Blood in sputum (hemoptysis): what it can be, causes, treatment
Content
- general information
- What is hemoptysis?
- Causes
- Respiratory Disorders
- Other diseases
- Symptoms and complications
- Main symptoms and signs
- Possible accompanying symptoms
- Diagnostics
- When to Seek Medical Help
- Differential diagnosis
- Treatment
general information
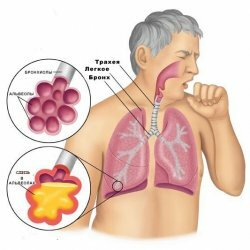
Blood in sputum (or hemoptysis, hemoptysis) Is a symptom that can be caused by many diseases. In fact, sputum with traces of blood can come from the trachea, bronchi, lungs, or any other part of the respiratory system.
The most common pathologies causing hemoptysis are bronchitis, bronchiectasis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and infectious diseases of the respiratory tract. However, blood in sputum can also result from lung cancer, heart disease, vascular lesions and chest injuries.
Once the underlying problem has been identified, the hemoptysis can be treated by choosing one of the available treatment options. The danger of the symptom is due to the amount of blood found in the sputum and the duration of hemoptysis.
Remember! Hemoptysis is manifested blood in sputum when coughing up.
What is hemoptysis?
Hemoptysis (i.e., blood in sputum) is a symptom of varying degrees that can range from simple mucus to traces or streaks of blood (minimal) to more pronounced signs such as expectoration of small threads or clots blood.
This blood loss, light red or dark red, is due to damage to the respiratory systemparticularly the lungs, trachea or bronchi.
Hemoptysis may be accidental or recurrent: in any case, it should never be neglected and should be distinguished from hemoptysis, that is, the discharge of noticeable quantities of bright red blood from the respiratory tract, without the presence of mucus.
Causes
The presence of blood in sputum can be caused by many pathologies.
Blood can come from tracheobronchial tree and / or from pulmonary parenchyma. The most frequently responsible pathologies are bronchiectasis, chronic obstructive lung disease, tumors and infectious diseases.
Respiratory Disorders

One of the most common causes of blood in sputum is respiratory infections (For example, pneumonia and bronchitis) of viral, bacterial, fungal and parasitic origin. In fact, these conditions cause local trauma at the level of the mucous membrane of the airways, so the sputum appears to be stained with traces of blood. In most cases, once the infection is gone, the symptoms go away.
Chronical bronchitis.
Blood in sputum is one of the most common symptoms of chronic bronchitis. This inflammation is characterized by a productive cough that lasts at least 3 months and may be accompanied by shortness of breath, barrel chest, cyanosis and the fingers of Hippocrates.
Recurrent and chronic inflammatory processes can predispose to the development of bronchiectasis, abnormal focal or prolonged airway dilatation, with mucus accumulation.
Read also:Aspergillosis
This pathological phenomenon is often associated with cystic fibrosis. In this context, blood in sputum can be an indicator of damage to the walls of the bronchi: the airways are markedly widened, which leads to a potential rupture of the adjacent artery; therefore, in addition to chronic cough and phlegm, patients who suffer from it can sometimes cough up blood.
Possible causes of hemoptysis are also primary (benign and malignant) or metastatic tumors lungs (such as renal cell carcinoma, colon cancer and mammary cancer).
Remember! Blood in sputum may be one of the earliest signs of lung cancer.
Blood in sputum can also occur if:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- pulmonary edema;
- embolism with pulmonary infarction;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- emphysema of the lungs;
- inflammation of the blood vessels in the lungs (vasculitis).
Blood in sputum when coughing up can also be caused by inhalation of foreign bodies (especially in children), severe trauma or damage to the lungs, and ruptured pulmonary artery.
Other diseases
Blood in sputum can also be caused by pathological conditions in neighboring organs that are not directly related to the respiratory system, including:
- stagnant heart failure;
- inflammatory lesions of the pharynx;
- swelling of the larynx;
- thyroid cancer;
- various types of infections (bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, ebola, etc.);
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- arteriovenous malformations;
- mitral stenosis;
- Goodpasture syndrome;
- rib fracture;
- collagen diseases (collagenoses);
- diseases associated with impaired coagulation (blood clotting process).
Sometimes the causes of blood in sputum are iatrogenic and can occur as a result of taking anticoagulant or thrombolytic drugs, cardiac catheterization, airway intubation, surgery, radiation therapy, bronchoscopy and other methods diagnostics.
Symptoms and complications

Blood in sputum is usually found after coughing. Depending on the causative cause, hemoptysis can manifest itself as a sporadic symptom (associated with one episode) or recurrent (manifests itself until the underlying pathology is eliminated).
Read also:Fluid in the lungs
Main symptoms and signs
- Depending on the organ affected and the severity of the lesion, hemoptysis can vary from salivary discharge with traces of blood to discharge of blood mixed with sputum.
- Depending on the amount of blood secreted, the sputum can be bright red, pink, or brown in color, similar to rust. Usually, the more intense the pigmentation of hemoptysis, the more serious the problem underlying this manifestation.
- In some cases, the blood in the sputum is frothy, as it mixes with air.
Possible accompanying symptoms
When the problem is of a certain severity, blood in the sputum may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- fever;
- shortness of breath and air hunger (shortness of breath);
- profuse night sweats;
- increased heart rate (tachycardia);
- weight loss;
- general malaise;
- sputum with an unpleasant and purulent odor;
- increased breathing rate (tachypnea);
- Difficulty breathing while lying down (orthopnea).
Warning signs to watch out for:
- persistent cough, in which more than a couple of teaspoons of blood mixed with phlegm are released;
- chest pain;
- blood in urine and / or faeces;
- dizziness.
Diagnostics
The study of the blood content in sputum begins with establishing the true causes of bleeding. In addition, it is necessary to differentiate hemoptysis from blood loss that occurs from the oral cavity and / or from the digestive tract. This requires an accurate disease history combined with careful clinical examination.
To determine the cause and determine the site of bleeding, the main diagnostic test is presented bronchoscopy. This method of examination allows you to examine the trachea and bronchi, as well as collect tissue or sputum samples, which will subsequently be subjected to microscopic analysis.
Etiologically, the physician may expose a patient with hemoptysis imaging tests: in addition to chest x-ray, important information is provided computed tomography of the lungs (CT), especially regarding the location and presence of bronchiectasis.
Read also:Pulmonary insufficiency
During the diagnostic procedure, other instrumental studies may be useful, including:
- echocardiography, a useful examination in determining pulmonary embolism, left ventricular failure and mitral stenosis;
- blood tests and studies of other blood parameters, including determination of PT or PTT;
- microbiological culture and sputum smear to analyze the presence of an infectious process.
When to Seek Medical Help
If there is blood in your sputum, you should always see a doctor, especially if it is profuse or associated with chest pain, confusion, and dizziness.
If hemoptysis occurs as a result of trauma or severe contusion to the chest, it is recommended that you contact your doctor as soon as possible. emergency department.
Differential diagnosis
When assessing the patient's condition, it is also important to exclude other sources of bleeding, such as the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract.
In particular, blood in sputum should be distinguished from:
- hemorrhage from the nose to the pharynx;
- hematemesis (blood from the digestive system, released during vomiting);
- throat irritation associated with severe coughing (usually the amount of blood secreted by saliva or mucus is minimal).
Treatment
As for treatment, options vary depending on the cause of the blood in the sputum.
Possible interventions include:
- The use of local vasoconstrictor agentssuch as epinephrine or vasopressin;
- Laser photocoagulation with bronchoscopy;
- Embolization pr angiography of bronchial arteries;
- Selective intubation to suppress bleeding in the lungs where it occurs.
Surgical interventionis the last tool of choice, eliminating blood in sputum. This may include lobectomy or pneumonectomy.