Hydrocephalic syndrome in children
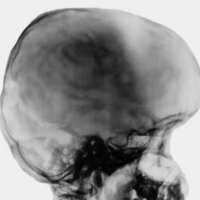
"Hydrocephalic syndrome" is a fairly common diagnosis in neurology, but this term is used only among Russian specialists. As a rule, this diagnosis is given to newborns, who suffer from perinatal encephalopathy. The syndrome is characterized by an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid( otherwise, cerebrospinal fluid) under the brain envelopes and in its ventricles. This accumulation of fluid is formed due to the fact that there is some obstacle to the outflow of fluid and other disorders associated with the reverse absorption of the liquor.
Causes of
Syndrome The main causes of this disease are:
- Neuroinfections;
- Fetal prematurity;
- Violations associated with the development of the child's brain;
- Brain lesions associated with ischemia or hypoxia;
- Negative factors during childbirth or problems during pregnancy;
- Emerging intrauterine infections, hemorrhages in the brain.
Problem in diagnosing
Modern medicine does not yet have sufficient methods to detect this disease. The methods of therapy of the syndrome are also very limited. There are cases when such a diagnosis is put to the child without sufficient grounds.
This unreasonableness of the diagnosis is confirmed by the conducted studies. The medical experts found that if a comprehensive health analysis is carried out that includes various examinations( x-rays, ophthalmology and neurology surveys, MRI, neurosonography, CT, echo, rheo- and electroencephalography), it will be found that in ninety-seven casesOf the one hundred, the diagnosis of "hydrocephalic syndrome" was incorrect.
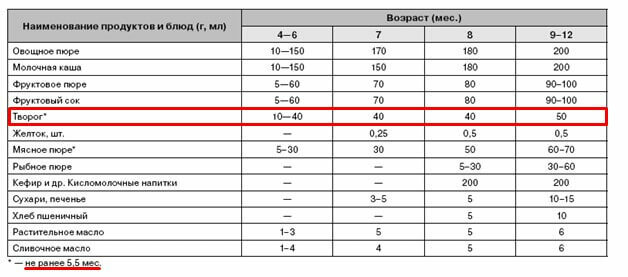
How can we determine if a child has a syndrome in his first year of life? This can be done if there are the following symptoms:
- Vomiting;
- Poor sucking;
- Convulsions;
- Frequent piercing crying;
- Expansion of venous vessels on the scalp;
- Drowsiness;
- Progressive swelling of the fontanelle, as well as the absence of ripple in it;
- Increased head size( more than sixty centimeters in circumference).
Symptoms for determining the presence of the disease in children after the year:
- The child holds his head in a fixed position, the expression of the child's face at this moment is tense.
- The child often has severe headaches, long in time, with periods of seizures. Pain intensifies in the morning, and often accompanied by vomiting.
- Examination of the fundus reveals stagnant discs of the optic nerves.
- The child's behavior is manifested by excessive lethargy, lack of mobility and apathy.
If parents have found similar symptoms in a child, then it must be immediately hospitalized. This is due to the fact that they can be the first signs of the development of the syndrome.
Exceptions to
Children at any age have fluctuations in blood and liquor pressure, which is a process that does not lead to the onset of the syndrome, especially if it is not a newborn baby.
In addition to this, exceptions can be frequent headaches, nausea and dizziness, which occur not only with GTS.These symptoms may indicate infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, disorders in the brain and others.
The big circle of a head too not always unequivocally speaks about GTS.Heads of large sizes can often be seen among newborns, but it has already been proved that this is not an indicator of the presence of this disease. The cause of a large circle can be, for example, a genetic predisposition. To make the diagnosis correctly and accurately, many factors need to be studied.
Treatment of
GTS therapy is usually performed with a drug called diacarb( or acetazolamide).The effect of the drug is aimed at increasing the outflow and reducing the production of cerebrospinal fluid. If diacarb does not show a sufficient therapeutic effect( the ventricles continue to increase, and other symptoms of the disease appear), the patient must be hospitalized in a neurosurgery clinic where he will undergo a shunting of the ventricles of the brain.