Features of the course of purulent inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity
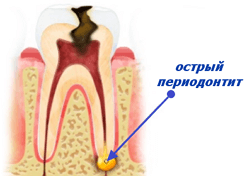
Purulent inflammatory diseases of the mouth.
dental practice in the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the mouth, with the various groups of drugs resorptive and topical( steroid, astringents and nonsteroidal agents diksemid, enzymes, calcium salts, vitamins, heparin ointment) is widely used antibiotics, antiseptics, synthetically by chemotherapeuticPreparations.
In order to conduct the most rational and safe pharmacotherapy, the physician should be aware of the specific mechanisms of action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of each of the listed medicinal groups. Is there a specificity of pharmacological regulation of inflammatory processes for each preparation, make possible the selection of individual drug therapy, particularly taking into account the etiology and pathogenesis of the disease and the availability of the patient comorbidity.
However, despite the fairly wide range of highly antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents, particularly flow suppurative inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity are one of the causes that make the traditionally applied treatment is not always effective and safe. In addition, the therapy used lowers the immunobiological reactivity of the body, and this is a particularly unfavorable factor in childhood, that is, when the protective functions of the body go through the stage of formation. The result in this case may be that acute processes gradually develop into chronic ones, and the period of remission becomes shorter.
In addition, the increasing concern of patients and physicians causes a rather tangible increase in the number of complications that are caused by antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. One of the first places among such undesirable effects is the emerging disturbance of the function of the gastrointestinal tract, because the oral cavity can be considered its initial department. Side effects result of application of such preparations are: cheilitis, glossitis, gingivitis, stomatitis, lichenoid lesions which are clinically indistinguishable from red lichen, etc.
established that the condition in which the epithelium of the oral mucosa, the composition and quantity of saliva.., The course of purulent-inflammatory processes in the maxillofacial department largely depends. The mucous membrane, which is intact, is a barrier preventing penetration of pathogenic flora into the body. It helps ensure that the balance between the body's defenses and the bacterial flora is not disturbed, creates a specific local immunity of the oral cavity.
Disrupted mucosal integrity. Impaired
mucosal integrity, as well as reducing the amount of saliva, leading to a decrease in the immune defense, which is accompanied by rapid growth and multiplication of microorganisms, including pathogenic occupy a prominent position. As a result, a foci of infection forms in the oral cavity. At the same time, a significant part of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs also affect the decrease in the immunobiological reactivity of the organism, create conditions for the development of superinfections and dysbiosis. Studies have shown that during the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity( periodontal and mucous membrane tissues), an increase in the activity of the immune system is necessary.
most promising avenue for increasing the effectiveness of therapy, allowing many prophylaxis( including infectious and inflammatory) disorders, as well as their recurrence, is the use of drugs with immunocorrecting properties. Immunostimulants, traditionally used in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory processes of the oral cavity, sufficiently affect the overall immunity. Their use must necessarily be guided by the immune status of the body, and if necessary requires the advice of an immunologist.
Preparations.
Among the drugs used to stimulate the immune processes, a special interest of dentists is the drug imudon. The medicine was created for specific immunotherapy for diseases of the oral cavity. Its composition includes a mixture of fungi and purified lysates of bacteria, which are most often the initiators of pathological processes in the maxillofacial region.
During the in vitro experimental studies on polymorphonuclear neutrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes of human peripheral blood, this drug exhibited antigenic properties. At the same time, the study of imidone on toxicity has shown that since this is a topical preparation, it does not enter the bloodstream and does not have any effect on the reproductive functions and metabolism of the experimental animals. These factors are sufficient to recommend imudonana approbation in dental practice. Tests have shown that it is effective in the treatment and prevention of periodontopathy and gingivitis, as well as prolonging the period of remission due to the immunostimulating action of the drug.
In addition, the researchers noted that treatment with this drug produced good results in the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity( gingivitis, stomatitis, including aphthous, gerpetic gingivostomatitis, etc.).