Rheumatoid arthritis: symptoms, treatment and diagnosis
 Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease of connective tissue with lesions of mainly peripheral joints, as well as internal organs.According to statistics, rheumatoid arthritis affects approximately 1% of people around the globe.The average age of the onset of the disease is forty to fifty years.Women are more often ill than men.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease of connective tissue with lesions of mainly peripheral joints, as well as internal organs.According to statistics, rheumatoid arthritis affects approximately 1% of people around the globe.The average age of the onset of the disease is forty to fifty years.Women are more often ill than men.
Reasons for the occurrence of
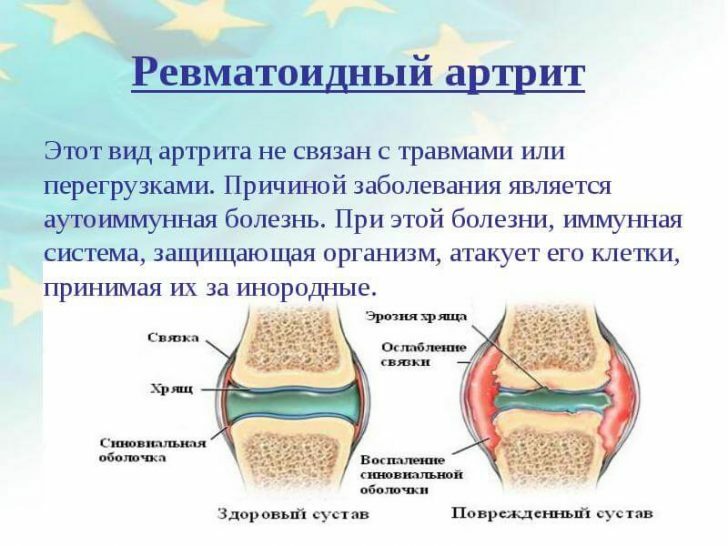
The nature of rheumatoid arthritis is very complex.The main cause of the pathology is considered autoimmune process, when the immune system perceives its cells alien and attacks them.It is suggested that such anomalous activity of the immune system is due to a genetic predisposition.
The factors triggering the disease include:
- Infectious agents( hepatitis, herpes, mumps, measles, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus);
- Subcooling;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Stress;
- Injuries and surgeries;
- Allergic reactions;
- Smoking.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs with joint damage as well as internal organs.
The severity of the clinical picture of the disease depends on the degree of activity of the pathological process:- I - Low activity;
- I I - Moderate;
- III - High;
- 0 - Remission.
The disease first manifests itself in the form of general, nonspecific symptoms.The man notes that he began to get tired quickly, feels weak.Periodically slightly increases the temperature, it would seem, for no apparent reason, there is sweating.Muscular pains, aches in the body are noted.Often the disease develops slowly, the clinical symptoms unfold within a few months, and sometimes even years.At this time, signs of joint damage begin to appear.Much less often the disease develops sharply or subacute.

Articular symptoms
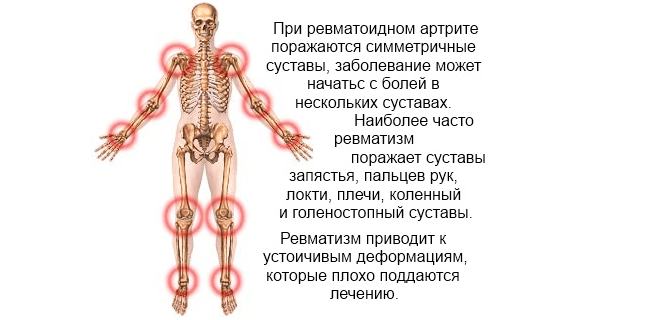
Rheumatoid arthritis has several characteristics that allow it to accurately differentiate it from other diseases.In most cases, the disease manifests itself in polyarthritis( lesion of more than three joints), less often with oligoarthritis( involvement of two joints) or with monoarthritis( a lesion of only one joint).
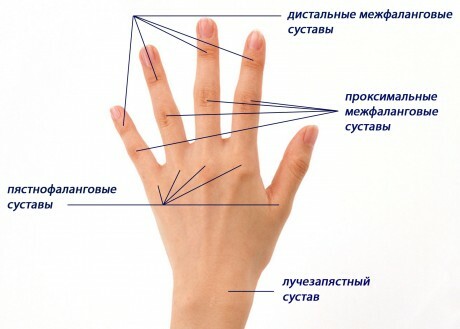
In rheumatoid arthritis joints are affected symmetrically, that is, if the joint of the finger on the left arm is affected, then on the right arm also inflammation of the analogous joint is observed. The following joints are most commonly affected:
- Pseudo-phalanx( with the exception of the thumb joint);
- Proximal interphalangeal;
- Plyusnefalangovye;
- Knee;
- Wristguards;
- Elbow;
- Ankles.
A characteristic feature of rheumatoid arthritis is the emergence of morning stiffness of .This symptom is characterized by the fact that after awakening a person notes the difficulty of mobility and the increase of tenderness in the joints.This symptom develops due to the fact that inflammatory exudate accumulates in the cavity of the affected joint at night, which limits the function of the joint.This condition lasts more than half an hour.Gradually, the stiffness disappears and the person begins to feel more comfortable, the mobility in the joint is restored.In general, rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by persistent aching joint pain.

Rheumatoid arthritis progresses in three stages. of the first stage of develops edema of the synovial joint of the joint and the production of inflammatory exudate, which is manifested externally by swelling of the joint, local increase in skin temperature, and pain.On the of the second stage of , connective tissue cells are actively dividing, which causes the synovial membrane to thicken.On of the third stage of , inflammatory cells produce a specific enzyme that leads to deformity of the joints, increased pain and loss of motor function.Depending on the location of the pathological process, such types of deformities of the hand as spindle-shaped fingers, the neck of a swan, and the type of a buttonhole can be observed.
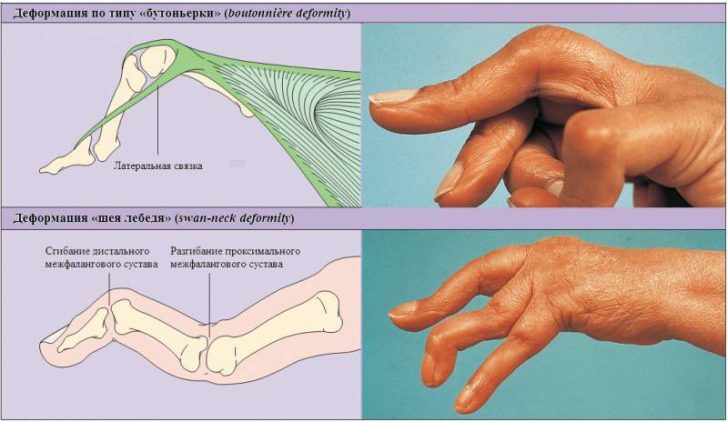
Extra-articular symptoms
Because rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease, many patients develop multiple internal organs. Often, organs such as:
- Skin;
- Heart;
- Light;
- Kidney;
- Body of vision;
- Nervous system.
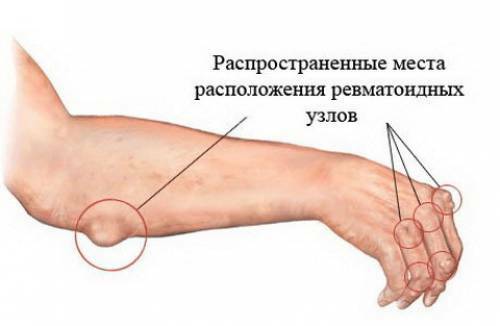 In 20-50% of patients, rheumatoid subcutaneous nodules occur.They are dense subcutaneous painless formations up to two centimeters in diameter.Often, nodules arise in the area of the elbow, the Achilles tendon, over the small joints of the hand.
In 20-50% of patients, rheumatoid subcutaneous nodules occur.They are dense subcutaneous painless formations up to two centimeters in diameter.Often, nodules arise in the area of the elbow, the Achilles tendon, over the small joints of the hand.
Rheumatoid nodules can also occur in internal organs, for example, in the lungs.Often, patients with rheumatoid arthritis are affected by pleural pleura with the development of pleurisy and interstitial tissue with the development of interstitial pneumonia.It is believed that mortality from pulmonary pathology among patients with rheumatoid arthritis is twice higher than in the general population.
Vascular damage manifests itself in the form of vasculitis, which underlies diseases of many organs.On the skin, vasculitis is manifested by hemorrhagic rash.
In rheumatoid arthritis, any layer of the heart can be affected: endocardium, pericardium, myocardium.Most often there is pericarditis - inflammation of the pericardial sac, sometimes accompanied by effusion.It should be noted that in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerotic vascular lesions are observed in young years.
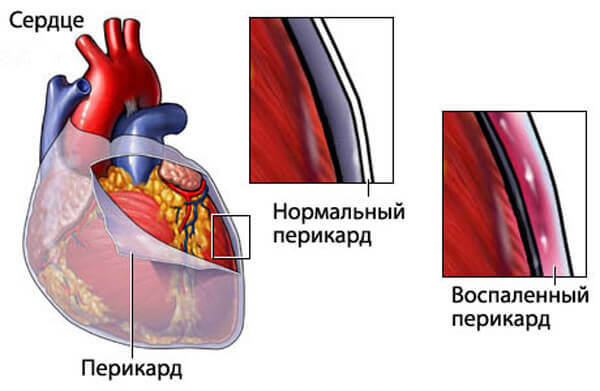
Kidney damage is a serious threat to life.With inflammation of the glomerulus, glomerulonephritis develops, which later can cause kidney failure.In patients with a long-term form of rheumatoid arthritis, amyloidosis of the kidneys can occur - the deposition of the pathological protein amyloid in them.
In addition, with this disease, the organ of vision can be affected in the form of dry keratoconjunctivitis, nervous system in the form of neuropathy, muscle damage - in the form of muscle weakness and pain.

Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis
Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is very extensive.Nonspecific, specific and auxiliary methods of investigation can be used to detect the disease.
Nonspecific diagnostic methods
 First of all, traditional clinical trials are conducted.The clinical analysis of blood determines the increase in the number of leukocytes, the acceleration of ESR, the reduction of hemoglobin.
First of all, traditional clinical trials are conducted.The clinical analysis of blood determines the increase in the number of leukocytes, the acceleration of ESR, the reduction of hemoglobin.
When biochemical blood test can detect an increase in the level of fibrinogen, sialic acids, as well as C-reactive protein, haptoglobin.However, such changes are nonspecific and can be observed in various diseases.
Specific diagnostic methods
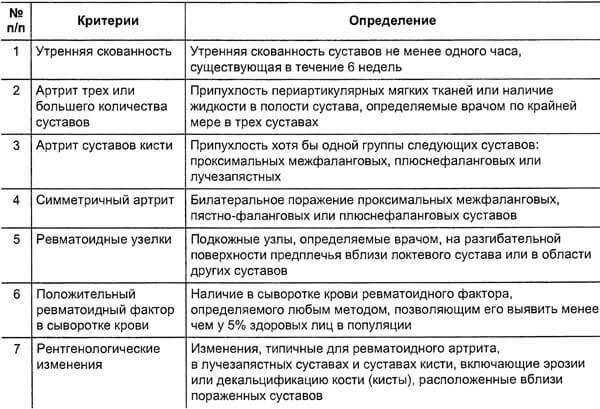
Confirming the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis allows the determination of specific markers of the rheumatoid process .In particular, approximately 60% of patients in the blood show rheumatoid factor .This autoantibodies to own immunoglobulins G. High factor titers correlate with the severity, rapid progression of the pathological process.If the patient was able to detect a rheumatoid factor - physicians talk about seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, if the factor is not found - about seronegative.
One of the most sensitive methods that allows to use it in diagnosis of the disease at an early stage of the disease, is the definition of anti-citrulline antibodies( ATSTSP) .Citrulline is an amino acid that forms during inflammation.Cells containing citrulline are recognized by the immune system as foreign, which is why antibodies are produced to them.In rheumatoid arthritis, the test for ACP is positive in about 80% of cases.
Supplementary diagnostic methods
 An auxiliary diagnostic method is the study of the synovial fluid .In the liquid, it is possible to detect such changes as a decrease in its viscosity, an increase in leukocytes and neutrophils, a change in color, transparency.By and large, similar changes are observed in other inflammatory diseases of the joints.Reliably confirms the presence of rheumatoid arthritis finding in the synovial fluid of the rheumatoid factor.
An auxiliary diagnostic method is the study of the synovial fluid .In the liquid, it is possible to detect such changes as a decrease in its viscosity, an increase in leukocytes and neutrophils, a change in color, transparency.By and large, similar changes are observed in other inflammatory diseases of the joints.Reliably confirms the presence of rheumatoid arthritis finding in the synovial fluid of the rheumatoid factor.
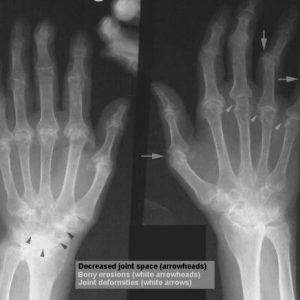
X-ray examination and arthroscopy are used to examine the affected joints.Early X-ray indications are near-articular osteoporosis, fuzzy joint contours, erosion on articular surfaces.
Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Recommended to read:Patients with rheumatoid arthritis should undergo treatment in a rheumatological hospital. The following drug groups are used in therapy:
- Symptom-modifying drugs;
- Disease-modifying( they are also basic) antirheumatic drugs;
- Disease-controlling drugs.

Symptom-modifying drugs
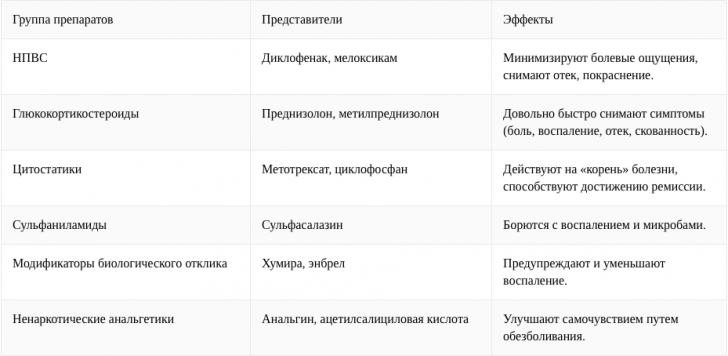
The purpose of this group of drugs is the rapid reduction of local inflammatory phenomena, pain, until the basic drugs act.This group of drugs include NSAIDs and glucocorticoids.
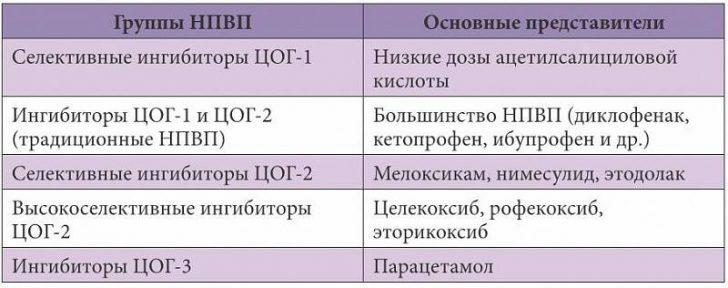
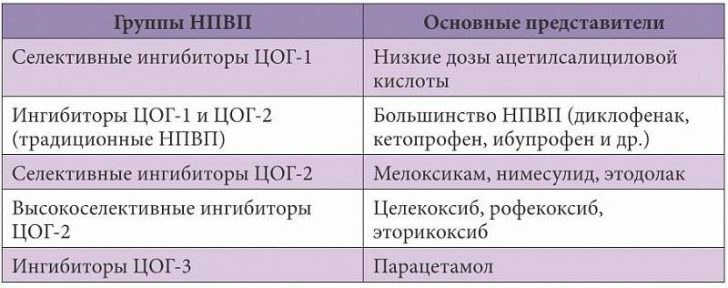
NSAIDs have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects.The anti-inflammatory effect is realized due to inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which takes part in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators.There are two of its isoforms: COG1 and COX2.Accordingly, NSAIDs are distinguished which primarily affect COX1 or COX2.The first include Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, to the second - Meloxicam, Celecoxib.Both have an anti-inflammatory effect.However, the blockers of COX2 do not exert an aggressive effect on the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract, in contrast to the blockers of COX1.
Glucocorticosteroids have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.Low doses of glucocorticoids are used as "bridge therapy" until the basic antirheumatic drugs begin to act.In some cases, large doses of glucocorticoids are administered in a few days, called "pulsterapia."Glucocorticoids are also used topically - by insertion into the affected joint.However, in this case, it is possible to suppress only local inflammation.
Basic antirheumatic drugs
These are drugs that have an effect not immediately, but due to their ability to interfere with the immune mechanisms of the disease, they can lead to a prolonged remission.
The basic preparations are:
- D-penicillamine;
- Gold preparations;
- Salazo compounds;
- Cytotoxic;
- Quinoline derivatives.
Principle of basic drug therapy: First, high doses of the drug are prescribed to suppress the inflammatory process.In the future, the dose of the drug is gradually reduced and reaches a therapeutic dose, which must be used for a long time.If after four to six months of treatment with one or another basic drug a positive result is not achieved - then, it is necessary to change the medication.
Disease-controlling drugs
The action of these medicines( also called biological agents) is aimed at inhibiting the synthesis of "anti-inflammatory" cytokines - TNF-a and IL-1.These are modern genetic engineering preparations that allow patients to be cured with resistance to the action of other drugs.
This group includes the following preparations:
-
 Remicade;
Remicade; - Humira;
- Rituxan;
- Kinneret;
- Embryla.
Despite its undeniable effectiveness, disease-controlling drugs also have disadvantages.The most important drawback is the high cost of drugs.Since it is necessary to be treated with these medicines for a long time, it turns out that not everyone can afford this kind of treatment.
Non-drug therapy
Non-drug therapy plays no less a role than treatment with medications.Thus, patients with rheumatoid arthritis need to adhere to a diet that is described in detail in the article "Diet for Rheumatoid Arthritis."Those who want to recover need to give up smoking, because it worsens the course of the disease.
Patients are shown moderate( not excessive!) Gymnastic exercises, massage.Favorably affects the course of the disease, sanatorium treatment and physiotherapy( balneotherapy, mud therapy, laser therapy, magnetotherapy, UHF, electrophoresis).Physiotherapy is carried out after remission of acute inflammatory process.With their correct application, it is possible to improve joint mobility and reduce pain.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer