Pulmonary pleurisy (in adults and the elderly): symptoms and treatment
Of all the diseases of the respiratory system, the most severe are inflammation of the lower respiratory tract, and of them pleurisy is a dangerous form of inflammation.
In this article we will look at what it is, talk about the symptoms and treatment of pulmonary pleurisy.
Is it possible to treat and how to treat inflammation of the pleura with folk remedies.
Content
- What is pleurisy
- Classification (types of disease)
- Causes of occurrence
- Symptoms of pulmonary pleurisy
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Pleurisy treatment
- Surgery (thoracocentesis)
- Physiotherapy procedures
- Treatment of pleurisy of the lungs with folk remedies
- Prophylaxis
- Forecast
What is pleurisy
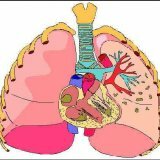
Pulmonary pleurisy is an inflammatory process in the pleural membrane, leading to the accumulation of fluid contents (exudate or fibrin) in the pleural cavity.
Arises as pathological condition, after various infectious lung diseases or formations adjacent to them. Very rarely occurs as an independent disease.
The pleura is the membrane that surrounds the surface of the lungs. It consists of a pair of petals that line the diaphragm, mediastinum, and the lining of the chest cavity.
In healthy people, the pleural cavity contains a lubricant in the form of serous fluid, it helps the lungs slide when breathing. The remaining fluid is absorbed by the lymphatic and blood vessels.

When an inflammatory or infectious process begins, edema, vasodilation, their permeability is impaired.
Two days after the onset of inflammation occurs vascular thrombosis. The pleura swells, cell infiltration begins. Then exudate appears.
Depending on the type of inflammation, it can be purulent, serous, fibrinous, hemorrhagic. After treatment, the exudate can dissolve, followed by the formation adhesive process. The purulent exudate does not dissolve, it is eliminated only by surgery.
Pleurisy of the lungs more often is detected in older men aged 60-70 years.
Classification (types of disease)
All pleurisy etiology is divided into:
- Infectious. The causative agent can be staphylococci, streptococci, mycoplasmas, fungi, a genus of opportunistic bacteria (Klebsiella), mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Non-infectious (aseptic). Development is promoted by oncological diseases, autoimmune pathologies (lupus erythematosus, Graves' disease), diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, myocardial infarction, trauma to the chest cavity.
According to the clinic of inflammation of the pleurisy of the lungs, they are divided into:
- dry pleurisy (non-perspiration);
- exudative (exudative);
- tuberculous.
According to the composition of the contents, exudative pleurisy is:
- Serous fibrinous - an inflammatory process characterized by the accumulation of serous contents. Fibrin forms on the pleural surface.
- Hemorrhagic - inflammation of the pleura, manifested by the accumulation of blood exudate in its cavity.
- Purulent. It is manifested by the formation of purulent contents in the pleural cavity. It can be wrapped or spilled. In the enclosed form, pus is in a confined space. Draft purulent pleurisy begins after the breakthrough of pus into the pleural cavity.
If pleurisy of the lungs begins during pneumonia, it is called parapneumonic, if after pneumonia it is called metapneumonic.
Read also:
— pneumonia symptoms in adults.
Parapneumonic pleurisy begins acutely, in the presence of pneumonia. Worried about a wet cough dyspnea, chest soreness when breathing. The amount of exudate is small.
Metapneumonic occurs more often in weakened bedridden patients. It begins after pneumonia, is difficult to treat and in most cases is complicated by pleural empyema (pyothorax, purulent pleurisy).
Causes of occurrence
Lower respiratory tract infections often contribute to the development of pulmonary pleurisy. From the primary focus with pulmonary tuberculosis, pneumonia, abscess, pathogenic organisms through the bloodstream or lymph enter the pleural cavity and cause its inflammation.
Infection of the pleura can occur during intracavitary surgery or with trauma to the chest.
Concomitant diseases of non-infectious origin can also cause the development of pleurisy. With oncological diseases, metastases are released, when they enter the pleura, they contribute to the release of exudate. Myocardial infarction very often complicated by effusion pleurisy.
Read also:Bronchiolitis
At severe disorders of the immune system (rheumatoid arthritis, hemorrhagic vasculitis, lupus erythematosus) develops exudative pleurisy. With such lesions, it is bilateral.
In older men, pleurisy can begin due to inflammation of the pancreas. With acute pancreatitis, enzymes have a toxic effect on the pleural membrane, causing the formation of fibrin.
Symptoms of pulmonary pleurisy

The symptoms of pleurisy depend on the form of inflammation and its stage.
The main symptom of dry pleurisy is a cough that causes chest pain. If the patient lies on the sore side, the discomfort decreases. Observed hyperthermia to subfebrile numbers, dry cough, general weakness. When breathing, there is a lag in the chest in breathing from the pathological side.
Exudative pleurisy develops sharply, appears fever, sweating, symptoms of intoxication. There is a rapid increase in shortness of breath, a feeling of heaviness in the chest. It is difficult for the patient to lie down, he takes a forced sitting position.
Symptoms of serous fibrinous pleurisy. It is characterized by the accumulation of serous exudate. At first it develops asymptomatically, then painful breathing appears, dry unproductive cough, hyperthermia,
The symptom of hemorrhagic pleurisy is a feeling of tightness in the chest, severe intoxication,pallor of the skin, cough streaked with blood.
Purulent pleurisy characterizes persistent increase in temperature up to 39-40 C, pain with breathing, shortness of breath, weakness, sweating.
Tuberculous pleurisy is characterized by irregularities low-grade fever, shortness of breath, dry cough, muscle pain. Often becomes empyema of the lungs.
Complications
With the timely identification of the cause of the disease and proper treatment, the disease ends with a full recovery.
In some cases, the following complications develop:
- Adhesive process in the lungs. It is a scar formation in the connective tissue of the pleura. More often formed after exudative pleurisy. With multiple adhesions, the respiratory system of the lungs is disturbed.
- Formation of pleural moorings. They are characterized by fibrinous layers on the surface of the pleura. Occur both after exudative pleurisy and after dry. More often localized in the upper lungs. Patients with this complication are worried about shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest during exercise.
- Pneumosclerosis. The process by which the lung tissue is replaced with coarse connective tissue. In areas of pneumosclerosis, the lung tissue loses its elasticity and does not perform a gas exchange function.
- Empyema of the pleura. A dangerous complication of pleurisy, leading to gangrene of the lung. It is characterized by a high body temperature of up to 40 C, unbearable chest pain. Heart and respiratory failure develops. Which is most often fatal.
- Respiratory failure. Suppurative inflammation or extensive inflammation of the pleura can cause respiratory distress.
Diagnostics

Diagnostic measures include:
- examination and questioning of the patient;
- clinical examination;
- X-ray examination and computed tomography;
- ultrasound procedure;
- general blood analysis;
- pleural puncture.
When examining a patient with pleurisy of the lungs, asymmetry of the chest is visible, the diseased part lags behind in the act of breathing. With a large accumulation of effusion, cyanosis of the skin may be observed, since the blood supply in the cervical veins is disrupted due to compression. The sore side of the chest looks more voluminous.
With percussion, a weakening of the percussion sound is noted, and the upper border is an oblique Damoiseau line, which is clearly visible on radiography. When listening to the lungs with a phonendoscope, the noise of pleural friction is clearly audible, it looks like the creak of snow. Breathing in places of accumulation of fluid is sharply weakened.
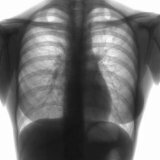
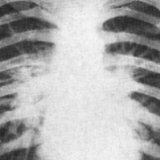
On the radiography symptoms of effusion pleurisy of the lungs are displayed as intense uniform darkening in the lower lobes of the organ. The high standing of the diaphragm is observed with a small accumulation of fluid. The mediastinum is displaced to the healthy lung. When taking a picture in lateroposition (the patient lies on his side), there is a horizontal displacement of the exudate.
Non-effusion pleurisy of the lungs in the picture is manifested by intense shadows of a heterogeneous structure, the sinuses are not defined. Pleural mobility is sharply limited.
In the general analysis of blood with pleurisy, there is a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in the level of leukocytes, an increase ESR. Eosinophilia and monocytosis are characteristic of tuberculous pleurisy.
Read also:List of expectorant drugs, inexpensive but very effective
Blood chemistry shows the presence of fibrinogen and high levels of sialic acids.
The main informative diagnostic method is thoracocentesis (pleural puncture). The patient is punctured in the pleural cavity under local anesthesia in order to take fluid. Exudate examination helps to determine the form of pleurisy and the infectious agent of the disease.
With tuberculous, traumatic pleurisy, erythrocytes are visible in the exudate. The color can range from pink to deep red.
With a purulent process, the exudate is cloudy, gray or gray-green in color; when gangrene has begun, it may have a fetid odor. If the exudate is transparent and odorless, serous pleurisy is diagnosed.
On ultrasound examination, there is an increased echogenicity in the place of fluid accumulation, a thickening of the pleura.
Pleurisy treatment
The main principle in the treatment of pleurisy is the identification and treatment of the underlying disease. Patients with pleurisy of the lungs need a balanced diet high in vitamins. Strict bed rest is shown.
Surgery (thoracocentesis)
Surgery for pleurisy in adults is necessary for purulent inflammation.

Thoracocentesis - is an emergency measure. With a large amount of effusion, pleural puncture is performed to free the cavity from fluid.
The procedure takes place in several stages.
No more than 1 liter of exudate is removed at a time. Pumping out a large amount of exudate can lead to acute heart failure and an abrupt expansion of the lung.
If necessary, antibacterial drugs are injected into the cavity. After the end of the procedure, tight bandaging of the chest is performed to prevent collapse.
Drug treatment
- Antibacterial therapy. Pulmonary pleurisy of infectious etiology is treated with antibiotics. Usually applied amoxiclav, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, sumamed. In the treatment of tuberculous pleurisy, it is used rifampicin, isoniazid.
- Corticosteroid therapy. Treatment of pleurisy for autoimmune pathologies is the use of hormonal drugs. Applicable prednisone.
Also in the treatment of pleurisy, symptomatic agents are used:
- Antitussive drugs. Patients with pleurisy are worried about a dry, painful cough. Therefore, they are prescribed drugs that inhibit the cough reflexcodeine, sinecode.
- Diuretic drugs. To remove excess fluid from the body, it is necessary to use diuretics - furosemide.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. To eliminate pain and relieve inflammation, medications are used - butadion, ibuprofen, analgin.
- Cardiac glycosides. To improve the contractile function of the myocardium - korglikon.
- Bronchodilators. To expand the bronchi, appoint euphylline, berodual. They relax the muscles of the bronchi, improve the function of the respiratory muscles.
- Infusion therapy. In case of severe intoxication, an intravenous solution is used. Ringer's.
Physiotherapy procedures
Physiotherapeutic procedures are effective in treating pleurisy. With their help, the evacuation of the effusion occurs faster, and adhesions also dissolve.
Physiotherapy procedures include:
- electrophoresis with calcium chloride;
- warming up;
- various compresses.
If pleurisy is caused by tumor metastasis, chemotherapy is given.
Treatment of pleurisy should take place in a hospital under the supervision of specialists. The therapy lasts from 2 to 4 weeks.
Treatment of pleurisy of the lungs with folk remedies
The combination of traditional medicine and the treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies will help to cope with this disease more effectively and quickly.
Treatment of pleurisy with folk remedies is to alleviate its symptoms.
Read also:Symptoms and treatment of bronchitis in adults
Anise-based folk recipes help to eliminate cough, have a bronchodilatory effect:
- 1 hour Brew a spoonful of anise fruit with 1 cup boiling water. Leave to infuse for 20 minutes. Drink ¼ glass 4 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
Expectorant based on radish and honey:
- Grate medium-sized black radish on a fine grater, squeeze the juice. Mix a tablespoon of black radish juice with 1 tablespoon of honey. Consume 2 tbsp. spoons 15-20 minutes before meals, 3-4 times a day.
Folk recipes with honey have anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effects.

Mucolytic agent for pleurisy:
- take 2 tbsp. tablespoons of butter, 2 boiled chicken yolks, 1 tsp. l flour, 2 tsp. spoons of honey. Mix all the ingredients and take a teaspoon 5 times a day.
A good effect is given by treatment with folk remedies in the form of compresses and rubbing:
- rubbing with camphor. Mix 50 ml of camphor oil with 5 ml of eucalyptus oil. Rub the chest 2 times a day;
- warming compress with animal fat. Mix 250 g of badger fat (can be replaced with pork) with 4 leaves of aloe. The aloe should be chopped up. Add 4 tbsp to the ingredients. spoons of honey, mix everything. Sculpt a cake and wrap in gauze. Apply to the chest 3 times a day.
At home, pleurisy can be cured with onion inhalation. This vegetable contains phytoncides that help cleanse and strengthen the respiratory system.
- Peel the onion, cut into small pieces. Put them on a gauze napkin, roll it up. Breathe over the onion bag 3-4 times a day.
Treatment with folk remedies for pleurisy can only be started after consulting a doctor. Folk recipes are an adjunct therapy in the treatment of pleurisy, therefore, should be used in conjunction with modern medicines. Treatment of pleurisy at home is possible only at the stage of recovery.
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures are based on the timely detection and treatment of diseases that cause inflammation.
To reduce the likelihood of illness, you must follow the rules:
- Strengthening the immune system. Take complex vitamins during the high season.
- Rejection of bad habits. Smoking harms the lungs and contributes to the development of pathological processes in them.
- Do not self-medicate. If even a not strong cough appears, you should be examined by a doctor.
- Exercise. Physical activity increases the body's resistance.
- Treat viral diseases in time. Very often late treatment ARVI leads to the development of complications, including pleurisy.
- Undergo a preventive examination. Once a year, it is necessary to undergo fluorography. It will help identify various pathologies in the early stages.
- Walks in the open air. Strengthen the respiratory system, help cleanse it.
Forecast
With adequate treatment, dry pleurisy has a favorable prognosis. But there may be lifelong changes in the pleura - adhesions, pneumofibrosis, mooring.
Purulent pleurisy of the lungs has an unfavorable prognosis. Difficult to treat. Has a chance of bursting of purulent contents into the chest, which can lead to sepsis.
Tuberculous pleurisy has the ability to recur repeatedly, so patients should be under close medical supervision for 2 months.
Pulmonary pleurisy in the presence of oncology also ends unfavorably. Metastases destroy the pleura, leading to severe intoxication and the development of respiratory failure.