Proliferation of glandular epithelium
Proliferation of glandular epithelium is an increase in the number of glandular structures in the cervical epithelium. This condition is not considered an independent nosology, but only an isolated cytological sign that does not always indicate a serious pathology.
The cervix( more precisely, its vaginal, accessible to inspection, part) and the vaginal cavity are covered with an epithelium of identical structure: multilayered flat. He is endowed with the ability of self-renewal and protective function.
The cervical canal is lined with epithelial cells of a different structure: these are tall, cylindrically shaped cells arranged in a single row. Multiple branching glands are integrated into the mucosa of the cervical canal, producing cervical mucus.
The state of the cervical epithelium is significantly influenced by cyclic hormonal processes, so when you examine it you can clearly see how it changes in different phases of the cycle. In the ovulatory period, the amount of secretion of cervical glands increases, and its consistency also changes.
The place where two epithelia, which are different in structure, are connected, called the "transformation zone" or "transitional".By localization it coincides with the external pharynx - the physiological narrowing of the cervical canal from the side of the vaginal part of the cervix. Thus, the structure of the mucous membrane of the cervix is not uniform and, therefore, functions ambiguously. When proliferating the glandular epithelium, there is an increase in the number of glands, a change in their shape and function.
It should be noted that the proliferating glandular epithelium can be localized exclusively in the cervical canal, and can leave its limits and be located on the cervix outside.
Proliferation of glandular epithelium of the cervix is diagnosed primarily with local inflammatory, dyshormonal or post-traumatic processes. The clinical picture depends on the etiology of this condition and varies widely from the absence of symptoms to a pronounced pattern of infectious inflammation. Glandular proliferation is often accompanied by pseudo-erosion of the cervix, when proliferating glandular epithelium is found on the vaginal part of the cervix.
Diagnosis of glandular proliferation on the cervix begins with a visual inspection, which allows you to detect unusual for the color of the mucosa not to the neck. To study the cellular composition of this site helps colposcopy and cytology.
Glandular proliferation is diagnosed in the study of the smear "on cytology."The cytogram of proliferation of glandular epithelium describes the increase in the number of glands, a change in their shape and structure.
Treatment of proliferation of glandular epithelium is not carried out in isolation, since the process disappears only after the elimination of its cause.
Causes of proliferation of glandular epithelium
Proliferation of glandular epithelium of the cervix has a fairly large number of causes, but not all of them correlate with the pathological process. So, for example, in some healthy, long-acting hormonal contraceptives, women in the study on the neck are found individual sites of proliferation of glandular epithelium.
Among the pathological causes of glandular proliferation of the epithelium of the cervix are more common:
- Infectious inflammatory processes with localization in the vaginal cavity( colpitis) and / or in the cervical channel( cervicitis) of various( including specific) etiology. Penetrating into the epithelium of the cervix infection triggers the protective mechanism of the glandular structures: in order to get rid of the undesirable microflora, the glands begin to intensively produce a lot of secret, trying to "wash off" the infection from the surface and prevent it from penetrating inwards. In this case, they can increase in size, become crimped and elongate, which contributes to a general increase in the volume of glandular tissue.
- Hormonal dysfunction. Since the cervical epithelium is closely associated with cyclic hormonal changes, its normal functioning can be disturbed by dyshormonal disorders, endocrine pathologies.
In pregnant women, moderate proliferation of glandular epithelium also occurs due to physiological hormonal changes, when the ratio of sex hormones changes, and the cervical epithelium does not receive the proper estrogenic effect.
- Injuries to the cervix. In case of traumatic births, abortions or incorrectly performed therapeutic and diagnostic manipulations, the integrity of the cervical epithelium is disturbed. Sometimes the glandular epithelium grows during the regeneration process.
Iron proliferation of the cervical epithelium often accompanies the formation of pseudo-erosion, when cells of the cylindrical epithelium "descended" from the cervical cavity with glands appear on the surface of the neck covered with multilayered epithelium.
Symptoms and signs of proliferation of glandular epithelium
As already noted above, glandular proliferation of the cervical epithelium as a cytological sign accompanies not one disease, and does not have an independent clinical picture.
The variety of laboratory and clinical findings often leads the patients into confusion and does not allow understanding the essence of this process. In fact, to correctly perceive all the processes associated with the proliferation of glandular epithelium, you need to know a few basic points:
- the proliferation of glandular epithelium implies an increase in the size and number of cervical glands, sometimes, the glandular epithelium expands so much that it provokes an increase in the total volume( hyperplasia)glandular tissue;
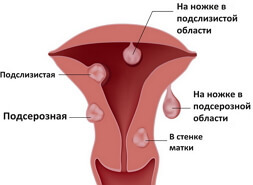
- proliferating glandular epithelium may be located on the cervix( vaginal surface) or in the cavity of the cervical canal, therefore the picture of this structural transformation is determined by its localization;
- proliferation of glandular epithelium is ambiguous not only in localization, but also in the degree of diffusion: it may be diffuse or focal, when only the areas of proliferating glandular epithelium appear on the background of normal mucosa, similar to "nodules";
- the severity of the proliferation process indicates the severity of the pathological process, moderate proliferation of glandular epithelium is more often combined with local inflammatory processes;
- on the cervix uteri proliferating glandular epithelium is often diagnosed in pseudo erosions( ectopias), and in the cervical cavity it can be present in the composition of glandular polyps, which, in fact, are the result of focal glandular hyperplasia.
There are no clinical manifestations of glandular proliferation of the cervical epithelium, but it is present in the pathologies that provoked it. In inflammatory processes, pathological leucorrhoea, vaginal discomfort are noted, and if the patient has hormonal dysfunction, menstrual disorders( dysfunctional uterine bleeding, intermenstrual blood allocation, anovulatory cycles) will be disturbed.
It is possible to reliably determine proliferating glandular epithelium only in laboratory, having studied the cellular composition of the cervical mucosa.
Diagnosis of the proliferation of glandular epithelium
When visually examining the cervix, the proliferating glandular epithelium can be seen as a region of the mucosa of an unusual species, often surrounding the external pharynx. The epithelium of the cervix has a multilayer structure, so it has a pale pink color. Cylindrical epithelium, covering the cervical cavity, is single-row, through it the underlying layer with blood vessels shines, coloring the mucosa in a more saturated, red, color. When a cylindrical epithelium appears on the cervix, it stands out clearly on a general pale background, so it is visible during normal examination.
Sometimes, in addition to the presence of a modified mucosa, small( less than 1 cm) hemispherical forms with a thin wall and translucent yellowish contents are clearly visible on the neck. These are the so-called "python cysts."They are formed from the nodular glands located in the lower third of the cervical cavity. Each such a natal iron is similar to a tube filled with a mucous secret that is evacuated outward through the opening of its excretory duct. When proliferating the glandular epithelium, the openings of the glandular glands sometimes overlap, as a result of blockage, a small cavity with liquid contents is formed - the cyst. Deeply located( above the external throat), the pencil cysts are not available for external examination. If the glandular epithelium proliferates with the formation of cysts, they speak of a glandular-cystic transformation.
If proliferating glandular tissue does not leave the cervical canal, visually the neck may look normal.
With accompanying inflammatory processes, typical symptoms are visualized: hyperemia of the mucous membranes and their pronounced edema, a significant amount of pathological discharge.
Since the proliferation of glandular epithelium is often infectious and inflammatory, laboratory diagnostics( smear "on flora", bak-sowing, PCR) is necessary for the presence of infection, including specific ones. In women with menstrual dysfunction, the definition of the concentration of the main hormones in accordance with the phaseicity of the cycle is necessarily included in the list of laboratory studies.
A detailed study of the site of the modified epithelium of the cervix helps colposcopy and cytology.
The proliferation of glandular epithelium is characterized by uneven, often focal, thickening of the mucosa, as well as the presence of different in size and shape of glands lined with endocervical epithelium.
The cytogram of proliferation of glandular epithelium is informative only in the situation when the process is localized on the surface of the cervix. If proliferates the glandular epithelium of the cervical canal and does not overcome the border of the external pharynx, a reliable diagnosis can be made only after histological examination of the scrap of the cervical cavity.
It should be noted that the proliferation of glandular epithelium of the cervical canal is often combined with a similar process in the endometrium, so a diagnostic search should not be limited only to the endocervical zone, it is also necessary to study the state of the intrauterine mucosa. Separate curettage of the cervical and uterine cavities is carried out with subsequent histological study.
Proliferation of glandular epithelium is classified as a benign process, if at the examination there is no pronounced atypical transformation of the epithelium.
Treatment of proliferation of glandular epithelium
Proliferation of glandular epithelium is not treated isolated from the disease that provoked it. Therefore, we can say that the treatment of glandular proliferation is similar to the treatment of infectious inflammation, ectopia, hormonal dysfunction or hyperplastic processes in the uterus.
If an infectious inflammation is detected, adequate antibiotic therapy is necessary. Treatment begins after the laboratory identification of the pathogen.
In the treatment of hormonal dysfunction it is necessary to compensate for the impaired ratio of sex hormones. The most commonly used tablets are hormonal drugs from the contraceptive group.
To eliminate the proliferation of glandular epithelium against the background of pseuderosion, one of the many methods of destruction( destruction) of the mucosa site with signs of proliferation is used:
- Diathermocoagulation. With the participation of electric current, the modified epithelium is "cauterized".
- Cryodestruction, or "freezing".
- Destruction of the site of glandular proliferation by laser.
- Radio wave destruction.
After the site of proliferating glandular epithelium is destroyed by any chosen technique, in its place regeneration processes are started, as a result the structure of the mucous surface of the cervix is restored.