Intracranial pressure in children
Contents:
- A bit of anatomy
- Symptoms of intracranial pressure in children
- When does elevated ICP occur?
- Diagnostic measures
- Treatment of
 Intracranial pressure( ICP) consists of several components: intracerebral fluid pressure, cerebral tissue elasticity, osmotic pressure of intracellular and extracellular fluid. Elasticity of the brain tissue, in turn, depends on the influx of arterial and outflow of venous blood. As can be seen, the symptoms of intracranial pressure in children depend on many factors.
Intracranial pressure( ICP) consists of several components: intracerebral fluid pressure, cerebral tissue elasticity, osmotic pressure of intracellular and extracellular fluid. Elasticity of the brain tissue, in turn, depends on the influx of arterial and outflow of venous blood. As can be seen, the symptoms of intracranial pressure in children depend on many factors.
This is a disease, but only a symptom, and occurs with different pathologies. How is intracranial pressure manifested in children? Parents do not always pay attention to the increased capriciousness and tearfulness, fatigue and sluggishness of their baby. Of course, this may be the norm, but may indicate serious problems.
A bit of anatomy
The cavity of the skull is a closed space. Its volume is filled with three components: the brain, blood and cerebrospinal fluid( CSF, CSF).It creates a "pillow" between the bone walls and the brain, protecting it from bumps, and regulates the constancy of ICP.Its volume ranges from 100-140 ml.
Cerebrospinal fluid is a derivative of blood, it is produced by the venous plexuses of the head and absorbed back into them. This process is regulated automatically, therefore, the permanence of ICP is maintained in the norm.
The norm of intracranial pressure in children varies with age, as well as during physical exertion, for example, when crying, so the figures given are relative:
- newborns - 1.5-6 mm Hg;
- children of the older group - 3-7 mm Hg.
The causes of the violation of the function of self-regulation are many, including the most serious ones, therefore at the first signs of intracranial pressure the child should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure in children
How can parents suspect a problem? The following manifestations will appear:
- The breastfeeds become restless, cry from the slightest irritant, sleep badly, eat little, often regurgitate, there may be vomiting.
- It is evident that the fontanel bulges out, the veins on the head are enlarged, filled with blood, and convoluted. Under the eyes bruises are formed.
- The child complains of a headache, especially in the morning or when the weather changes, which is amplified by changing the position of the body, sharp turns of the head. Nausea and vomiting, unrelated to eating, and not relieving the condition, worry.
- Complaints of dizziness, "flies" before the eyes, impaired vision.
- The child quickly gets tired even from those loads with which he coped earlier, becomes whimsical, whiny and irritable.
When does elevated ICP occur?
Any pathological condition that causes changes in brain, blood or CSF volumes can cause high intracranial pressure in the baby. These include meningitis, encephalitis of various nature. At the same time, there is a sharp increase in the blood filling of the brain, because of the inflammatory reaction, the permeability of the vascular wall increases, the development of the cerebrospinal fluid increases. The brain swells, becomes larger.
To dangerous pathologies leading to an increase in ICP, include tumors, traumatic hematomas, abscesses( cavities with pus).Any increase in brain size, the appearance of additional tissue leads to an increase in ICP.In addition, the appeared element can block the current path of the intracerebral fluid.
The child of ICP rises in hydrocephalus, a congenital or acquired disease, in which there is an obstacle to the outflow of the liquor( occlusal), excessive synthesis or disruption of normal absorption( communicating).
Important! High VCHD leads to constant compression of the brain. This is the reason for the death of neurons, because of what intellect, memory, attention suffers.
Diagnostic measures
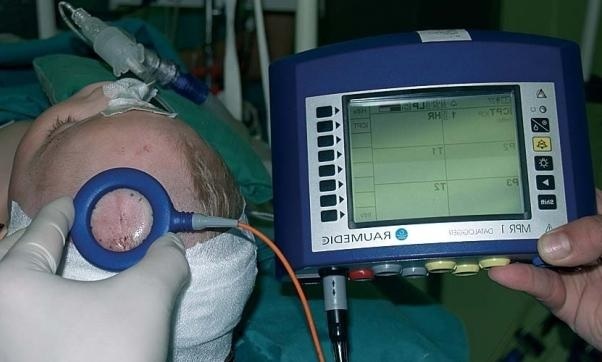
How to check intracranial pressure in a child? For accurate diagnosis, invasive methods are used:
- Lumbar puncture. Under the anesthesia, a needle is inserted into the area between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae with a connected manometer, the scale of which indicates the amount of pressure.
- Measurement of ICP during an operation on the brain. The patient is injected with a sensor into the ventricles of the brain, connected to a manometer and monitored.
Important! There are no other precise methods of measuring ICP for today. Since intracranial pressure in a child is determined by invasive methods only in critical conditions( for example, severe neuroinfections or craniocerebral trauma, hydrocephalus), with the suspicion of pathology, it is recommended to carry out non-invasive diagnostics.
 Non-invasive diagnostic methods:
Non-invasive diagnostic methods:
- Examination of the fundus reveals edema of the optic disc, overcrowded and convoluted vessels of the fundus, foci of hemorrhage.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are a series of images that show a system of dilated cerebrospinal fluidways, volume formation, and degree of brain damage. MRI is more informative, used more often.
- Electroencephalography is the recording of electrical impulses of the brain, reflecting its function. By the changes in the EEG curve, the area and extent of the lesion are established.
- Neurosonography - ultrasound, suitable for young children with uncomfortable fontanel. Measure the size of the cerebrospinal fluidways, identify the presence of formations.
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels - determines the speed and direction of the blood flow. Assign if suspected thrombosis of blood vessels.
Important! Edema of the optic disc and impaired blood flow to the fundus reduce vision.
Treatment of
How to treat intracranial hypertension in a child depends on the severity of the symptoms and the factor that caused the syndrome. In mild cases, drug therapy in combination with exercise therapy and physiotherapy is sufficient. Sometimes only surgery can help.
Medications:
- Diuretics.
- Potassium preparations( asparks, panangin) normalize electrolyte balance and improve brain nutrition.
- Corticosteroid hormones reduce edema and the degree of inflammatory reactions.
In hydrocephalus, shunting is used. During the operation, a catheter is installed, which connects the ventricle of the brain and the atrium or abdominal cavity, to which an excess of CSF is diverted.
Increased intracranial pressure is a serious symptom indicative of a brain disease. It requires a timely call to a specialist, identifying the cause and adequate therapy to prevent the development of complications.
write the question in the form below: