Mendelssohn syndrome
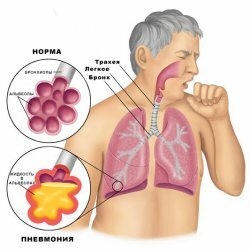
 Mendelssohn syndrome refers to acute inflammation of the respiratory tract due to ingestion of acidic gastric juice. The syndrome predominantly occurs in obstetric anesthesiology. However, the ingestion of acidic, enzyme-rich stomach contents in the lower respiratory organs is also found in patients of different categories who are under general anesthesia and without it. Refers to a number of deadly complications from anesthesia. Lethal outcomes are observed in 60% of cases. More often lethality is observed in obstetric anesthesia, more than 70%.
Mendelssohn syndrome refers to acute inflammation of the respiratory tract due to ingestion of acidic gastric juice. The syndrome predominantly occurs in obstetric anesthesiology. However, the ingestion of acidic, enzyme-rich stomach contents in the lower respiratory organs is also found in patients of different categories who are under general anesthesia and without it. Refers to a number of deadly complications from anesthesia. Lethal outcomes are observed in 60% of cases. More often lethality is observed in obstetric anesthesia, more than 70%.
Causes of
The main cause of the appearance of the syndrome can be considered vomiting or regurgitation in a patient in a coma. The following series of causes of the Mendelssohn Syndrome are also distinguished: a full stomach( when the patient takes food 3-6 hours before the operation), alcoholic intoxication, narcotic state, pregnancy( from the 22nd week of the term), obesity, increased intragastric pressure, inflammatory processes of the esophagus and t. P.A high risk of aspiration occurs during anesthesia in cases of emergency surgical intervention, with operative labor( caesarean section).
Pathogenesis of
Mendelssohn syndrome can occur in two ways. In the first, the aspirated contents are of a solid substance with a weakly acid or neutral reaction, more often it is food that the patient used. In the second case, the very acidic contents of the stomach get into the respiratory tract, which causes burns of bronchial mucosa and trachea. On what aspirated content falls into the respiratory system and will depend on the diagnosis and course of the disease. If aspiration of food can lead to stagnation of average bronchioles and lack of oxygen, ingestion of gastric juice leads to chemical burn of the mucous membrane of bronchioles, bronchi and trachea, which causes acute oxygen deficiency.
As the tests have been established, a severe chemical burn of the respiratory tract arises from aspirated gastric juice, whose pH level is 2.5, more light burns cause a liquid with a pH of 1.5.In the first minutes after aspiration of the contents of the stomach into the trachea, the mucosal edema occurs, which causes Mendelssohn's Syndrome with acute shortness of breath.
Clinical picture
It is determined that the course of the disease develops very quickly and does not depend on the nature of the aspirated content, passes through three phases.
The first phase: in the first few minutes after aspiration, acute respiratory failure caused by bronchospasm, development of pulmonary edema occurs. Patients with tachycardia, cyanosis of the skin, severe cough, shortness of breath. Whistles and a variety of wet rales are audible in the lungs. The central venous pressure rises. Sometimes doctors confuse the first phase of the syndrome with attacks of bronchial asthma.
The second phase: after a while there is an expansion of acute oesophrenia and temporary partial relief is manifested. Breathing slightly leveled, pressure decreases.
The third phase: on the third day there is a fever, a strong cough. There is a swelling of the bronchi, which leads to a new outbreak of deterioration in the patient's health. There is a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood, blood circulation is violated, pressure is falling. Developing hypoxia.
The patient's condition is restless, there is even a disturbance of consciousness, a clouding of the mind. The lethal outcome comes from pulmonary edema, the pathology of which is not suspended. Sometimes the primary changes are so severe that they cause a cardiac arrest.
Emergency Care for Mendelssohn Syndrome
The first step is to remove the contents of gastric juice or food from the respiratory tract. This can be done with a gauze swab( for cleaning the mouth) or a special medical suction. Before hospitalization it is necessary to introduce a flexible plastic tube into the trachea, which will ensure mechanical ventilation of the lungs - this is called intubation of the trachea. To avoid secondary aspiration, it is necessary to perform Sellik's treatment( press on the cricoid cartilage, which will squeeze the esophagus between the cartilages of the spine and larynx, this will become an obstacle to regurgitation).
Hospitalization
If the patient develops Mendelssohn's syndrome, it is necessary to consult a physician and a pulmonologist. Even when it is possible to suspend bronchiolospasm and pulmonary edema, the patient still needs to be hospitalized in the emergency department in order to avoid serious complications. After elimination of the first phase of Mendelssohn Symptom, corticosteroids should be administered. For the prevention of aspiration pneumonia, the use of antibiotics is necessary. If the first phase of the syndrome has passed to the third, long-term ventilation is used. Introduce a shock dose of antibiotics that enter the penicillin series. You can transfer the patient on a stretcher with an elevated leg end at 15 degrees. In the ambulance, it is necessary to carry out artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Prevention of Mendelssohn Syndrome
Remember, the best prevention of the appearance of the syndrome is an empty stomach. This applies to patients before the operation and to those cases when in the alcoholic state when vomiting in the respiratory tract gets gastric juice and food particles. To avoid the occurrence of Mendelssohn's Syndrome, the following should be observed:
- Do not feed, do not water a patient before surgery. If this regime was violated, then it is worthwhile to postpone the planned operation in order to avoid aspiration. In an emergency, it is worth to empty the stomach by inserting a probe with a double dose of antacid.
- To increase the tone of the cardiac pulp of the esophagus, it is worthwhile to include metoclopramide half an hour before the anesthesia is injected.
- After the introduction of medications, the patient is left in the Fauler position and is further prepared for the operation.
- Introduce anesthesia with an intravenous anesthetic( kaoipsol, diprivan, thiopental, etc.), set the mask oxygen compensation.
- After the onset of anesthesia, a dose of muscle relaxant is injected with Sellick. This method helps to prevent ingestion of gastric juice into the oropharynx.
- After the operation is completed, restore breathing, consciousness, muscle tone.
- Women who are in labor should be given medications that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach.
After surgery, the patient can pull additional tubes only after complete recovery of consciousness, muscle tone, independent breathing, etc. Extubation of the tubes allows the patient to clear his throat and spit out the remnants of saliva and other contents. The patient continues to be monitored in intensive care and in the intensive care unit. Patients who have suffered severe Mendelssohn syndrome, subsequently suffer from impaired lung function, they develop restrictive and obstructive disorders.
Analyzing the causes of the syndrome, one can come to the conclusion that a major drawback in the action of anesthesiologists is the failure to follow the correct algorithm of the action of a technical and preventive order. In court cases often there are no explanations of anesthesiologists about the reasons for the failure of emptying the stomach, inserting the probe into the stomach, etc.