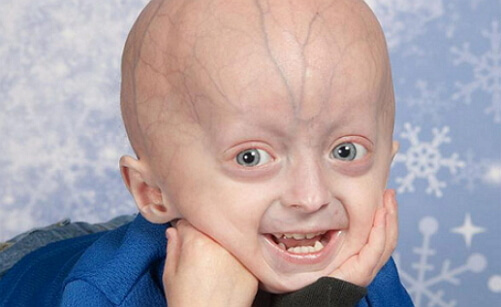
Marfan's Syndrome
 Marfan syndrome is a hereditary systemic disease of connective tissue, characterized by pathological changes in the nervous system, cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system and other systems and organs of the human body. Marfan syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant type and is found in people of all races, almost in the same sex ratio. It is definitely established that with Marfan's syndrome the main defect is directly related to collagen defects, although the probability of lesions of elastic fibers of connective tissue
Marfan syndrome is a hereditary systemic disease of connective tissue, characterized by pathological changes in the nervous system, cardiovascular system, musculoskeletal system and other systems and organs of the human body. Marfan syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant type and is found in people of all races, almost in the same sex ratio. It is definitely established that with Marfan's syndrome the main defect is directly related to collagen defects, although the probability of lesions of elastic fibers of connective tissue
is not excluded. Marfan's syndrome causes the occurrence of
This syndrome is a rare enough genetic disease and occurs in about 1 person out of 5000. As a result of numerousIt was found that this disease is caused by mutation of the fibrillin protein gene in the fifteenth chromosome, which subsequentlyLeads to anomalies in the structure and production of fibrillin.
According to statistical data, in about 75% of cases the gene of Marfan syndrome is transferred from the parents of this disease to their children. In the remaining 25% of cases, when not one of the parents does not have this disease, genetic mutations that can provoke the emergence of Mafan syndrome, arise spontaneously in the sperm or in the ovum at the moment of conception. The causes of this mutation to date have not been fully elucidated, but with 50% of the probability that babies born with this mutation will transmit this disease to their children
Marfan Syndrome symptoms and signs
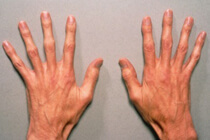
People with Marfan syndrome are often much higher than theirRelatives and peers and differ asthenic physique. When compared with the size of the trunk, their limbs are disproportionately long, and the range of arms is often much larger than their height. Fingers of legs and hands in most cases are thin and long. People with Marfan syndrome can distinguish the similarity of facial features: a small jaw, deeply set eyes, elongated skull, improper growth of teeth, high Gothic sky. In Marfan syndrome, the following systemic diseases of the body are observed in humans:
From the side of the 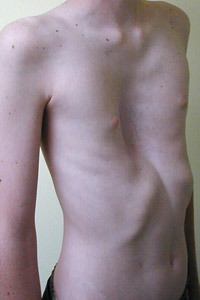
skeleton In addition to long limbs and excessive growth, Marfan syndrome can cause such problems of skeletal development as curvature of the spine( scoliosis) and deformation of the anterior chest wall( "chicken breast"chest).Also in patients with this syndrome, common problems are flat feet and softness of the joints
From the side of the eye
More than 50% of patients with Marfan syndrome have a so-called "lens dislocation".In addition, near-sightedness( myopia), increased intraocular pressure( glaucoma), clouding of the lens( cataract) and exfoliation of the retina
are quite often observed in such people. From the side of the vessels and heart
The most serious complications of Marfan syndrome associated with the heart are considered. This syndrome over time can cause a wall dissection and an extension of the root of the aorta, which carries blood from the heart muscle throughout the body. Due to a sudden rupture of the aorta, a fatal outcome may occur. Often there are problems with the heart valve( more often aortic or / and mitral), which begins to close tightly enough, so that the blood flows back to the heart. Because of this leak, arrhythmia develops( irregular heartbeats), dyspnea and heart murmurs. In addition, flowing valves cause a significant increase in the heart, making it difficult to work.
Other symptoms that can affect the nervous system, lungs and skin( especially in adolescents and young children), usually less serious and less common
Marfan's syndrome diagnosis
The most easily diagnosed Marfan syndrome is diagnosed when the patient himself, or someone -Either of family members there are signs of lens dislocation, chest deformation, kyphoscoliosis or aortic dilatation. With an aneurysm of the aorta and ectopia of the lens, the diagnosis is established even in the absence of a family history and external marfanoid traits. All patients with suspected Marfan syndrome are examined using echocardiography and a slotted lamp
Marfan's syndrome treated with
Unfortunately, to date, there are no specific tools and techniques for the treatment of Marfan syndrome( as well as for the treatment of other hereditary connective tissue diseases).The main goal of the existing symptomatic treatment is the treatment of complications and the prevention of the development of this disease. Some experts recommend using anaprilin( propranolol) to prevent severe aortic changes, but its effectiveness is not proven. In some cases, surgical plasty of the mitral and aortic valves, as well as the aorta, is indicated.
With progressive scoliosis, it is shown that the physiotherapeutic procedures are performed and the skeleton is mechanically strengthened. If the deflection angle exceeds 45 *, surgical correction is performed.
The prognosis of the future life of people with Marfan syndrome is mainly determined by changes in the cardiovascular system. Rupture of the pulmonary trunk or aortic aneurysm is most often the cause of death in this disease.