Features of urethral stricture in men
Symptomatology and surgical treatment of urethral stricture in men
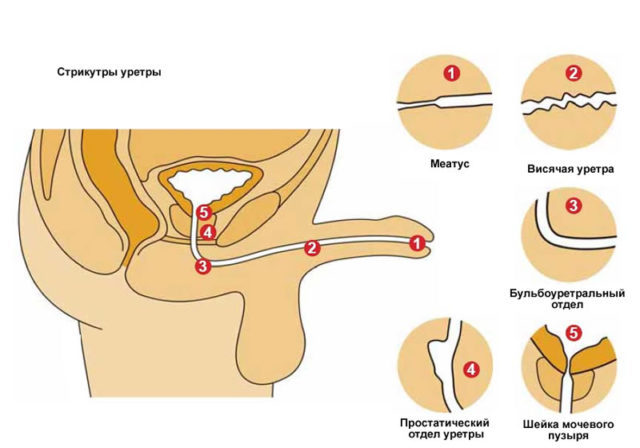
Urethral stricture - is an anatomical narrowing of the urethra, resulting in difficult urination. This is a fairly common pathology, revealed 2% of males and 1% of women.
In most cases, stenosis occurs in men as they urethra is much longer than in women and is more susceptible to injury.
Some urologists say that actually male patients with such a diagnosis is much more than just 2% have misdiagnosed prostatitis, cystitis or prostate adenoma.
And identify the stricture of the urethra in men and to treat it only after serious research.
The narrowing of the urethra may occur in people of any age. Most often it occurs in front of the urethra.
The causes of urethral stenosis
pathology causes could be:
- Injuries genitals.
- Fracture of the penis.
- Penetrating knife or gunshot wounds to the front of the urethra.
- Catheterization (particularly during long operations).
- Surgery.
- Fractures of the pelvis as a result of work-related injuries or falls from a height.
- Radical prostatectomy.
- Sexually transmitted diseases, which are the causative agents of Trichomonas, Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, gonococci.
- Tuberculosis of the genital organs.
- Chemical damage to the urethra resulting in self-medication.
- The deterioration of blood supply to the genital area in systemic vascular atherosclerosis or diabetes.
Classification
Strictures are classified according to the nature and causes of urethral damage.
By the nature of the flow.
- The primary form. It is diagnosed in case if the patient has the disease is detected for the first time.
- Recurrent. It determined if after treatment the disease progresses again after bougienage, coronary stent or urethroplasty.
- Complicated. Complications are considered fistulas or abscesses.
By the nature of the disease.
- Traumatic. The cause of their injuries are the penis resulting from strokes, injury or medical procedures.
- Inflammatory. Is the result of inflammation of the urethra caused by pathogenic microorganisms are sexually transmitted.
- Congenital. The reason why there is such a pathology has not been established.
- Idiopathic. In this case, the reasons for urethral stenosis appeared in adulthood can not figure out.
At the place of localization.
- Capitatum, penile and bulbar stricture formed in the external opening of the urethra.
- Prostatic and membranous. Stenosis of the rear part of the urethra.
In count.
- Identity. Narrowing occurs only in one place.
- Multiple. Stricture formation in several areas of the urethra.
To size.
- Short. narrowing the length of not more than one centimeter.
- Average. Restriction length from one to two centimeters.
- Long. The restriction length greater than two centimeters.
On the extent of damage.
- Subtotal strictures. In this case the 2/3 urethral damage.
- Panuretralnaya stricture. It narrowed almost the entire urethra.
- Obliteration. urethral lumen is absent and there is complete obstruction.
symptoms
On the restriction of the urethra indicate problems with urination. Determine the disease can be further feature:
- To start urinate need to make an effort.
- Urine stream weakens and sprayed, despite the tension of the abdominal muscles.
- After the end of urination there is a feeling that the bladder is not completely emptied, and new desires.
- In some men, the disease is accompanied by incontinence.
Additional symptoms that indicate the disease:
- Aching pain in the lower abdomen and genital area.
- Weak emission of semen during ejaculation.
- The semen or urine admixture of blood appears.
- Appear mucus after urination.
- Pain can occur and burning in the urethra during urination.
- Urine volume decreases.
- In the event that narrowed almost the entire urethra drops urine is released.
- When obliteration of the urine does not come out of the bladder. This is a very dangerous condition and without the timely assistance possible death.
complications
Violation of the outflow of urine leads to the fact that the ring-shaped muscle at the outlet from the bladder overstrained and thereafter atrophies. As a result of its contractile capacity decreases.
The bladder is emptied completely ceases, and in its lumen collects residual urine.
If it is more than 100 ml volume, this is a serious disease and can cause diseases such as:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Cystitis.
- Orchitis.
- Prostatitis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Renal insufficiency.
- Diverticulitis.
- Hydronephrosis.
Diagnostics
In order to diagnose disease doctor collects history, figuring out how long ago the problems started and what preceded it. The patient may be asked to make a diary in which he will have to fix the frequency of urination, urine volume, urge intolerance, possible leakage of urine. It will also need to record the amount of fluid consumed.
In addition, conduct surveys:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Bacteriological examination of prostate secretions and urine.
- Complex ultrasound examination urinary organs.
- Uroflowmeter (determination of the amount of urine, act duration and rate of urine flow).
- Urethrography (x-ray of the urethra with contrast).
- Imaging of the pelvic organs (if necessary).
- Endoscopy (examination of the affected area with the endoscope).
Treatment
urethral stricture treatment with medicines or folk methods is almost impossible.
In order to solve the problem it is necessary to carry out probing, urethrotomy or urethroplasty.
urethral probing
This is one of the most common treatments for urethral stricture in women and men. Its essence lies in the fact that by means of a special tool made of a durable material expanding constricted portion.
To get rid of urethral stricture every time bougie is introduced with a larger diameter. Before the beginning of the session the man should hold hygiene.
The patient is seated in a special chair. Head of the penis and the tool itself is treated with a special gel, and the doctor begins to gradually introduce a bougie into the urethra. It is promoted as long as it reaches the bladder. Then left for 5 - 10 minutes removed and replaced with a larger diameter tool. Bougie change until there are difficulties in extracting them.
After the procedure, the urethra is treated with antiseptic and prescribe antibiotics to avoid the development of the inflammatory process.
Disadvantages:
- The result is a temporary bougienage. procedure does not improve the blood circulation in the affected area, so over time (in some cases even in a month), stenosis appears again, with the narrowing becomes longer, and tissue scarring increases.
- During the procedure can damage the urethra.
- After bougienage may occur inflammation in the genital area.
internal urethrotomy
This method is used in the strictures of not more than 1 cm. The procedure lasts about thirty minutes. 8 hours before urethrotomy can not take food or drink water. Before starting conducted hygiene. The patient is given general anesthesia or epidural and placed in a chair.
Then the penis is introduced cystoscope, to detect strictures. By means of special cold knife scar tissue is cut and expanded urethra. The doctor then conducts further study the bladder. After the procedure, a catheter is inserted into the urethra.
Disadvantages internal urethrotomy:
- The possibility of damage to the urethra, and the development of inflammation.
- Re-formation of urethral stricture and the need for another operation.
- Pain in the penis.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Tissue scarring.
- The possibility of bleeding.
- Pain when urinating.
urethral stenting
Procedure applies if the patient has severe health problems and it is contraindicated general anesthesia. This is a minimally invasive method of treatment of urethral stenosis.
In order to remove the restriction set inside a tube mesh or spiral structure. It can be constant or dissolve over time.
Spend urethral stenting is performed under local anesthesia.
procedures Disadvantages:
- Urethral mucosa can grow through the hole in the stent, which not only covers the course of the urine, but also creates some difficulties in removing the device.
- Possible encrustation of the stent.
- Stent migration, quite serious complication, it can not only cause urinary retention, but also complicate the extraction device.
- Due to the improper selection of the length of the stent or selecting a location may occur leakage of urine.
urethroplasty
Urethroplasty - a surgical operation, through which restore normal urethral lumen. There are many of its methods, depending on the size of the stricture, its location and complications.
Before the surgery, the man must have passed all the necessary tests. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Reconstruction operate through an incision in the skin between the scrotum and anus. During a certain period, the patient remains in the hospital under medical supervision.
When the total defeat of the urethra is necessary to fully restore the urethra along the entire length. For this transplanted tissue, taken from the inner surface of the forearm. rather complicated method, but perform urethral reconstruction is possible in a single step.
If the narrowing of the urethra and are in short bulbar or membranous department, the affected area is excised, and two normal end connect. In the event that this is not possible, eliminate the defect by other tissues such as the skin of the penis, or buccal mucosa. Field of the catheter which is set for the period from 10 to 21 days.
Depending on the complexity of the urethroplasty tasks can be carried out in two stages, or even several, between which is from 4 to 12 months. The method selected individually after determining the patient's problems.
Disadvantages:
- Recurrence of the stricture.
- Narrowing meatus.
- The appearance of fistulas.
- Deformation of the penis.
- Urinary incontinence.
- Problems with erection.
See also:Why there is strong sweating neck?
At the same time may occur a few complications.
rehabilitation period
After carrying out the procedures to expand the urethra needs some rehabilitation period. At this time it is necessary to adhere to the following rules:
- Regularly take antibiotics and painkillers, prescribed by the doctor.
- If a catheter for him to take care of regularly.
- Within 2 weeks after surgery should refuse to take a bath, swimming pool, sauna, baths or swimming in open water.
- Perhaps to scar tissue again blocked urethra catheter is necessary to put and take out a few times a week.
- Within a month after the procedure, you can not lift weights and do hard physical labor.
- It is necessary to use a sufficient amount of liquid. It is not recommended to drink carbonated drinks and alcohol.
- You need to eat right and abandon the use of salty and acidic foods.
- For two weeks after the surgery can not have sex.
- In the event that there are problems with urination, a catheter is not draining urine, change the amount of urine, urinary frequency, there are signs of inflammation or a large amount of blood in the urine is an urgent need to consult a doctor.
disease prevention
In order to prevent narrowing of the urethra in men must adhere to the following rules:
- Avoid casual sex.
- During sexual intercourse with new or unreliable partners to use condoms.
- At occurrence of symptoms such as pain during urination time, a rash or discharge immediately seek medical advice.
- In the treatment of urological diseases or venereal fulfill all requirements of a doctor.
- Avoid injury to the genitals.
- Do not abuse miramistinom solutions and Chlorhexidine used for prevention of sexually transmitted diseases and are entered directly into the urethra. With high sensitivity to such drugs, even a small concentration of substances may cause a burn mucosa.
If you have problems with urination can not self-medicate, and the mandatory need to seek help from a urologist. In the early stages of the disease can quickly get rid of. Lack of timely treatment could lead to the fact that the need to carry out several major operations.
Found error in text? Select it and click Ctrl + EnterAnd we were all correct!
A source: https://venerbol.ru/uretrit/striktura-uretry-u-muzhchin-lechenie.html
urethral stricture
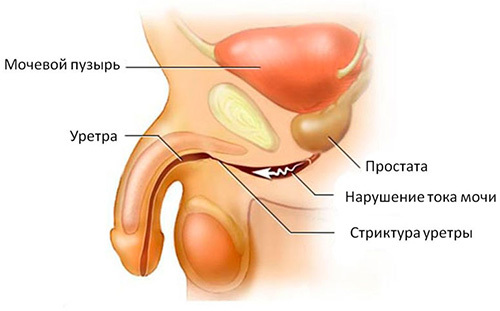
urethral stricture - pathological narrowing the inner lumen of the urethra, resulting in micturition disorders of varying severity.
Urination with urethral stricture becomes difficult, and often painful, it is accompanied by spraying a jet of urine and a sense of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Diagnosis of urethral stricture requires urodynamic studies urethrography and ureteroscopy, ultrasonic bladder volume measurement of residual urine laboratory tests. When urethral stricture may require probing urethral resection portion anastomotic strictures with the performance or substitution urethroplasty.
Stricture of the urethra in urology occur in 1-2% of men and 0.5% women.
Primary distribution of urethral strictures in men due to the greater length and complexity the structure of the male urethra, as well as its exposure to a lighter injuries and other damages factors.
The potential danger of unrecognized or incompletely healed urethral stricture is likely to develop urinary tract infections tracts (cystitis, pyelonephritis), urolithiasis, urinary bladder diverticula, complete blockage of the flow of urine, hydronephrosis, renal failure.
Classification of urethral strictures
Etiology distinguish urethral stricture congenital and acquired (traumatic, inflammatory, iatrogenic) character. According pathomorphosis distinguish primary, recurrent and complicated urethral stricture.
Violation of patency of the urethra with urethral stricture may be partial or complete.
Stricture may be localized in front of the urethra (in the region of the outer holes - meatus, capitatum, penile or bulbar card) or posterior urethra (in prostatic or membranous department).
In length urethral stricture are divided into short (up to 2 cm) and long (length - more than 2 cm). With the defeat of 2/3 of the length of the urethra say subtotal strictures; the narrowing of the lumen of substantially all of the urethra - of the total (panuretralnoy) stricture. Complete loss of luminal obstruction of the urethra and it is regarded as obliteration of the urethra.
Congenital urethral stricture quite rare (about 2%) and are caused mainly by the front valve constriction of the urethra. More often urologists encountered with acquired urethral stricture, which can be caused by trauma (70%), inflammatory processes (15%), iatrogenic causes (13%).
Post-traumatic urethral stricture, usually develop as a result of blunt perineal trauma, penetrating injuries of the urethra, sexual excesses (foreign bodies urethra, penis fractures), fractures of the pelvis (as a result of avtotravm, falls, work injuries), chemical, thermal, damage to the urethra.
Iatrogenic urethral stricture may be caused by careless handling and carrying urological operations - ureteroscopy, cystoscopy, bougienage, catheterization, remove stones or foreign bodies, TURP, radical prostatectomy, penile implant, brachytherapy. In women, the urethra stricture may occur after birth trauma, vaginal hysterectomy, cervical amputation and so forth.
Urethral stricture inflammatory genesis can develop as a result of the transferred urethritis (gonorrhea, chlamydia, tuberculosis), balanitis, nonspecific degenerative processes (sclerosing lichen) and etc.
The development of a urethral stricture may be associated with diseases accompanied by deterioration of blood supply and urethral tissue metabolism - systemic vascular atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, diabetes, arterial hypertension.
In terms of development of pathogenic urethral stricture passes several stages: urothelium damage and disruption of the integrity of mucosa, urinary streaks formation, layering secondary infection, proliferation and granulation tissue leading eventually to the scar-sclerotic processes.
The symptoms of urethral stricture
Patients with urethral stricture concerned impossibility of adequate urination characterized weak flow of urine, the need to stress the abdominal muscles during miktsii, spray urine stream, sensation of incomplete bladder emptying, Dribble Urine and t. d.
Against the background of urethral stricture may appear pelvic pain, blood in urine or semen, reduced ejection forces ejaculate.
The presence of urinary tract infections manifest abnormal urethral discharge and painful urination.
When severe stricture of the urethra degree urine can be released drop by drop, in some cases, developing a complete blockade of the outflow of urine, requiring immediate assistance urologist.
Diagnosis of urethral stricture
In the analysis of history is necessary to find out the possible reasons - illness and the circumstances leading up to the development of symptoms of urethral stricture.
In patients with suspected inflammatory stricture urethra shown laboratory smear genital infection methods PIF, PCR diagnosis and bacteriological seeding.
Urinalysis can detect red blood cell, pyuria, Piura and other deviations from performance standards. With bacterial inoculation test urine is detected exciter urinary tract infections, antibiotic sensitivity is determined by the selected flora.
A routine screening test for suspected urethral stricture is Uroflowmetry, allowing to estimate the urine flow rate. When urethral strictures during uroflow prepared characteristic curve with a plateau phase and an elongation time miktsii.
The complex examination of the important role played by cystometry, profilometry, videourodinamicheskoe study.
Ultrasound of the bladder, made immediately after urination to determine residual urine volume, to get an idea of the degree of decompensation functions.
Radiological assessment of the location and extent of urethral stricture are in progress urethrography, anterograde cystourethrography, multislice cystourethrography.
Radiopaque techniques also allow us to determine the presence of false moves, urethra diverticula, stones, urethra and bladder.
endoscopic diagnostic methods (ureteroscopy, cystoscopy) allow to inspect the area of stricture of the urethra, to establish probable cause to perform a biopsy of tissue for pathological examination.
Choice of treatment urethral stricture done purely individually depending on the location, extent and length of the scar-sclerotic processes.
When simple, single and unextended strictures Treatment usually starts with bougienage urethra. For this purpose are used bougies-dilators of various diameters and shapes (straight, curved) or urethral balloon catheters.
Bougienage drawback is the high incidence of urethral stricture recurrence.
To prevent the re-narrowing of the urethra resort to the installation of the urethral stent capable of maintaining adequate clearance stenotic urethra.
However, the frequent movement or migration of urethral stents made of the method spread fairly limited.
For short (less than 0.5 cm in length) urethral strictures located in or bulbomembranoznom bulbar urethra, can be carried cut stenotic site - internal urethrotomy under visual endoscopically control.
When urethral strictures length of 1-2 cm is preferred resection holding open the urethra to the anastomotic Urethroplasty "end to end". Excision of urethral stricture is longer than 2 cm requires urethroplasty using graft from the patient's own tissues (prepuce skin, buccal mucosa).
Prediction and prevention of urethral stricture
The lowest percentage of urethral stricture recurrence is observed after reconstructive operations on the urethra. After bougienage urethra or urethrotomy likelihood of restenosis is greater than 50%. After treatment, the stricture of the urethra, patients should be observed at the urologist and follow the character of urination.
Preventing the development of urethral stricture is an STD prevention, timely treatment for urethritis medical supervision, careful holding endouretralnye procedures, the exclusion of injuries and other adverse factors. Prevention of recurrent urethral strictures requires the selection of an adequate method of disease treatment.
A source: http://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_urology/urethral-stricture
Urethral stricture in men: Symptoms and Treatment
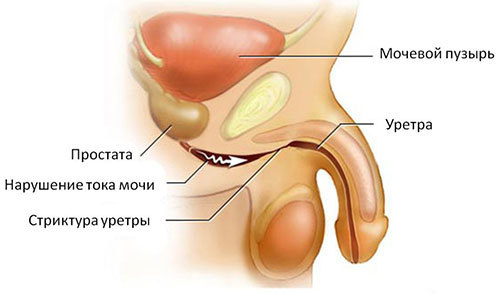
Under the stricture of the urethra in men should be understood luminal narrowing of the urethra until its complete obliteration due to scarring.
Anatomy of the male urethra
The urethra (urethra) - long tube, the end of the urinary tract.
See also:Why men can not routinely use peppermint?
The urethra is a tubular body which is the final section of the lower urinary tract. It starts just behind the outlet of the bladder and opens slit-like opening on the glans penis.
In clinical practice, the urethra can be divided into 3 main segments:
- prostate (column extends in prostate cancer);
- membranous (muscle fibers surrounded by raising the anus and deep transverse perineal muscles, which provide the function of retention of urine and normal act of urination);
- spongy (continues from urogenital diaphragm to the external opening of the urethra, the urethra is surrounded by a spongy body; urethral mucosa in this department contains a large amount of mucous glands and lacunae).
Each of these different structural features and the functions performed, that is taken into account during treatment.
Reasons for the formation of strictures
Any mucosal lesion spongy urethra and body leads to the formation of rumen, capable of changing the diameter of the urethra. Most frequent causes of urethral strictures are:
- traumatic effects (blunt or penetrating trauma pelvic ring, perineum and genitals; damage resulting in intraurethral manipulation and surgical interventions; chemical burns);
- inflammation (gonorrheal urethritis; xerotica obliterans balanitis; urethral damage due to prolonged stay of the catheter, endoscopic procedures and operations that promote micro-traumas mucosa and provide access to the penetration of infectious agents);
- congenital anomalies.
Inflammatory stricture urethral sponge is characterized by:
- hidden onset;
- slow progressive course;
- lack distinct boundaries spongy tissue damage;
- alternating areas of active inflammation with complete spongiofibrozom;
- periurethral fibrosis with involvement in the pathological process of testicular membranes, muscles and tissue of the perineum.
In some patients, the cause of urethral stricture can not figure out. In this case, no history of injury is detected, urethritis, etc. catheterization. In such cases, it may be diagnosed as "idiopathic stricture."
Classification
Depending on the localization of urethral stricture are:
- prostatic;
- membranous;
- spongy.
They can be single or multiple. One short stricture can be located in the membranous department, a few others - in the spongy. Often, they have not only a different location, but different reasons.
Untreated and uncomplicated narrowing of the urethra is considered primary, complicated variant of the disease develops with recurrent disease process, the formation of fistulas or abscesses.
Longest stricture share:
- long (over 20 mm);
- Short (20 mm);
- subtotal and total spongy (corresponding to 75% or more);
- defeat the whole urethra.
In clinical practice, there are the following degree of narrowing of the urethra:
- light (diameter of the narrowing of the urethra to 50%);
- moderate (75%);
- severe (more than 75%);
- complete obliteration.
Clinical manifestations
The clinical picture of urethral stricture is diverse manifestations, the severity of which depends on the location, the degree of contraction and its causes. Among them are the main ones:
- frequent urgency;
- urgency of urination;
- straining and pain during urination;
- its delay;
- attenuated jet stream and its discontinuity;
- spatter;
- nocturia;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- undermining after urination.
All these pathological symptoms are not considered specific, they may be present in other urological diseases. However, when the urethral stricture there is a certain sequence of their appearance: initially dominated by manifestations associated with impaired emptying, and then they are joined by the accumulation of symptoms.
The most typical feature of the disease is sluggish jet and intermittent urination, which later added dropwise urine at the end of the jet. With the decrease of the lumen of the urethra grow these manifestations. At its restriction to a quarter or more are always present symptoms of chronic urinary retention.
No less important symptom of this disease is pain. It appears from the beginning of urination, ends with him, and always accompanied by a sluggish stream. This symptom is more pronounced and idiopathic inflammatory stricture and may be omitted in traumatic disease genesis.
The presence of infection and inflammation in the urethra adds pathological symptoms, but they are due to not very stricture and chronic prostatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, and so on. D.
Traumatic stricture is often accompanied by signs of associated injuries (pelvic bones, rectum) and their complications (chronic pelvic pain).
complications
The long existence of urethral stricture in men leads to disruption of the flow of urine, tissue ischemia, and the penetration of infection in the urethra, resulting in complications develop:
Diagnostics
Urethral stricture may be suspected when a doctor questioning the patient, comparing complaints and medical history. To confirm the diagnosis carried out inspection and objective study. An important role is played here by additional tests:
- Retrograde urethrography (enables to determine the location, the degree of extension and contraction);
- antegrade cystourethrography (when the urethra is passable, the contrast fills it nadstrikturnuyu part; if patency is absent, the contrast agent is distributed in proximal urethra to restriction);
- urethroscopy (held under unclear results of the above studies or unknown reasons for this pathology biopsy);
- cystourethroscopy (necessary for suspected stenosis bladder neck or urethral obstruction in prostate hyperplasia);
- ultrasound examination of the urethra (allows to distinguish between the normal structure of the sponge body and scar tissue; its carrying out is shown in inflammatory and complicated strictures);
- spongiografiya (allows you to more accurately determine the distal spongiofibroza border);
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the urethra and bladder with contrast (used in difficult cases, and if repeated relapses of the disease);
- bacteriological examination of urine and discharge from the urethra;
- biochemical research of blood (serum creatinine);
- excretory urography (shown by the presence of lesions of the upper urinary tract).
Accurate information on strikturnoy disease, changes in urinary and sexual organs, resulting in the diagnosis is essential to determine the management of patients.
Treatment
In severe cases, the disease is carried urethral resection.
At the present stage of medical science, there are several options for treatment of urethral strictures. These include:
- surveillance;
- probing;
- internal optical urethrotomy;
- urethral resection with anastomosis;
- substitution urethroplasty.
Patients with no or small amount of complaints with normal urinary tract and the small amounts of residual urine in the bladder can be supervised by a doctor. In this case, necessarily subject to an annual inspection. Such patients should be aware of the possible risk of disease progression and the need for active treatment in the future.
Bougienage urethra - one of the oldest methods of palliative treatment. The purpose of such intervention is to expand the stricture to the normal diameter (for the urethra).
To this end, the urethra bougie introduced a certain size after local anesthesia and leave for 15-20 minutes. This procedure is repeated periodically.
It determines the frequency of physician, focusing on urinary parameters.
Internal optical urethrotomy in efficiency equivalent to probing. It is used for short strictures of traumatic urethral sponge. Its essence lies in the dissection of scar contraction zone.
It provides an extension of the urethra if epithelialization ahead excessive growth of scar tissue that does not always happen. After the intervention is recommended 3-6 months' probing or autokateterizatsiya.
The majority of patients after surgery have a progression of the pathological process and the need to open surgery.
Urethral Resection with end anastomosis is an effective radical treatment of traumatic strikutur membranous part of the urethra and spongy. However, with lesions of the urethra spongiofibrozom such interference accompanied by frequent relapses of the pathological process. Avoid this possible by applying anastomotic urethroplasty.
Substitution urethroplasty - one of the most complex surgical procedures on the urethra. It is used for urethral stricture length of more than 2 cm, as well as in cases when other methods are not effective. Selection of technics reconstructive surgery depends on the location and length of the narrowing, as well as the presence of complications.
To which the doctor ask
Treatment of urethral strictures is engaged in the surgeon-urologist. With the development of complications may need to consult a nephrologist, andrologist. If you suspect a prostate pathology examination is appointed at the oncologist.
conclusion
Provided early diagnosis and correct choice of tactics of the patient's urethral stricture persists. This allows you to not only get rid of the unpleasant symptoms, but also to prevent the development of complications.
In the program "Live healthy!" Elena Malysheva of urethral stricture (see. with 33:30 min).:
A source: https://myfamilydoctor.ru/striktura-uretry-u-muzhchin-simptomy-i-lechenie/
Stricture (narrowing) of the urethra in men
Narrowing of the lumen of the urethra (urethral) leads to disruption of urine patency of its lumen, until the total delay urination.
Urethral stricture - a disease which is based on multiple causes and contributing factors. It is most common in men because their urethra has a number of anatomical features. It is quite narrow, long, convoluted, as well as some of its areas, there are anatomical curves.
Treatment of urethral strictures in men requires an individual approach in each case, as determined extent of the pathological process, the degree of narrowing of the urethral lumen and the severity of urodynamic disorders.
anatomical aspects
As mentioned above, the disease is most often diagnosed in the stronger sex, so it is necessary to consider briefly the features of the structure of the urethra in men.
Anatomically, it decided to allocate the following departments of the urethra:
- prostatic portion (urethra, which is surrounded by the prostate gland);
- membranous portion (it is surrounded urogenital diaphragm);
- penile portion (department, which is located between the urogenital diaphragm and the outer opening of the urethra).
Anatomical and physiological features of the urethra
See also:Why pain occurs in the penis
Stricture prostatic department arise in total form of prostatitis, which requires adequate treatment is not only narrowing the space, but also simultaneous operations on the prostate gland.
Classification
The basis of the pathological process of classification on a number of criteria.
According to the etiology of the disease:
- traumatic stricture (occurring on the background of any damage to the urethral mucosa or deeper layers);
- inflammatory stricture (inflammatory component lies in a process basis, and the replacement of normal tissue fibrous);
- iatrogenic (against the background of medical errors, wrong manipulations, etc.);
- congenital stricture (narrowing are of different lengths and localization, appearance is due to genetic disorders);
- idiopathic (the narrowing of the urethra of unknown etiology).
Pathologic changes:
- primary stricture (not complicated, first emerged, previously untreated);
- recurrent stricture (previously diagnosed in a patient, complicated by an abscess, Svishchev progress, etc.).
On the level of localization of the stricture:
- prostatic separated;
- membranous separated;
- bulbar;
- capitate separated;
- the external opening of the urethra.
Narrowing of the urethra can occur at any of its over
In length (length of the stricture)
- short (less than 2 cm);
- long (more than 2 cm);
- total stricture (lesion of the urethra along its entire length).
By the number of restrictions:
- single stricture;
- multiple strictures.
According to the degree of narrowing of the lumen of the urethra:
- Process degree of light (lumen narrowing of the urethra does not exceed 50%);
- moderate degree of restriction (75%);
- restriction severe (more than 75%);
- a complete obliteration of the lumen (no traffic).
The formation of scar tissue which replaces the normal epithelium of the urethra and narrows its lumen may be due to the following reasons:
What is the narrowing of the ureter
- Traumatic effect on the body wall, in which the urethra is damage or complete breakdown (for pelvic fractures bones, the symphysis pubis, symphysis rupture, the introduction of foreign bodies into the lumen of the urethra, such as a catheter or bougie passed and etc.).
- The introduction of infectious agents of different origin in the mucous membranes, which leads to marked inflammation and narrowing of the body. The most common cause of urethral strictures becomes gonococcal infection to be treated for a long time is missing or inadequate.
- Congenital narrowing of the urethra, is usually diagnosed at an early age (in this case should be excluded infectious or traumatic nature of the disease process).
- Prolonged urinary catheter in patients with cancer in the prostate gland, which is not amenable to surgical treatment.
- Idiopathic narrowing of the lumen of the urethra diagnosed in approximately 15% of patients.
Such a diagnosis is the absence of a history of data injury, infectious processes, any manipulation, etc.
Inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) causes a permanent narrowing of the urethral lumen
When it comes to traumatic injury of the urethra, it is most often a full body a break, and the divergence of its ends, it always produced large hematoma. The process of formation of scar tissue which replaces normal layers of the urethra, in which the background begins its restriction.
Fibrotic process can affect not only the structure of the urethra, but also involves the surrounding tissue (e.g., muscle and other tissue and perineal).
The main symptoms of urethral stricture are:
- easing pressure jet of urine ( "weak" jet), sprinkling it in different directions, change of direction, etc .;
- appearance of unpleasant or painful sensations that accompany the process of emptying of the bladder;
- the need to make efforts to start the process of urination, the urine can be released in small drops;
- feeling crowded bubble, which remains even after emptying;
- involuntary possible "leak" of urine that occurs when small physical exertion or at rest condition;
- presence of pain in the lower abdomen above the pubis, which irradiate the rectum or crotch thighs;
- appearance in the blood urine or semen, and other pathological ingredients.
In patients with urethral strictures observed weakening of potency
complications
When the first symptoms indicating narrowing of the urethral lumen, the need for specialized medical care, as the condition can lead to a number of serious complications, such as:
- urethral fistula formation moves to adjacent organs (e.g., in the lumen of the rectum);
- formation of abscesses or abscesses;
- stone formation above the level of the restriction;
- infectious processes in the genital organs of acute or chronic origin (prostatitis, epididymitis, etc.);
- infectious processes in different parts of the urinary tract (pyelonephritis, cystitis, pyonephrosis and others);
- total septic condition (sepsis);
- chronic renal failure and others.
General examination of the patient begins with a digital examination of the penis and its appendages, and rectal palpation of the rectum and prostate.
Laboratory and instrumental methods of investigation include the following procedures:
- general blood and urine tests (evaluated presence of an inflammatory component, its severity, as well as other abnormal shifts in the results);
- biochemical blood investigation (determined by serum creatinine and urea, total protein and its fractions, and other indicators as required);
- urine culture in nutrient media (with suspected infectious nature of the process);
- urethrography retrograde (a procedure that allows to identify the constriction of the urethra, its length and severity, as well as the presence of sinus tracts, stones, etc.);
- ureteroscopy (endoscopy method by which the physician visualizes the urethral walls, the presence of these defects, strictures and other pathological entities);
- Ultrasound of the urinary system and transrectal prostate examination (reveals the pathological processes in the prostate, their size, the presence of stones, etc.);
- MRI or CT urogenital system using the contrast agent (in the present methods time widely used, as it allows to quickly find the stricture, its exact extent and etc.).
Introduction ureteroscope is necessary not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for the treatment of (dissection of scar tissue)
patient management tactics
Treatment of urethral stricture (narrowing of the urethra) pursues in itself the following objectives:
- full restoration of patency of the urethral lumen, ie, cure the sick and to prevent any complications;
- normalization of urination;
- improving the overall quality of life of the patient.
Therapy patients can have several directions.
Dynamic monitoring of patients
This tactic is selected in the following cases:
- the patient is completely absent any complaints or symptoms are minimal;
- in the bladder remains small residual urine volume (less than 80-100 ml);
- no recurrence of infection in the urinary system organs.
This group of patients subject to annual medical examination using the methods required laboratory diagnostics tool (life).
The indications for it are:
- long structures (5-6 cm length) which have the same degree of narrowing throughout its length;
- a small degree of narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, which will hold bougienage procedure without injury to the mucous membranes;
- patient refusal of other treatments;
- higher risk of complications during surgery (general grave condition of the patient, presence of comorbidities);
- bougienage well tolerated procedure that was carried out earlier, as well as the duration of benefit.
Procedure bougienage urethra does not carry the goal of a complete cure of the patient, as it takes its constant repetition at certain time intervals
Internal optical urethrotomy
The essence of the procedure is endoscopic excision rumen restriction sites (using the urethroscope and special device, capable of removing abnormal tissue). To treat the stricture uretrydannym by men and women, enjoyed a laser source of heat or cold knife.
The method is accompanied by frequent relapses of the pathological process, which occur quite early (2-3 months), which relates to his unpromising methods of treating strictures of any origin.
Internal optical urethrotomy may be effective only in case of the minimum fibrosis when the doctor can be completely excised fibrous tissue.
Removing a portion of the urethra (his resection) to form end anastomosis (using its own tissue by urethral tension of each other). This method is used for narrowing a small extent, it has a good long-term results.
substitution urethroplasty
"The gold standard" treatment. It got its spread in the pathological process of great length (2-3 cm), localized in different parts of the urethra. The most frequently affected tissues for replacement, using the material obtained from the patient's cheek mucosa (buccal graft).
Stages of uretroplatiki
prevention
Measures to prevent urethral strictures are as follows:
- prompt treatment of any inflammation in the urethra (especially gonococcal origin);
- in traumatic urethral walls need timely surgical care and an adequate amount of surgical intervention (preference should be given to modern methods of treatment);
- in order to avoid iatrogenic strictures that occur as a complication of a mis-entry catheter must be competent medical staff training technique of catheterization;
- it is important to avoid the introduction of any foreign objects into the urethra (the correction of sexual behavior);
- personal hygiene, use of contraception, which prevents penetration of infectious agents in the urinary tract;
- general strengthening of the immune status, the gradual hardening of the body, to maintain an active lifestyle.
conclusion
Inflammation of the urethra require timely treatment, because they can lead to such state as urethral stricture, which threatens patient near urodynamic disorders and serious complications.
No matter what symptoms bother the patient (at the initial stages, perhaps their absence), it is necessary to provide skilled assistance with the use of modern methods of treatment. Unfortunately, even the long-term and adequate treatment, the patient does not always guarantee a full recovery, and does not protect it from possible recurrence of the pathological process.
A source: http://2pochki.com/bolezni/striktura-suzhenie-uretry-muzhchin



