Types of dental fillings - which one to choose?
 Hard tissues of teeth, unfortunately, can not regenerate( recover).For this reason, the fragments of enamel and dentin, affected by the carious process, or the breakaway fragments need to be replaced with artificial materials.Restoration can be done by placing seals or making inlays.Significant defects require orthopedic treatment.
Hard tissues of teeth, unfortunately, can not regenerate( recover).For this reason, the fragments of enamel and dentin, affected by the carious process, or the breakaway fragments need to be replaced with artificial materials.Restoration can be done by placing seals or making inlays.Significant defects require orthopedic treatment.
Filling of teeth: purposes and used materials
Sealing has two main objectives:
- Removal of affected tissue during preparationThe tooth stops the further development of caries and prevents its complications.
- The seal replaces the defect, which is important from an aesthetic and physiological point of view.
All materials used for restoration of tooth crowns must necessarily meet the following requirements:
- safety for the body( no toxic effects);
- strength( resistance to mechanical and chemical influences);
- high aesthetic qualities.
Note: correctly placed seal should ideally be completely invisible( at least for a layman).
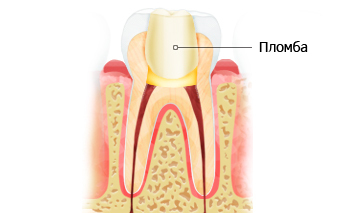
Before the seal is inserted, a number of preparatory works are carried out, which include:
- mechanical removal of the affected tissue;
- cavity formation in compliance with certain requirements;
- tooth insulation from saliva;
- treatment of cavity with antiseptic solution.
Immediately the sealing involves:
- overlapping the insulating pad( if necessary);
- surface treatment with adhesive( or pickling of enamel);
- insertion into the cavity of the material and its compaction;
- seal modeling;
- exposure to a special lamp( for photopolymers);
- grinding and polishing after final curing.
Why do I need seals?The answer to this question in the video review is given by a dentist:
Classification of dental seals
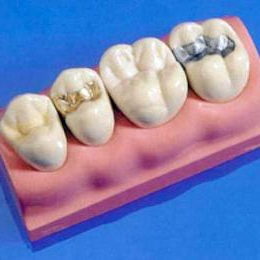 All seals can be divided into temporary and permanent seals.The first can serve for temporary isolation of the cavity into which the medicinal preparation is introduced( some materials contain medicines).A temporary filling can also be delivered if the dentist is not completely sure that pulpitis will not develop( such seals can be called "diagnostic").
All seals can be divided into temporary and permanent seals.The first can serve for temporary isolation of the cavity into which the medicinal preparation is introduced( some materials contain medicines).A temporary filling can also be delivered if the dentist is not completely sure that pulpitis will not develop( such seals can be called "diagnostic").
Temporary fillings differ from permanent ones in their composition.To produce them, less durable materials are used, which allows the doctor to easily remove such temporary sealing after 1-3 days during the next visit of the patient.A common material for such seals is artificial dentin, which is kneaded on water.With its help, in particular, arsenic paste, necessary for devitalization( destruction, removal) of a pulp( a neurovascular bundle) of a tooth is fixed and isolated.
Important: arsenic is a poisonous substance.A small amount of the drug containing arsenic is introduced into the cavity of the tooth in order to "kill the nerve".
Permanent seals made of quality material, and delivered in compliance with all rules, are designed to stand for many years and even decades.
Please note: if the seal was lost within a few months, then there was a violation of the technology, or the doctor did not take into account the mechanical loads( i.e., the installation of an artificial crown was required).
Metal seals
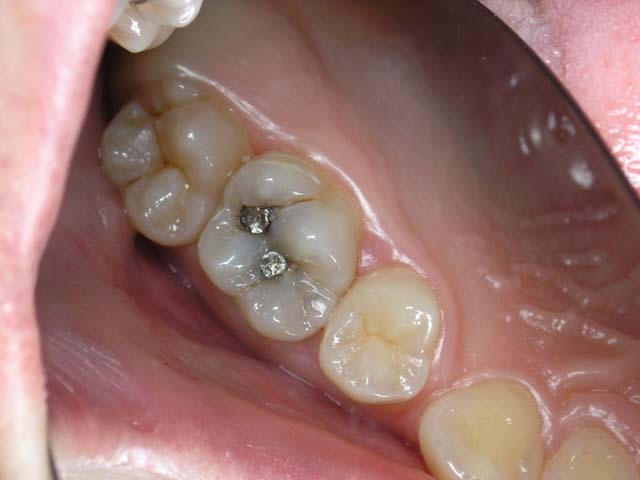
Metal seals are made of amalgam - alloys of some metals with mercury.Most common until recently was silver amalgam.Before stating such a seal, the doctor should carefully mix the finely divided silver powder with mercury.Work with this dangerous for health required compliance with particularly stringent regulations.To be fair, it should be noted that the finished amalgam is almost non-toxic( tobacco smoke contains much more mercury).
The minus of this variety of seals is the probability of the development of the effect of "galvanism"( the appearance of a weak current) in the presence of metal crowns or bridges in the mouth.Disadvantages are also the isolation of the seal against the background of the tooth( characteristic metallic gloss), the curing time( up to 3 hours) and the expansion coefficient, which differs significantly from the index for the natural tissues of the tooth( chipped with cold and hot food).Obvious advantages - the possibility of setting metal seals in a damp cavity, their negative shrinkage and fantastic durability.To this day, dentists can detect in the patient's mouth an amalgam delivered in the last century.
Cement seals
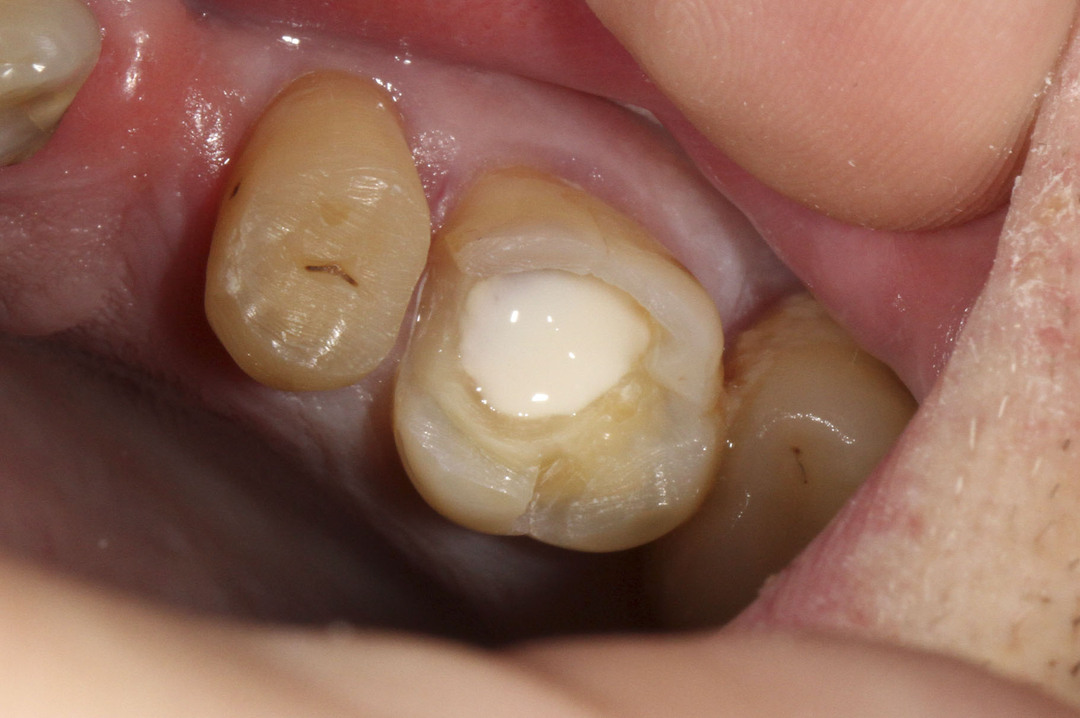 Several varieties of cements are used in dentistry, but for the sealing process, as a rule, either phosphate or glass ionomer ones are used.
Several varieties of cements are used in dentistry, but for the sealing process, as a rule, either phosphate or glass ionomer ones are used.
Please note : Cement refers to two-component materials.When mixing, the powder and liquid are mixed.
Fillings from phosphate cement have been placed relatively recently by everyone in the framework of providing free dental care.Undoubted advantages of materials of this category are their cheapness and simplicity in their work.Mechanical strength, i.e., resistance to abrasion leaves much to be desired and, in addition, there is a poor "marginal fit" to the walls of the formed cavity.As a result, a gap gradually forms between the filling and the walls of the crown defect, into which food remains fall, and secondary caries develop.To increase the mechanical strength of these cements, a fine powder of silver was often introduced into the composition of these cements, but this did not solve the problem with poor marginal fit.
Glass ionomer cements, which are characterized by a fairly high degree of affinity with hard tooth tissues, are much more perfect material.They include fluoride ions, which promote enamel remineralization.Due to this circumstance, glass ion-inoculum fillings are often placed on children's milk teeth.Adhesive properties of such cements are much higher than those of phosphate ones, which partly solves the problem of marginal fit.However, the seals of this category are not characterized by high mechanical stability and no additives have helped to solve this problem cardinally.
All cement has a very short "operating time".After kneading the composition, insert it into the cavity and form a seal in a matter of minutes.Then the material begins to "grasp" quickly, that is, to lose the necessary plasticity.
Plastic seals
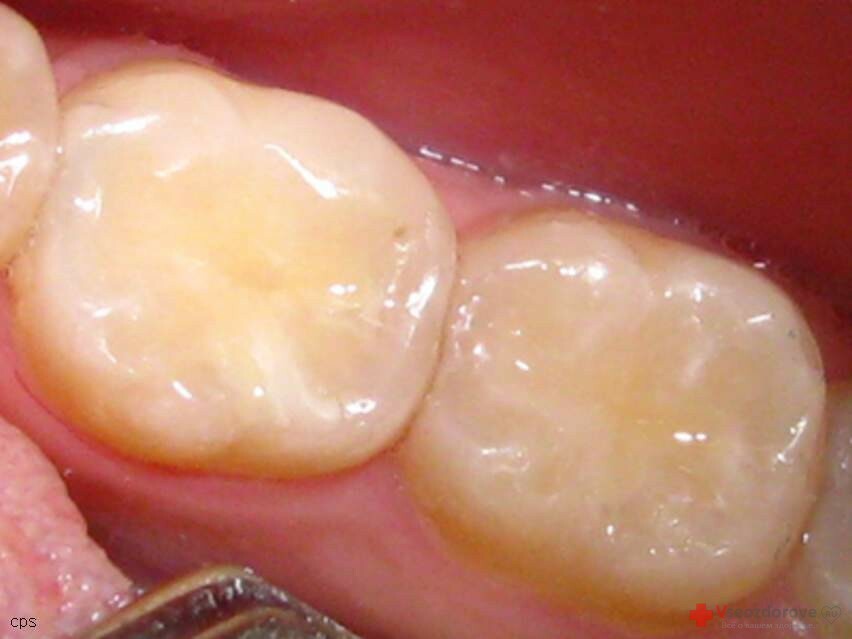 The breakthrough in dentistry was the emergence of plastic and composite seals.Most plastics for sealing are based on acrylic acid compounds.The material is characterized by high mechanical strength, which ensures the durability of the seals provided they are correctly set.The merits can also be attributed to the ability to pick up the material by color.In some cases, after grinding and polishing, the plastic may be indistinguishable in appearance from the healthy enamel.
The breakthrough in dentistry was the emergence of plastic and composite seals.Most plastics for sealing are based on acrylic acid compounds.The material is characterized by high mechanical strength, which ensures the durability of the seals provided they are correctly set.The merits can also be attributed to the ability to pick up the material by color.In some cases, after grinding and polishing, the plastic may be indistinguishable in appearance from the healthy enamel.
But the shortcomings of plastic seals are many.During the polymerization, a huge amount of microscopic pores is formed, which subsequently becomes the cause of the development of secondary caries.The porous surface is an excellent basis for the reproduction of microorganisms, which contribute to the development of a number of diseases of the oral cavity.Aesthetic virtues also quite quickly come to naught;The material has the property to darken, especially - under the influence of food dyes and nicotine.A serious disadvantage is the toxicity of acrylic plastics.An aggressive chemical compound acts on the pulp.If the seal is installed on the tooth, from which the nerve is not previously removed, even if there is a qualitative insulating gasket made of cement, the likelihood of developing pulpitis is very high.
There are significantly fewer drawbacks in two-component( "pasta-paste") composites based on epoxy resins.The toxicity of the composition takes place, but it is not as pronounced as in acrylic polymers.The fillings from composites are being washed even more slowly, but the fragility is somewhat higher.They are perfect for filling a defect on the chewing surface of a crown, for example, but it is not recommended to restore a cutting edge with them.
Light-curing fillings( photopolymer seals)
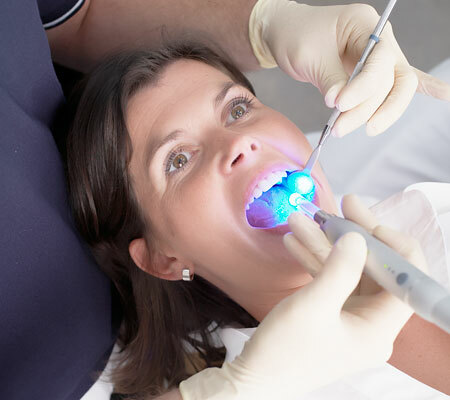 Photopolymers( helioplumbs, light seals) are the most modern materials.Formulations of pasty consistency have the property of hardening under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the source of which are special dental lamps.
Photopolymers( helioplumbs, light seals) are the most modern materials.Formulations of pasty consistency have the property of hardening under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the source of which are special dental lamps.
The doctor can not take much time in the process of entering the material into the cavity and the final formation of the seal, which among other things ensures the high quality of the seals.There is no need to grind a considerable volume after curing;It is only necessary to polish fine abrasive nozzles to give shine.The widest range of colors makes it possible to achieve the perfect color match with the color of the surrounding healthy enamel.A qualitatively delivered and polished seal from a photopolymer can not always be detected even by a specialist.High aesthetic properties make it possible to use such composites to restore the frontal( most noticeable during a smile or during a conversation) group of teeth.The toxicity of the material is minimal, as is the degree of shrinkage.The abrasion is also low, due to which light-cured fillings can serve for many years.
If the material situation allows, then, of course, we recommend giving your preference to photopolymer seals.In this case, the costs are fully justified!
You can see how the installation of composite seals takes place by looking at this video review:
Tabs
Tabs are a cross between a seal and a small tooth crown prosthesis.In fact, it is a ready seal made in a dental laboratory and then fixed by a doctor in the prepared cavity by means of a composite material.The installation process is very similar to fixing the crown.
The following types of tabs are distinguished from the materials from which the structures are made:
- plastic;
- composite;
- ceramic;
- metal.
According to the manufacturing technology, the following varieties are to be distinguished:
- tabs simulated in the oral cavity;
- tabs manufactured on the model.
In the first case, after preparation of the tooth, a softened dental wax is applied to the cavity.Then a tab that replaces the defect is completely formed, and the wax model is transferred to the foundry at the clinic where an absolutely identical metal structure is cast on it.
In the second case, the mold is removed from the tooth after the cavity is prepared with an elastic material based on silicone.A plaster model is molded on the impression, on which a wax-up wax is modeled and the model is transferred to the necessary material( plastic, composite, etc.).A ceramic insert can also be created on the model.
Such "microprostheses" have a lot of advantages over traditional ones and seals.
They are flawlessly adhered to the walls of the cavity in contrast to the seals in which the formation of the so-called."Undercuts" with insufficient compaction during the production process.Ceramic models are characterized by excellent aesthetic properties, thanks to the translucence of the material and a wide range of colors.
By means of tabs, it is possible to create an irreproachable "contact point" between adjacent teeth from the anatomical point of view.The erosibility of the tabs is even less than that of a healthy tooth enamel, not to mention composite fillings.Models with overlapping of hillocks can in some cases be an excellent alternative to artificial crowns, requiring thorough preparation of all dental surfaces.In addition, there is no need to pre-depopulate the tooth, as modern ceramic "microprostheses" are completely non-toxic.
The minus of relatively inexpensive plastic products is the porosity of the material, and the metallic models leave much to be desired for aesthetic properties.
Plisov Vladimir, dentist