Emphysema of the lungs: what is it, symptoms, treatment, life prognosis
Uncertainty scares people. Having heard from the doctor the diagnosis of "emphysema of the lungs", a person with fear in his eyes perceives this news.
Despite the seriousness of the diagnosis, not everything is so bad, the main thing is timely and competently started treatment.
In this article, we will help you understand what it is and how to treat the disease.
Content
- What is pulmonary emphysema?
- Epidemiology
- Causes of pulmonary emphysema
- Classification of pulmonary emphysema
- Symptoms and signs of pulmonary emphysema
- Complications of pulmonary emphysema
- Diagnostic methods for the study of pulmonary emphysema
- Therapy (how to treat pulmonary emphysema)
- Drug treatment
- Physiotherapy and other therapies
- Surgery
- Nutrition and folk remedies
- Prevention and recommendations
- Life prognosis for patients with pulmonary emphysema
What is pulmonary emphysema?
Emphysema of the lungs is a disease of the respiratory tract characterized by abnormal expansion of air spaces of distal bronchioles, which is accompanied by destructive and morphological changes alveolar walls.
The transformation of lung tissue is caused by pathological changes that contribute to the formation of voids with air, which contribute to an increase in the size of the lungs. As a result of emphysema, the septa between the alveoli (an anatomical cell in the lung that facilitates the breathing process) is destroyed.
The disease is quite common, it affects up to 4% of the world's population. The male population over the age of 50 is twice as susceptible to the disease. Currently, pulmonary emphysema is diagnosed in people by the age of 30, and there are cases of congenital lung pathology.
Epidemiology

Emphysema of the lungs almost always occurs in connection with the so-called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
It is estimated that about 5-10 out of every 100 adults suffer from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The disease mainly occurs in smokers.
Emphysema of the lungs can also be caused by a hereditary deficiency of a particular protein. This so-called alpha-1-antitrypsin, however, is very rare: only about 10% of people suffer from it in Russia.
Causes of pulmonary emphysema
To date, the most common cause of pulmonary emphysema is smoking. Almost always, the disease develops in connection with COPD, which affects mainly smokers. The combination of persistent inflammation and inhalation of cigarette smoke results in the destruction of the alveoli.
The main risk group:
- people with a congenital form of pathology associated with a lack of whey protein during fetal formation (the so-called alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency);
- smoker, including passive;
- people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
All this violates the plasticity of organ tissues and increases pulmonary pressureresulting in emphysema.
There are several factors that affect the change in tissue ductility:
- changes occurring in the bodyrelated to the person's age. Violation of blood supply in the body of an elderly person increases his sensitivity to the negative effects of the environment. A decrease in the immune system leads to a long recovery after the transfer of infectious diseases of the respiratory system;
- systematic inhalation of contaminated air industrial origin, including cigarette smoke. Vapors of cadmium and nitrogen oxide are especially dangerous. Microparticles of substances settle on the walls of the bronchioles, which leads to damage to the vessels of the respiratory system;
- respiratory tract infection. Lung disease (causes: ARVI, flu, pneumonia, bronchitis etc.) causes the activation of lymphocytes - as the body's immune defenses. The process has a negative effect on the alveoli by dissolving the alpha-1-antitrypsin protein. Mucus does not allow air to pass from the cells of the alveoli, which leads to stretching of the lung tissue;
- congenital deficiency of the serum protein group (alpha-1-antitrypsin). Pathology consists in a violation of the functions of an enzyme of the hydrolysis class, which does not provide a protective function in the body against bacteria, on the contrary, it serves as a destroyer of the walls of the alveoli;
- systemic circulation disorders in the lungs, hormonal disorders. Violation of the ratio of androgens and estrogens leads to a loss of the ability of the muscles of the bronchioles to contract, which contributes to the formation of air space in the lungs.
Pulmonary pressure rises due to severe diseases of the respiratory system, profession, penetration foreign particles in the bronchi and blockage of oxygen, which cannot find an outlet and presses on the organs respiratory system.
Read also:Sarcoidosis of the lungs, what is it: modern ideas about the causes, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Classification of pulmonary emphysema
Emphysema is classified according to the following features:
- the nature of the course of the disease: acute form (occurs suddenly, ambulance intervention is necessary) and chronic emphysema of the lung (slowly developing, difficult to diagnose at the initial stage);
- origin of the disease: primary (a self-developing disease, often congenital) and secondary (complication after a previous illness);
- the level of lung damage: focal (a separate part of the organ is damaged) and diffuse (the lung tissue is completely affected, a complete organ transplant is often necessary);
- anatomical features of the course of the disease: hypertrophic form (severe form of the disease, there is no inflammatory process, there is a lack of respiratory function), centrilobular form (with an increase in the lumen of the trochea, an inflammatory process develops with the formation of mucus in large quantities), paraseptal form due to the patient's pulmonary tuberculosis (possible damage and rupture of the organ), pericarform (formed near scars on the lungs), subcutaneous form (bubbles are formed under the skin), bubble form (bullous emphysema of the lungs, there are large vesicular formations on the lung tissues);
- causes of occurrence:age form (change in the state of blood vessels due to age), lobar form (congenital sign of obstruction of one of the bronchi), compensatory form (occurs when the lobe of the lung is removed, the body tries to compensate for the created space by increasing the other lobe).
The most dangerous form is bullous emphysema of the lungs. It proceeds secretly, without any obvious symptoms. Bubbles, called bullae in medicine, can grow up to 20 cm in size. The accumulation of air and gases in the pleural part can be fatal.

Most of the patients suffering from bullosa emphysema are smokers with more than 20 years of experience, a category of people whose work is associated with harmful working conditions.
In humans, there are about 3 million in the lungs. small "sacs" with fragile walls (alveoli). When a person inhales, they are filled with air, increasing the volume of the lungs, when they leave, part of the air remains, but the volume of the lungs decreases.
Gradually, the walls of the alvels are destroyed, which leads to the formation of cavities in place of "sacs", the blood supply to the respiratory tract is disrupted, which subsequently leads to chronic emphysema of the lungs.
Most addicted smokers have chronic lung disease by the age of 60.
Symptoms and signs of pulmonary emphysema

The difficult initial diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema is associated with its symptoms. Many symptoms of pulmonary emphysema are observed in other pathologies. The individual characteristics of pulmonary emphysema include:
- dry (unproductive) cough;
- dyspnea when you exhale;
- dry wheezing in the respiratory organs;
- a sharp decrease in body weight;
- pain in the chest area;
- violation of cardiac activity with a lack of oxygen.
The main signs of the presence of pulmonary emphysema are cough and shortness of breath. Dyspnea at the initial stage is felt only during physical exertion on the body, over time it develops into shortness of breath when moving without physical exertion, especially when responding to weather events. Shortness of breath is temporary.
Weight loss is also an individual symptom of pulmonary emphysema. The process is associated with the intense work of the pulmonary muscles during exhalation.
When diagnosing, special attention is paid to the tone of the skin and mucous membrane (bluish tint). Cyanosis associated with the lack of blood filling small capillaries in the lungs. The shape of the fingers changes.
The chronic form of pulmonary emphysema is accompanied by obvious external signs: shortened neck, barrel-like rib cage.
Complications of pulmonary emphysema
A change in the work of the respiratory system affects the cardiovascular and nervous system. Due to air starvation, the heart valve begins to pump blood with greater intensity, which puts additional stress on the heart.
Heart strain is one of the reasons tachycardia of the heart, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiopulmonary insufficiency, coronary heart disease.
Chronic emphysema of the lungs disrupts the functioning of the nervous system, contributing to sleep disturbances, the work of brain cells, and the development of mental illness.
Read also:Bronchiolitis
Complications of pulmonary emphysema lead to chronic infectious diseases of the respiratory system, pneumothorax, heart failure right ventricular form.
Diagnostic methods for the study of pulmonary emphysema

If you suspect pulmonary emphysema, a person needs an urgent appeal to a physician or a pulmonologist, who are determined with the choice of the method for confirming the diagnosis (diagnosis).
The main methods of diagnosis are:
- questioning the patient, a detailed conversation with the patient about the symptoms of the disease;
- listening to the thoracic region and examining the patient's skin;
- general blood test, including gas composition;
- spirometry;
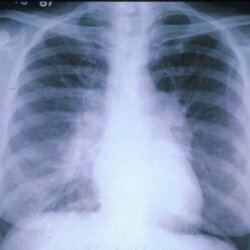
- MRI or CT;
- plain radiography;
- determination of the heart border;
- topographic percussion and auscultation.
When collecting information (anamnesis), information is found out: about the presence of shortness of breath, a bad habit (smoking), the duration of the cough, the state of the body during physical exertion. It is necessary to carry out percussion (tapping on the body), in which the following signs are revealed, indicating the presence of pulmonary emphysema:
- difficulty in establishing heart boundaries;
- restriction in lung mobility;
- omission of the lower edge of the lung;
- a dull sound in the lungs.
Listening through the phonendoscope gives the specialist the opportunity to establish: dry wheezing, rapid breathing, signs of tachycardia, muffled heart sounds, increased exhalation, a weakened breathing process.
Instrumental examination of the lungs is carried out using: X-rays (radiography), radio waves (magnetic resonance imaging), a computer with the introduction into the body special contrast agent, radioactive isotopes (scintigraphy), spirometer device, blood gas analysis using ulnar artery puncture, blood test (general analysis).
Therapy (how to treat pulmonary emphysema)
When treating pulmonary emphysema, pulmonologists have three main goals:
- eliminate symptoms (shortness of breath, weakness, etc.);
- stop the further development of the disease;
- prevention of mild failure;
It is impossible to talk about a complete cure of the disease, especially in the chronic stage.
Drug treatment
Treatment consists of several groups of drugs. The first group includes drugs that reduce the level of enzymes that contribute to the destruction of lung tissue. The second group (mucolytic action) promotes the discharge of mucus, reduces coughing, protects the respiratory system from infectious diseases.
The drugs of the third group help to improve the metabolic process in the respiratory organs, additionally nourish the lung tissues. The fourth group - bronchodilator drugs, which reduce the swelling of the bronchial mucosa.
Additionally, the use of the following drugs is required:
- theophylline remedies for relieving muscle load on the muscles of the respiratory system;
- glucocorticosteroids to dilate the bronchi, providing an anti-inflammatory effect.
Physiotherapy and other therapies
Therapeutic procedures are effective in the form of electrical stimulation, oxygen inhalation, and special physical education.
Oxygen inhalation is a long-term procedure (up to 18 hours a day) being in an oxygen mask, where an oxygen stream is supplied at a maximum rate of 2 to 5 liters per minute.
Breathing gymnastics consists of specially selected exercises to help strengthen the respiratory muscles. Classes must be carried out 4 times a day, lasting 15 minutes. The complex is performed as follows:
- exhalation with an obstacle: Exhale 20 times slowly into a glass of water through a cocktail straw;
- diaphragm breathing: a deep breath at the expense of 1,2,3, inflating the stomach at the expense of 4, exhale, cough while straining the press;
- squeezing from a lying position: lie on your backs, bend your legs, clasping your knees with your hands, inhale as much as possible air into the lungs, while inhaling, raise your stomach, straighten your legs, cough with a tense press.
Transcutaneous electrical stimulation is performed using a current to aid in the exhalation process. The current impulse is selected individually and helps to relieve the fatigue of the lung muscles.
Read also:Signs of pneumonia in an adult without fever: is it possible?
Surgery
In exceptional cases, a decision can be made about surgical intervention. The following types of operations are applied:
- replacing the affected lung with a donor organ. The operation is used in rare cases, since there is a risk of organ rejection, a large priority for transplantation;
- removal of the affected area of the organ using thoracoscopy. Under the control of special video equipment, the affected area of the lung is removed. The technique allows the operation to be performed using 3 small intercostal incisions.
- surgical removal of part of the lung (removal of up to 25% of the organ is possible);
- bronchoscopic surgery is carried out using a special device that is inserted into the patient through the oral cavity and removes the affected area.
Nutrition and folk remedies
Diet plays an important role in treatment. Preference should be given to vegetables and fruits containing trace elements and vitamins vital necessary for the body, eating food low in calories, excluding fatty, fried dishes.
The patient's drinking regimen should be up to 1.5 liters of water per day.
In addition to drug treatment, traditional medicine can be used as an adjunct to the main treatment.
The main recipes recommended for the treatment of pulmonary emphysema are based on herbal decoctions:
- mother-and-stepmothers (1 tbsp. a spoonful of dried leaves for 2 cups of boiling water, use up to 6 times a day, 1 tablespoon);
- potato flowers (1 h. spoon in a glass of boiling water, drink half a glass up to 3 times a day).
It is possible to carry out potato inhalations by inhaling vapors from potatoes cooked in their uniform.
Prevention and recommendations
To prevent emphysema of the lungs, the state has developed a program to combat smoking.
People who smoke need to be assisted in the fight against bad habits, including medication.
Treatment of the respiratory tract should not be neglected and the transition of the disease into a chronic form should not be allowed.
Timely vaccination of the population, annual examination and fluragraphy is one of the main conditions for the prevention of pulmonary emphysema.
Life prognosis for patients with pulmonary emphysema

No specialist can say for sure about the life expectancy of a patient with a diagnosis of pulmonary emphysema. The prognosis of life largely depends on the patient himself, his psycho-emotional attitude to treatment.
An important role is played by the stage of the disease, correctly selected treatment, and timely diagnosis.
You can not self-medicate, it can be fatal. In this case, the life prognosis of patients with pulmonary emphysema is unpredictable.
Despite the nature of the disease and its chronic form, it is possible to delay the onset of a person's disability by taking specially prescribed drugs. Such drugs are prescribed to the patient for life.
With a severe form of the disease, the patient's life prognosis is more than 1 year from the moment the disease is detected.
Studies have shown that disease survival depends on the severity of:
- a mild form of emphysema, subject to proper treatment and a healthy lifestyle, allows the patient to live more than 4 years in 80% of cases;
- a moderate form of pulmonary emphysema, subject to proper treatment and a healthy lifestyle, allows the patient to live more than 4 years in 73% of cases;
- with a severe course of the disease, subject to proper treatment and a healthy lifestyle, in 54% of cases, the life expectancy of patients is more than 4 years;
- with the most severe form of pulmonary emphysema, subject to proper treatment and a healthy lifestyle, in 26% of cases, the life expectancy of patients is more than 4 years.
The patient himself must strive for life. Give up smoking and alcohol, take daily walks in the fresh air, follow the doctor's prescriptions, all this can live even much longer than the period indicated in the statistics.