Asthenozoospermia: what is it in men, causes, symptoms, treatment
Content
- Introduction
- A quick overview of what sperm are
- What is asthenozoospermia?
- Determination of asthenozoospermia according to WHO
- Epidemiology
- Synonyms for asthenozoospermia
- Causes of asthenozoospermia
- Symptoms and complications
- Complications
- When to see a doctor?
- Diagnostics
- Basic rules for obtaining a reliable spermiogram
- Examination of the causes of asthenozoospermia
- Treatment
- Asthenozoospermia, infertility and artificial insemination using in vitro fertilization
Introduction
Asthenozoospermia Is a disease that affects men and is characterized by a decrease in the content of mobile spermatozoa during the production of ejaculates.
A sufficient amount of motile sperm is essential for reproductive purposes; in fact, those who suffer from asthenozoospermia - especially when it is an acute form - have some difficulty in conceiving a child.
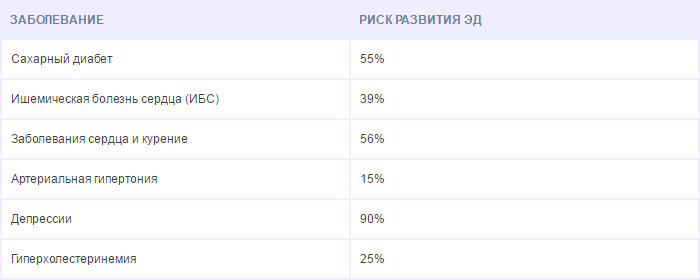
Causes and risk factors for asthenozoospermia include diseases and conditions such as varicocele, alcohol abuse, smoking, use of illegal psychoactive substances, urinary tract infections, testicular cancer, teratozoospermia, malnutrition, severe fever, etc.
For the treatment of asthenozoospermia, it is important to treat the underlying causes of the disease.
A quick overview of what sperm are

Sperm are male gametes, i.e. cells responsible for reproductive function in men.
Produced by the testes (male reproductive organs), on the occasion of the so-called spermatogenesis, spermatozoa are very small cellular elements (5-7 micrometers) and have a very special structure that includes:
- headcontaining the cell nucleus and acrosome;
- intermediate partrich in mitochondria;
- tailagile and challenging disasters.
The specific morphology of the sperm is fundamental to the reproductive process, as it allows them to meet and fuse with the egg within the female reproductive system.
What is asthenozoospermia?
Asthenozoospermia Is a medical term that indicates a decrease, below the reference value corresponding to normality, the percentage of motile sperm in the ejaculate, that is, in semen.
Asthenozoospermia is a condition that is of great interest to men who want to have children, as a decrease in the number of motile sperm is associated with decline male fertility (male infertility).
Determination of asthenozoospermia according to WHO
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a man suffers from asthenozoospermia in two cases:
- when less than 32% of his sperm has progressive mobility
or alternatively
- when the sum between the percentage of sperm with progressive motility and the percentage of sperm with non-progressive mobility (the amount, which in a professional term is called full mobility) is less than 40%.
At this stage, for the less experienced and doubtful, it is necessary to highlight the points of "progressive motility", "non-progressive motility" and "complete mobility" of spermatozoa:
- Progressive mobility → Progressive motility occurs when sperm show that they can move in a straight line when their ability to move is analyzed. Most progressive motility sperm are ideal for reproductive purposes;
- Non-progressive mobility → Sperm have non-progressive mobility, which, after analyzing their ability to move, moves, but absolutely not in a straight line. For reproductive purposes, high sperm counts with non-progressive motility are negative.
- Full mobility → This term includes all spermatozoa with a certain motility, whether progressive or not, and excludes all immotile spermatozoa, i.e. unable to move.
Read also:Symptoms and treatment of cystitis in women
table. Reference values that establish the normality of male ejaculate, according to the latest WHO data (2010).
| Parameter | Units | Reference values |
| Ejaculated volume | Milliliter (ml) | > 1.5 ml |
| Sperm concentration | Millions per milliliter (million / ml) | > 15 million / ml |
| Total sperm count | Millions | > 39 million |
| General sperm motility | % sperm | > 40% |
| Progressive sperm motility | % sperm | > 32% |
| Sperm viability (viable sperm) | % sperm | > 58% |
| Sperm with normal morphology | % sperm | > 4% |
Epidemiology
Statistics on the prevalence of asthenozoospermia among the male population are extremely scarce and unrealistic.
The only sufficiently reliable information on this issue (prevalence of asthenosuspermia) concerns the number of men with complete asthenosuspermia (*): one case in every 5000 males.
*Note: "Complete asthenozoospermia" is a term that indicates the complete absence of motile sperm in the ejaculate.
Synonyms for asthenozoospermia
In the medical field, asthenozoospermia is also known as asthenospermia.
Causes of asthenozoospermia
Doctors and researchers believe that several conditions are included in the list of causes and risk factors for asthenozoospermia, including:
- The presence of special antibodies that "attack" the sperm (antisperm antibodies);
- Alcohol abuse, smoking, or excessive use of drugs such as hashish or marijuana;
- Age is over 45 years old. Statistical studies have shown that, starting from this age, a slow decrease in sperm motility is observed in men;
- Exposure to toxic substances such as pesticides, fertilizers, chemical solvents, etc .;
- Availability genital infectioncarried by one of the organs through which sperm and seminal fluid usually flow (prostate, seminal vesicles, epididymis and urethra);
- Have testicular disease (eg, testicular cancer or hydrocele (dropsy of the testicle));
- Teratozoospermia. It is a sperm abnormality characterized by the presence of deformed sperm (eg sperm without a tail);
- Varicocele. This is a pathological change in the veins of the testicle (or sperm), as a result of which the latter appear dilated, and one or both testicles are swollen;
- Lack of nutrients due to improper diet;
- Severe febrile conditions or the consequences of severe febrile conditions;
- Chemotherapy and / or radiation therapy for pelvic cancer
- Behavioral habits that lead to a rise in temperature at the testicular level (for example, frequent use of saunas, a tendency to wear light clothing, etc.).
Read also:Blood in the urine of a woman, men: what can it be, how to treat it?
Symptoms and complications
Asthenozoospermia by itself does not cause physical symptoms; however, it is quite closely related to the symptomatic framework, since, as reported in the previous chapter, it is often associated with broadly symptomatic conditions.
So, for example, in the case of asthenozoospermia caused by varicocele, it is likely that the subject (human), in addition to a reduced number of motile spermatozoa, dull pain in the testicle, swelling of the testicle, discomfort in the groin area, etc..
Complications
As indicated in part, men with severe asthenozoospermia tend to develop infertility, preventing them from having children.
When to see a doctor?
A man with asthenozoospermia should see a doctor, in particular a urologist or andrologist, when:
- wants to have children, but the condition from which he suffers (asthenospermia) is an obstacle to his desire;
- this is manifested by a related symptomatological picture, incompatible with the conduct of a normal life. In this case, the cause of asthenozoospermia is a condition that has a certain clinical significance, which deserves due attention and adequate treatment.
Diagnostics
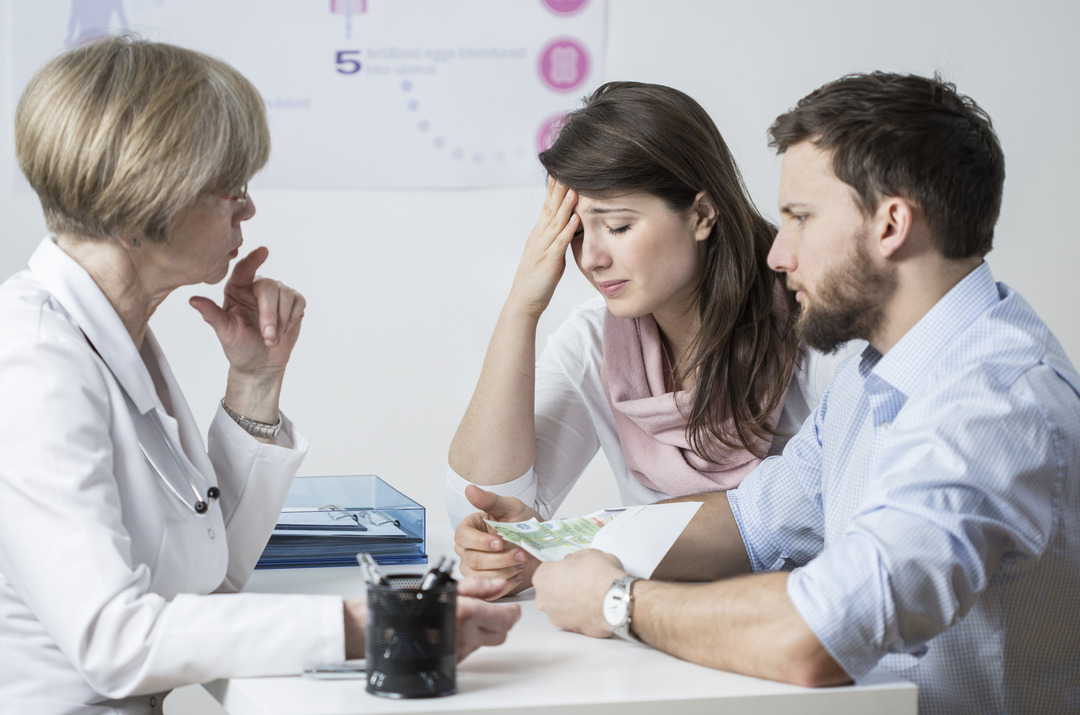

To diagnose asthenozoospermia, doctors rely on a test known as spermiogram.
A spermiogram is a laboratory study that allows you to observe a number of important characteristics a semen sample to assess the fertility of the man who owns the aforementioned sample sperm.
Semen characteristics measured by a spermiogram include:
- semen viscosity;
- liquefaction of semen;
- sperm count;
- sperm motility.
Once the presence of asthenozoospermia is established, the next step is to study of the causes decreased sperm motility; such a study may require the performance of various diagnostic tests, including instrumental studies.
Basic rules for obtaining a reliable spermiogram
For spermiogram results to be reliable, adherence to some of the rules that are preparatory to the above laboratory test is fundamental; in more detail, these preparatory rules include:
- Complete abstinence from sexual activity 3-5 days before the tests;
- Ejaculation must be obtained exclusively by masturbation;
- Ensure adequate hand and penile hygiene before masturbation;
- Collect all the sperm produced (so to speak, to a drop);
- For collection, use a suitable sterile container (classic urine containers will do);
- Close the used container hermetically to avoid accidental leakage of the collected semen sample;
- After collecting the samples, send the semen sample to the analytical laboratory as soon as possible (within 30-60 minutes) to avoid heat shock. Currently, these problems no longer exist because analytical laboratories provide subjects with the ability to collect in the laboratory room itself;
- Inform the medical staff of the laboratory about any methods of treatment or diseases that are present or have passed within the last three months;
- Inform the laboratory medical staff of any non-compliance with one of the above preparatory rules in order to understand whether the semen collection procedure should be repeated or not.
Read also:How thrush manifests itself in men: symptoms, photos, methods of treatment
Examination of the causes of asthenozoospermia
The search for the causes of asthenozoospermia always begins with objective examination and anamnesis (patient history); therefore, even according to the results of these two examinations, it is possible to continue and undergo: blood and urine analysis, sperm culture, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the testicles, ultrasound of the lower abdomen, etc.
Treatment
Asthenozoospermia therapy is based on treating or eliminating a trigger factor.
Therefore, for example, in men with varicose asthenospermia, treatment of the latter will be a way to combat the decrease in the presence of motile spermatozoa.
As you can easily imagine, among the causes of asthenosuspermia there are trigger conditions that are more susceptible to successful treatment than others, and this, of course, affects the degree of restoration of normal mobility sperm.
Asthenozoospermia, infertility and artificial insemination using in vitro fertilization
For some time, men who want to have children but cannot have them because they suffer from asthenozoospermia may rely on a certain method. assisted in vitro fertilization, known as ICSI or intracytoplasmic sperm injection.
Without going into details, the method ICSI provides a specific collection of sperm with progressive motility from the ejaculate sample in order to fertilize the egg.
Currently, intracytoplasmic sperm injection is one of the most effective unconventional in vitro fertilization methods available for men with asthenozoospermia problems seeking to become fathers.