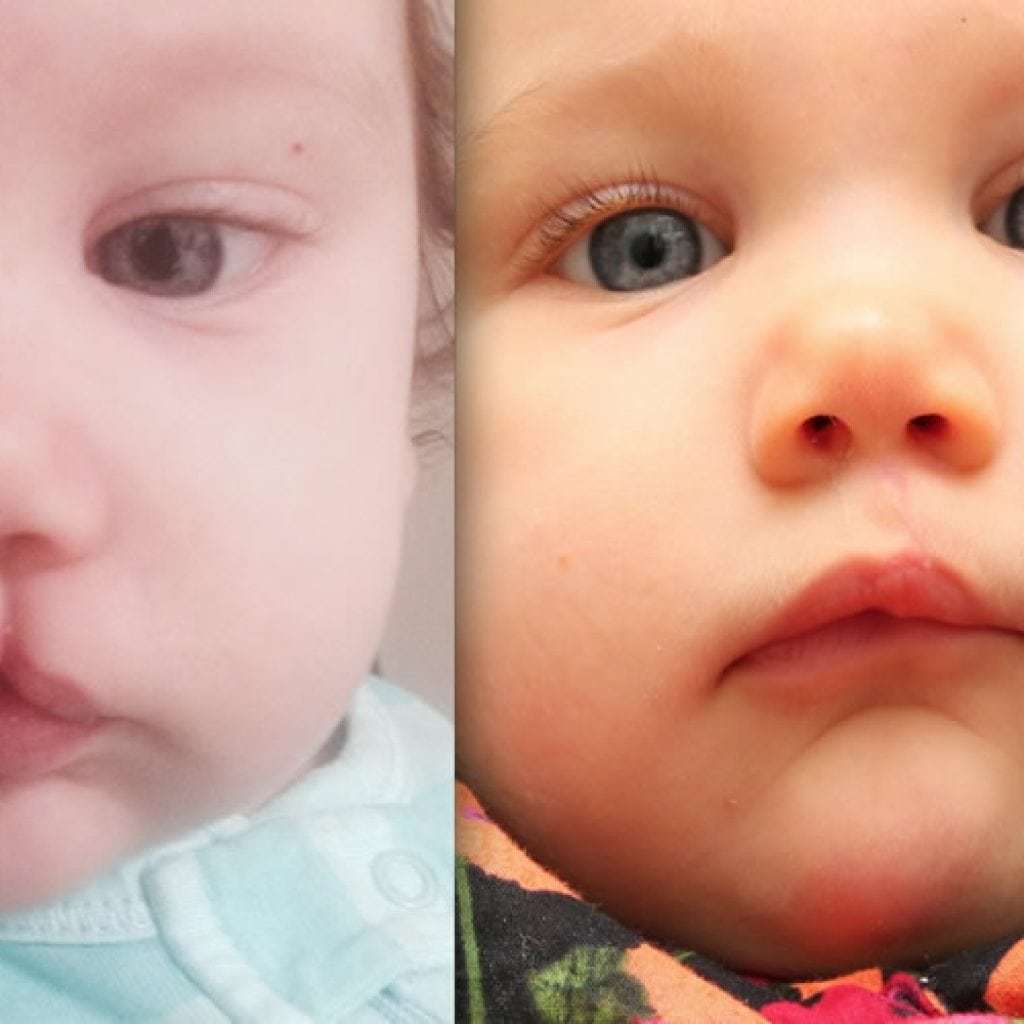
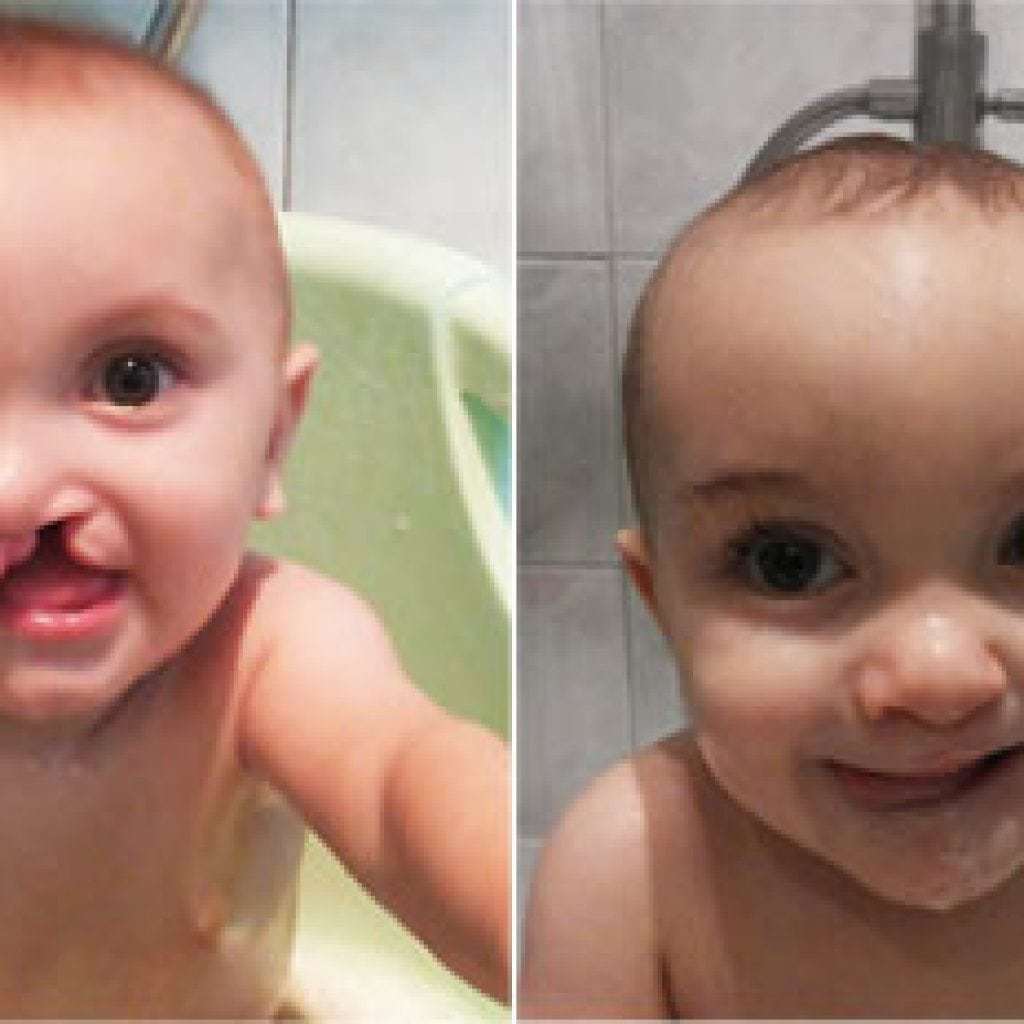
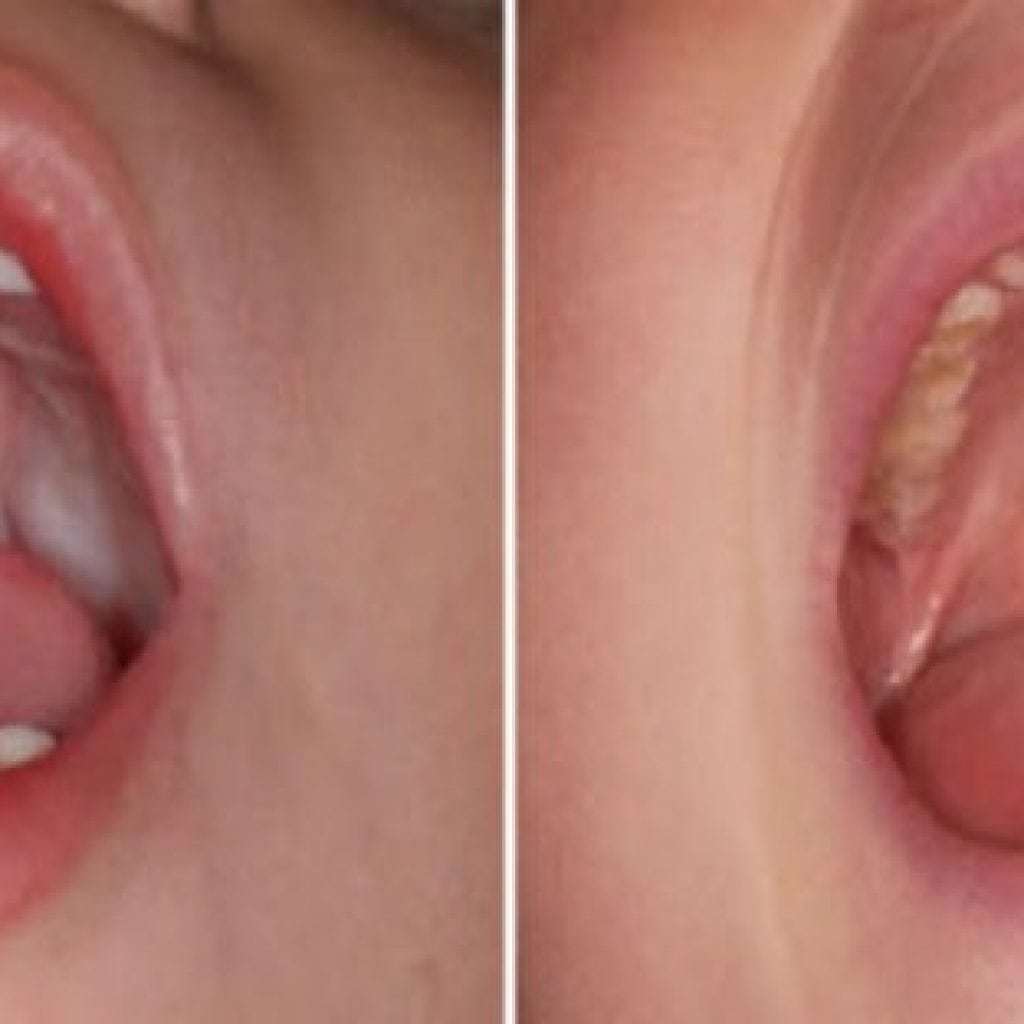


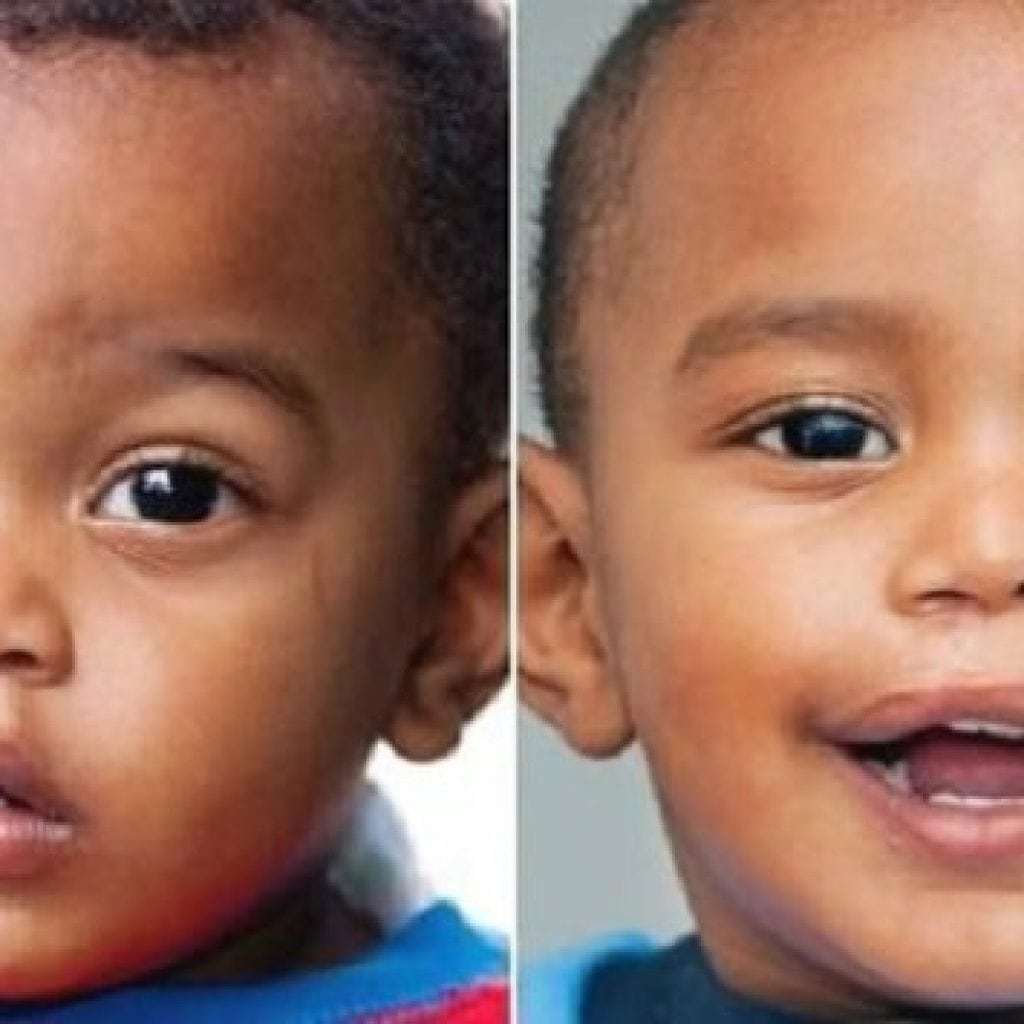

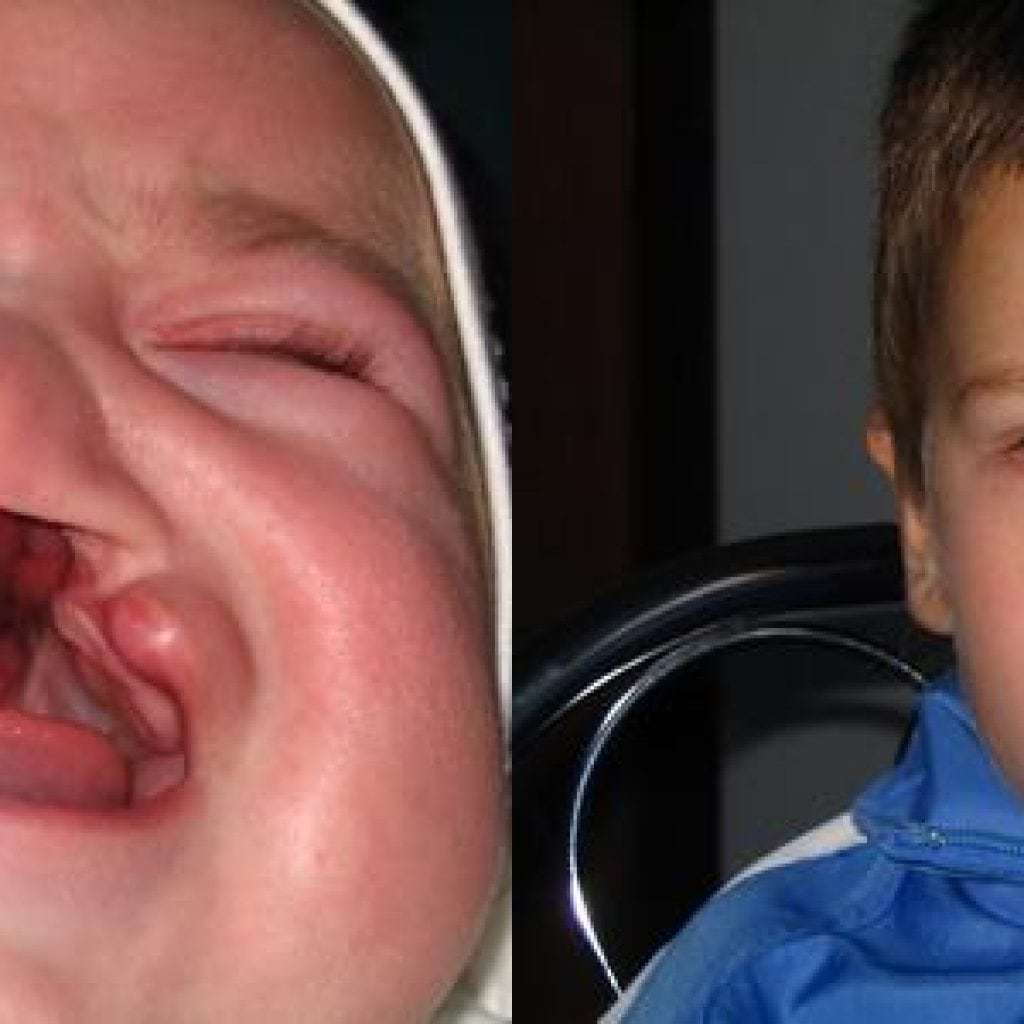
Prophylaxis
In order to reduce the risk of having a child with such a defect, the expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle and follow all the doctor's recommendations. After all more than 50% the success of pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby in this case depends precisely on the behavior of the mother and her immediate environment.
Forecast
The prognosis is very favorable. Thanks to modern methods of plastic surgery, orthopedics and speech therapy, children with such a diagnosis are almost indistinguishable from those around them and lead an absolutely fulfilling life. It is important to take the long-term treatment and rehabilitation of the child seriously.
At an early age, babies can have problems with feeding and weight gain, and, accordingly, with neuropsychic development. Therefore, you should master specialized feeding techniques and use additional sources of nutrients (energy complexes, vitamins).
Even if the defect is successfully corrected, the child is shown regular follow-up by specialists - maxillofacial surgeon, neurologist, otorhinolaryngologist and orthodontist. The child will visit these doctors at least once a year. up to 17-19 years olduntil all tissues of the maxillofacial area are fully formed.