Babes in babies: symptoms, treatment, prevention

The forced oblique position of the head, which is caused by abnormalities of the development of the sternocleidomastoid muscle or cervical spine, or birth trauma is called torticollis.Clinically, the child's torticollis manifests itself by tilting the head to the shoulder and turning the face in the opposite direction.In addition, the pathology under consideration is characterized by the limitation of head turns, secondary changes - for example, strabismus, gait disturbance, headaches.
Table of contents: Causes and types of torticollis in children Pathology taking into account the factors that led to thisCauses and types of torticollis in children
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish between congenital and acquired torticollis in children. Congenital torticollis is present in the child at the time of birth and most often in this case, his mother reveals the abnormal course of pregnancy:
- severe forms of toxicosis;
- anhydrase;
- threat of miscarriage.
Congenital torticollis in children can develop with fetal injury, multiple pregnancy, fetal position
.Doctors do not exclude that the cause of congenital torticollis may be:- disturbances in the process of birth - for example, if a woman has a narrow pelvis, or there was a weak labor activity and forced stimulation of the process, or the medical staff was forced to use obstetric tools as obstetric aid;
- labor with caesarean section;
- birth injury to a newborn.
The appearance of the acquired torticollis is possible at any age.
Types of pathology, taking into account the factors that led to this
There are several types of torticollis in the child - articular( arthrogenic), dermo-desmogenic, osteogenic( bone), neurogenic, myogenic( muscular).
Congenital / acquired muscular torticollis in children
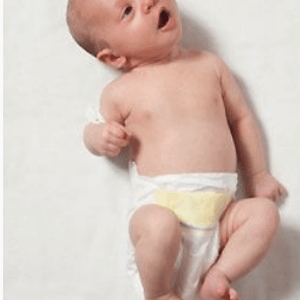 This type of pathology is associated with a violation of the nodal( sternocleus-mastoid) or trapezius muscle.There may be underdevelopment of the muscle, its ischemic contracture on the background of insufficient blood supply, shortening / scarring after muscle fiber tearing.Most often, with congenital muscular krivoshee in children, there is a combination of developmental defect and muscle injury during childbirth.
This type of pathology is associated with a violation of the nodal( sternocleus-mastoid) or trapezius muscle.There may be underdevelopment of the muscle, its ischemic contracture on the background of insufficient blood supply, shortening / scarring after muscle fiber tearing.Most often, with congenital muscular krivoshee in children, there is a combination of developmental defect and muscle injury during childbirth.
Note: if muscular torticollis is of the nature acquired, the cause of its occurrence may be acute / chronic myositis of the nodding muscle, sarcoma, ossifying myositis and Grisel's disease.
Congenital / acquired osteogenic and arthrogenic torticollis in children
It is always a consequence of disorders of the development of the cervical spine - for example, it may be the fusion of the cervical vertebrae, or the fusion of additional vertebrae.
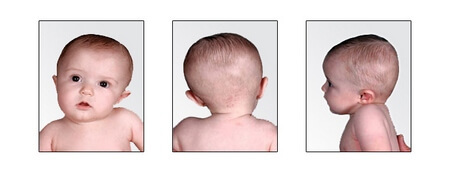
Separately it is worth mentioning the acquired krivoshee osteogenic and arthrogenic species. This type of pathology can occur for the following reasons:
- fracture of cervical vertebrae;
- tuberculosis;
- actinomycosis;
- destruction of vertebrae against the background of osteomyelitis;
- is a tumor lesion of the vertebrae.
Congenital / acquired neurogenic torticollis in children
 Intrauterine hypoxia or fetal infection and muscular dystonia syndrome may be the cause of this type of pathology.If we are talking about the acquired curvature of a neurogenic nature, its causes can be the transferred diseases - poliomyelitis, tumors of the central nervous system, encephalitis, infantile cerebral palsy.
Intrauterine hypoxia or fetal infection and muscular dystonia syndrome may be the cause of this type of pathology.If we are talking about the acquired curvature of a neurogenic nature, its causes can be the transferred diseases - poliomyelitis, tumors of the central nervous system, encephalitis, infantile cerebral palsy.
Note: on the background of diseases of the parotid glands, clavicle or mastoid can develop a reflex torticollis.It is also called pain, it is of a short-term nature and disappears immediately after passing a full course of therapy for the underlying disease.
Congenital / acquired dermo-desmogenic torticollis in children
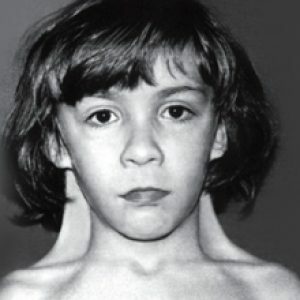 There is such a pathology in the pterygoid neck and the Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome.In medicine, diagnosed and acquired dermo-desmogenous torticollis, which occurs due to extensive scarring of the skin, the progression of cellulose phlegmon.
There is such a pathology in the pterygoid neck and the Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome.In medicine, diagnosed and acquired dermo-desmogenous torticollis, which occurs due to extensive scarring of the skin, the progression of cellulose phlegmon.
Note: doctors differentiate and compensatory krivosheyu, it is also called secondary.In children, it is associated with either pathology of the eyes, or with a hearing disorder.In some cases, torticollis can occur in absolutely healthy children - it will be called installation / positional, its development is associated with improper care for the baby: incorrect placement of the child and wearing it on the hands with a turn of the head in one direction, one-sided placement of toys.
Symptoms of torticollis in children
If a child has an early form of congenital torticollis, its signs will be visible immediately after birth, or in the first few days of a newborn's life.If there is a late form of congenital pathology, then the clinical picture will manifest itself maximally for 2-3 weeks of the baby's life.In this case, the mild degree of congenital torticollis in children may not be recognized by parents and even by a pediatrician for several months.
Characteristic clinical picture:
-
 When examining a toddler, the physician pays attention to the fixed inclination of the head to the shoulder and the turn of the chin in the opposite direction.
When examining a toddler, the physician pays attention to the fixed inclination of the head to the shoulder and the turn of the chin in the opposite direction. - If there is congenital muscular torticollis, the child will have an enlarged nipple( sternocleus-mastoid) muscle, and any attempts to force the head of the baby into a normal position cause pain, accompanied by crying and protest of the baby.
- The child will have an asymmetry of the face, that is, the eye / eyebrow and the ear on the side of the inclination of the head will be located lower than on the opposite side.
- If a bilateral torticollis is diagnosed, the baby's head will be thrown back and brought to the sternum, and any neck movements will be severely restricted.
- In case of development of osteogenic torticollis, shortening and bending of the neck in one direction, low head set and limited movements of the head in the cervical section are visually observed.
- If there is a neurogenic torticollis, both the parents and the pediatrician will immediately note the high tone of the skeletal muscles on one side and the decrease on the other side of the neck, the infant's hand on the side of the lesion will be compressed into a cam, the leg bent.It is worth knowing that with the neurogenic curvature in children, all head movements persist in normal volume.
Many parents are sure that the pathology under consideration will immediately manifest as an asymmetry of the face, but in fact this symptom appears only to 5-6 years of the child's life. And at this age will be noted:
- underdevelopment of the auricle;
- flattening of the cheek on the affected side;
- incorrect development of jaws;
- low location of the eye.
It is very important to carry out diagnostic measures in a timely manner and begin treatment of the pathology in question. The fact is that in the absence of corrective procedures, the child can develop a whole complex of complications:
- deformation of the skull, facial skeleton and spine;
- later eruption of milk teeth;
- asymmetric crawling;
- poor balance;Valgus deformation of feet;
- ;
- scoliosis;
- delay formation of sitting and walking skills;
- osteochondrosis.
In addition, a child with uncorrected torticollis will suffer from hearing and vision impairment, headaches, strabismus, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Diagnostic measures
If a child has a number of signs of torticollis, children's specialists are invited for consultation: neurologist, otolaryngologist, ophthalmologist and traumatologist-orthopedist. During the diagnosis of torticollis in children, the following examinations are carried out:
- complex spinal examination - ultrasound, computed tomography, radiography, magnetic resonance imaging;
- electroneurography;
- electomyography;
- ultrasound examination of soft tissues and neck muscles.
It is compulsory for a child to be given an ultrasound examination of the hip joints and neurosonography - these diagnostic procedures will exclude, or confirm the presence of concomitant pathologies with a crank.
Principles of treatment of torticollis in children
Treatment of the pathology in question should begin from the moment of its diagnosis.A very important role is played by the stimulation of the head turns( the child must follow the movement of the toys), the correct wearing of the newborn on the hands and the use of special healing arrangements to give the head proper position.
Of course, the therapy scheme is selected on an individual basis, but there are also general principles for treating torticollis in children:
-
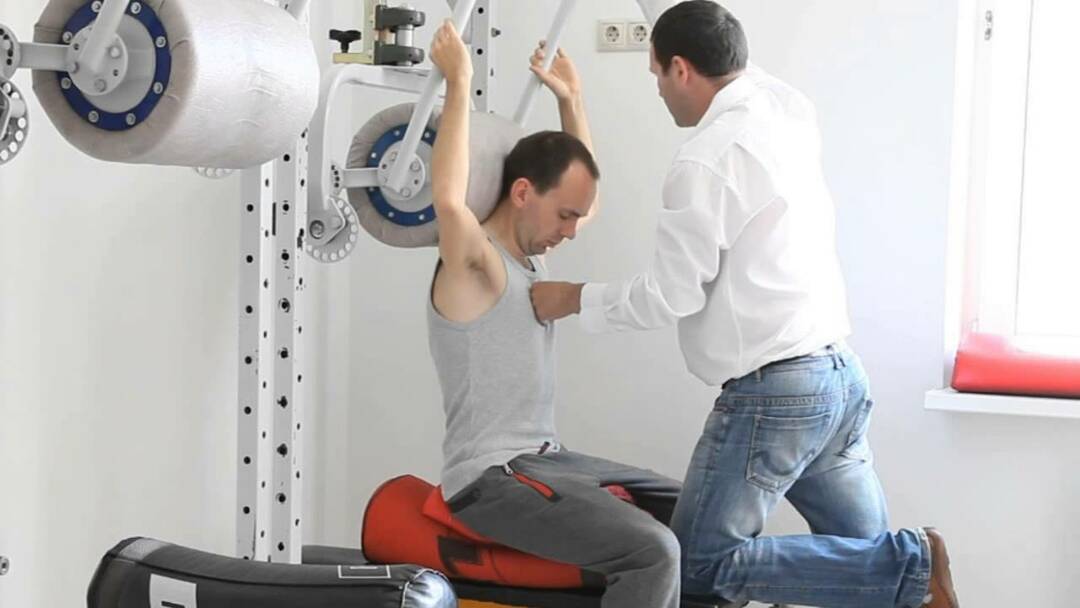
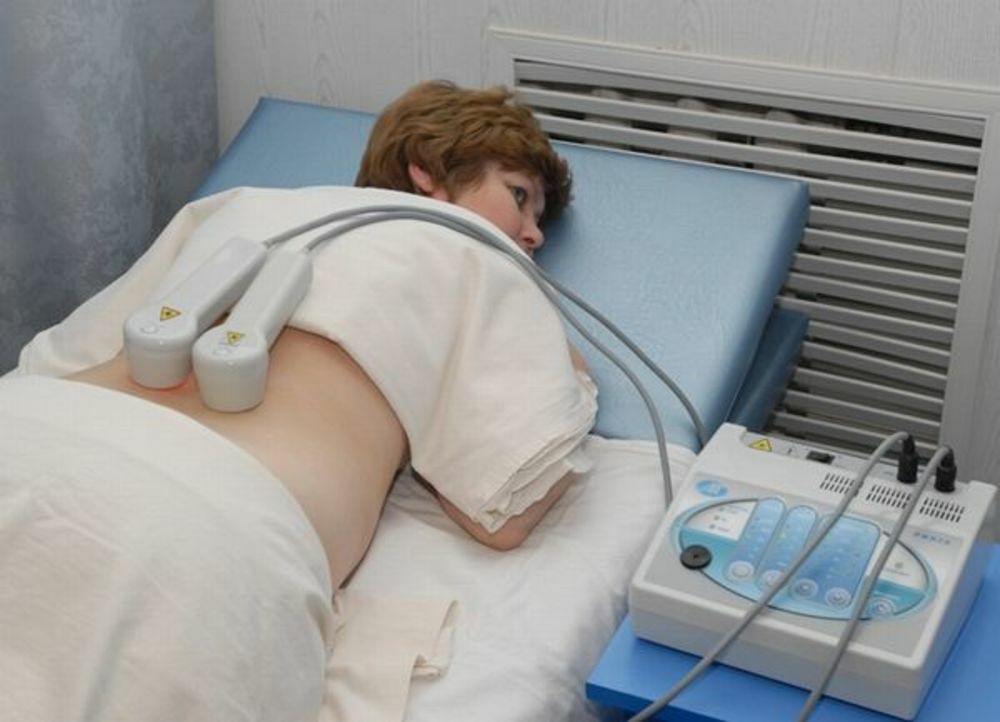
 In case of muscle type of disease: courses of physical therapy and massage, physiotherapy( in particular UHF, paraffin and electrophoresis applications), Therapeutic swimming.Specialists can recommend to parents to use for the baby wearing a cervical orthosis, stretching with the help of Glisson's loop or wearing a collar of Shantz.If the therapeutic measures did not produce the desired effect, then at the age of one and a half to two years the child undergoes a surgical correction of the muscular torticollis - the doctors perform a dissection or plastic lengthening of the nodal( sternoclecho-mastoid) muscle.
In case of muscle type of disease: courses of physical therapy and massage, physiotherapy( in particular UHF, paraffin and electrophoresis applications), Therapeutic swimming.Specialists can recommend to parents to use for the baby wearing a cervical orthosis, stretching with the help of Glisson's loop or wearing a collar of Shantz.If the therapeutic measures did not produce the desired effect, then at the age of one and a half to two years the child undergoes a surgical correction of the muscular torticollis - the doctors perform a dissection or plastic lengthening of the nodal( sternoclecho-mastoid) muscle. - Bone-joint torticollis: stage-by-stage corrective immobilization of the cervical spine taking into account the age of the baby and the severity of the pathology in question.Such treatment is performed using a plastic headband, a shantz collar or a gypsum thoracovascular bandage.If the subluxation of the child is not possible, the doctors resort to a spinal fusion of the cervical spine.
- In the case of a neurogenic patient, the patient is medicated, which is aimed at reducing muscle tone, lowering the excitability of the nervous system.Simultaneously with pharmacotherapy, the child is given a general and / or local massage.
- Dermo-desmogenic torticollis is not subject to therapeutic treatment.Restore the health of the child will help only excision of scars and / or skin plasty.
Important! A child with a history of torticollis should be under the supervision of a pediatric orthopedist up to the age of majority( 18 years) - this rule is valid even if the innate torticollis has been adjusted.
Forecasts of doctors in diagnosing the pathology in question are quite favorable - in 80-90% of cases it is possible to achieve complete elimination of deformity.But if the torticollis occurred in older children and is secondary in nature, then, as a rule, there is no absolute recovery.
Krivosheya in children is a serious enough pathology, which must necessarily be treated.Ignoring the recommendations of doctors can lead to severe consequences, up to the development of deformation of bones / vertebrae and disruption of all organs and systems.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category