Brahidactyly
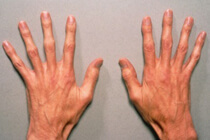
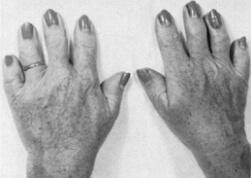 brachydactyly - is hypoplasia of the phalanges, which manifests itself in the shortening of the toes on the feet and hands resulting from genetically deterministic defect is inherited. Manifestations of this anomaly are a decrease in the length of the feet and hands, short-cutness, hypoplastic nail plates, and in some cases, syndactyly. As diagnostic measures, DNA diagnostics and ray methods of bone visualization are at the forefront, and only the surgical method of eliminating the defect should be considered as effective therapeutic measures. It should be borne in mind that the occurrence of brachydactyly is possible not only with a decrease in the size of individual phalanges, but also because of their complete absence.
brachydactyly - is hypoplasia of the phalanges, which manifests itself in the shortening of the toes on the feet and hands resulting from genetically deterministic defect is inherited. Manifestations of this anomaly are a decrease in the length of the feet and hands, short-cutness, hypoplastic nail plates, and in some cases, syndactyly. As diagnostic measures, DNA diagnostics and ray methods of bone visualization are at the forefront, and only the surgical method of eliminating the defect should be considered as effective therapeutic measures. It should be borne in mind that the occurrence of brachydactyly is possible not only with a decrease in the size of individual phalanges, but also because of their complete absence.
The causes of brachydactyly
This pathology is characterized by a rather high incidence rate in the overall structure of genetic developmental defects, and this fact is explained by the dominant type of transmission of the defective gene, i.e. For the development of a child brachydactyly enough that one of the parents was the carrier of the defective gene. The incidence of brachidactyly in the general structure of hereditary anomalies of the hands and feet is about 24%.
In the era of development of diagnostic technologies, as well as genetic engineering methods, conditions for early prenatal diagnostics of brachidactyly are created by the method of triplex three-dimensional ultrasound examination during pregnancy.
No preparations have yet been developed for the use of etiotropic empirical treatment, but a large number of scientific studies on this issue are currently under way. Medico-genetic counseling of the family, which consists of at least one member suffering from this type of anomaly, provides for mandatory warning by a geneticist about the risk of a baby with brachidactyly. The category of people who are subject to genetic counseling primarily includes parents who have a baby with brachydactyly, both people who want to start a family with a patient with brachydactyly, and families whose parents suffer from this anomaly.
Symptoms of Brachydactyly
In a situation where brachydactyly is an isolated developmental disorder, the clinical manifestations of the child will be minimal, and it should be treated as an exclusively cosmetic defect. However, it should be borne in mind that in most cases this pathology acts as a syndrome and is a manifestation of more gross congenital genetic diseases.
The most common congenital pathology, in which brachydactyly develops on a par with other vices, is Down's syndrome. With this hereditary anomaly, in addition to brachydactyly, the child displays other phenotypic signs( epicanthus, brachycephalic type of skull, funnel-shaped chest, shortening of the neck).
brachydactyly with Poland's syndrome combined with amazia and deformation of the ribs and in the disease Aarskogo-Scott of the child at the same time, there are signs korotkopalostyu phimosis, mental retardation and joint laxity.
In a situation where brachydactyly a child combined with the presence of choanal atresia, hypoplastic frontal sinuses, low growth and signs of secondary hypothyroidism, and in some cases, mental retardation, should be suspected in this patient's syndrome median cleft facial skull.
If a child has brahidactyly without evidence of adhesion to phalanges or polydactyly, then in most cases this anomaly does not restrict the function of the hand or foot. With more pronounced malformations of phalanges, there may be a disruption in the function of interphalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints, which greatly complicates the supporting and motor function. In addition, in most cases, brahidactyly is combined with a dysplastic lesion of the nail plate of the affected finger, which has no aesthetic appearance and needs correction. The shortened fingers have an unusual configuration, due to some flattening and splitting of phalanges.
should distinguish such special embodiments brachydactyly as ectrodactyly at which the marked hypoplasia exclusively distal phalanges with preservation of normal bone structure metacarpals and adactylism, which is the most severe form korotkopalosti, since for a given pathology brush shortening is caused by the total absence of oneOr several phalanges.
Types of brachydactyly
To distinguish all variants of bone anomalies of phalanges, in trauma and orthopedic circles it is customary to classify brachidactyly according to clinical types.
Brahidactyly A is accompanied by shortening of the middle finger, deviation of the phalanges, as well as dysplastic changes in the nail plates. These changes can occur in different severity variants, therefore it is common to divide brachodactyly type A into five clinical variants.
The type of Farabi, or type A1, involves changing all phalanges of the middle finger as a vestigial structure in combination with shortening the proximal phalanx of the thumbs of the feet and brushes, as well as the overall growth retardation.
The Mora-Brit type, or type A2, is manifested by the presence of all phalanges of the middle finger of the lobes of the hands, but their significant shortening. A remarkable fact is the preservation of the normal development of the remaining phalanges on the hands and feet. In addition to shortening the phalanx of the middle finger, the shape of the phalange of the middle finger changes toward a rhomboid shape with concomitant radial deviation. A variant of this type is brachidactyly, combined with clinodictyly of the fifth finger.
Clinodactyly of the fifth finger, or type A3, consists in shortening and radial deviation of the exceptionally medium phalanx of the fifth finger on both hands.
With type Temtami, or type A4, shortening of the second and fifth fingers of both hands is observed due to underdevelopment of the middle phalanx. With the localization of pathological changes on the feet, there are valgus-heel clubfoot.
Type A5 is accompanied by a pronounced shortening of the second and fifth fingers on the hands, due to the complete absence of the middle phalanx in combination with dysplasia of nail phalanges.
The principal difference between brachodactyly of type B is that the child has an anomaly of development of nail phalanges with concomitant syndactyly of the second and third finger. A typical for this variant of brachydactyly is the simultaneous damage of the hands and feet. The above changes are accompanied by anomalies in the development of bone tissue of the spine, skull and teeth.
Brahidactyly type C is a severe congenital pathology, in which, in addition to shortening the proximal phalanges, underdevelopment of metacarpal bones is noted, as well as fusion of phalanges with each other. Children suffering from this pathology, are characterized by short stature, and in some cases even mental retardation.
Brachydactyly type D has the second name "brachodactyly of the thumb" and is the most common anomaly in the development of phalanal bones. It is noteworthy that this type of underdevelopment of phalanges of the first finger is observed equally often both on the upper and lower extremities.
Type E is a rare pathology, in which the shortening of the hand or foot does not develop as a result of the bone defect of phalanges, but as a consequence of the isolated underdevelopment of metacarpal bones. In addition, the phenotypic manifestations of this anomaly is the symmetrical underdevelopment of the clavicles.
Treatment of brachydactyly
Due to the fact that brachodactyly is an abnormality of the development of bone tissue with a typical localization in the projection of phalanges of brushes and feet, the only effective method of correcting these changes is surgical. Conservative methods that involve the use of physiotherapeutic manipulations should be considered as additional therapeutic measures in the postoperative period, as well as preventive measures in preventing the development of secondary deforming arthrosis of small joints of the feet and hands.
Surgical techniques allow not only to eliminate existing interphalangeal seams, but also to increase the linear dimensions of brushes and feet. As an operational aid for lengthening the size of the hand or foot, autotransplantation, pollicization and distraction are used. When eliminating interphalangeal fusion, not only bone, but also tendon-muscle, as well as skin plasty, is performed.
The use of surgical treatment with brachidactyly is acceptable only for the purpose of eliminating the violations of the motor function of the limbs and, to a lesser extent, to eliminate the cosmetic defect.