Meningitis in children: symptoms, treatment
Contents:
- Types CNS
- Causes of meningitis
- disease Symptoms of meningitis detection methods
- Treatment
- Conclusion
 meningitis called the inflammatory process that occurs in the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. The child distinguishes between general infection, cerebral and meningeal symptoms of meningitis. The pathological process occurs more often in the soft membranes of the spinal cord, the brain. In children, signs of meningitis depend on inflammatory changes in cerebrospinal fluid. Symptoms of meningitis in children, whose immune system is weak, develop rapidly.
meningitis called the inflammatory process that occurs in the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. The child distinguishes between general infection, cerebral and meningeal symptoms of meningitis. The pathological process occurs more often in the soft membranes of the spinal cord, the brain. In children, signs of meningitis depend on inflammatory changes in cerebrospinal fluid. Symptoms of meningitis in children, whose immune system is weak, develop rapidly.
Because of the disease, it is possible to develop organic brain damage( there is a violation of nervous activity).The incubation period of meningitis( the time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms) in children and adults is from 2 to 10 days. The first signs of meningitis in a child do not differ from those characteristic of a common cold, which makes it difficult to diagnose this neuroinfection in the early stages.
Types of neuroinfections
Pathology can be an independent disease( primary) or a consequence of pathology( secondary).Depending on which shells of the brain are damaged, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- panmeningitis;
- pachymeningitis;
- leptomeningitis;
- arachnoiditis.
With panmenigitis, the pathological process occurs in all shells. Pachymeningitis is characterized by a predominant lesion of the hard shell. Disturbances in the soft, arachnoidal sheaths are referred to as leptomeningitis. When arachnoiditis pathological changes occur only in the arachnoid shell.
 Find out how meningitis manifests in adults: photos, causes, incubation period, consequences.
Find out how meningitis manifests in adults: photos, causes, incubation period, consequences.
Read if the meningitis is contagious: the ways of getting meningitis.
Because meningitis is manifested in children as pronounced intoxication and cerebral syndromes, as well as the changes took place in the cerebrospinal fluid, usually distinguished mild, moderate and severe forms of the disease. Neuroinfection can occur in fulminant, acute, subacute and chronic forms. Depending on the nature of cerebrospinal fluid distinguish: hemorrhagic, serous, purulent meningitis.
Causes of development of meningitis
Pathology develops due to the penetration of foreign microorganisms. Pathogens are bacteria, viruses, protozoa, fungi. You can get infected from a person or other bacteria.
Neonates disease appears due to poor pregnancy( lack of oxygen in the fetus, premature birth, intrauterine infections).In children under 10 years of age, the symptoms of meningitis develop due to purulent diseases, acute respiratory viral infection, intestinal infection, head trauma. The causes of the development of the disease are:
- immature immune system;
- high blood-brain barrier permeability;
- insufficient weight;
- hypothermia of the body;
- grueling exercise.
Symptoms CNS Symptoms
referred to obscheinfektsionnym, cerebral, meningeal. To general infectious symptoms include:
- hyperthermia( high body temperature);
- loss of appetite;
- rapid breathing;
- tachycardia;
- fever and chills( trembling, painful sensation of cold);
- pale color or flushing of the skin, non-inflammatory rash( hemorrhagic).
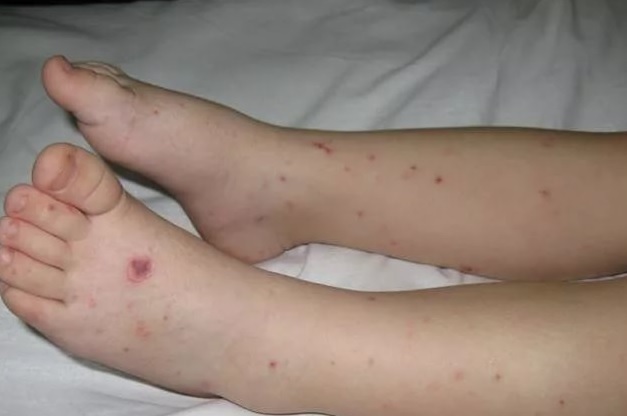 migraine, nausea, nebula of consciousness and seizures( of varying degrees of severity, up to an epileptic seizure) are characteristic of cerebral syndrome.
migraine, nausea, nebula of consciousness and seizures( of varying degrees of severity, up to an epileptic seizure) are characteristic of cerebral syndrome.
meningeal syndrome is characterized by the presence of postures "hook" of children, increased muscle tone of the neck, hypersensitivity( high sensitivity to stimuli).See how the meningitis looks like in a child, you can in the photo. In newborns, the appearance of a venous mesh on the head, eyelids, and deviations that are associated with a large fontanel.
Methods for detecting the meningitis
In order to diagnose this infectious disease, the physician collects epidemics( data on the children and the terrain with which the patient was in contact) confirms the meningeal syndrome. Consultations with such doctors as:
- neurologist are also necessary;
- children's ophthalmologist;
- pediatric otolaryngologist;
- neurosurgeon.
If suspected of a disease, a diagnostic test is prescribed for a spinal puncture. This makes it possible to investigate the cerebrospinal fluid, and also to differentiate meningitis from meningism( there is no inflammatory process, but there are symptoms characteristic of neuroinfections).
At the discretion of the doctor, the following measures are carried out: magnetic resonance imaging, an electroencephalogram, a brain X-ray, neurosonography.
Treatment of
If suspected in children of meningitis, treatment is carried out in a hospital. The patient is provided with complete peace and bed rest, and a special, gentle diet is prescribed. They control the hemo- and liquorodynamics, physiological functions.
To treat the disease, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Their administration is carried out by intramuscular and intravenous route. Children who are in serious condition, the drug is administered endolumbular way( into the spinal canal).Treatment with antibacterial drugs is 10-14 days. In the case of viral origin, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
The prognosis of neuroinfection treatment depends on the causes of the development and severity of the disease, timeliness and adequacy of treatment. The prognosis is usually favorable, the mortality rate does not exceed 5%.
 Learn how to recognize serous meningitis and the cause of the disease.
Learn how to recognize serous meningitis and the cause of the disease.
Symptoms and methods for overcoming tuberculous meningitis: preventive measures.
Causes and mechanism of purulent meningitis development: diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Prevention of meningitis in children consists of vaccination, personal hygiene. The patient is placed in the hospital, and in the institution where he stayed recently( kindergarten, school, etc.), they carry out quarantine measures. Conduct a bacteriological study in those individuals with whom the infected child was in contact. More information about the symptoms of the disease in the video.
write the question in the form below: