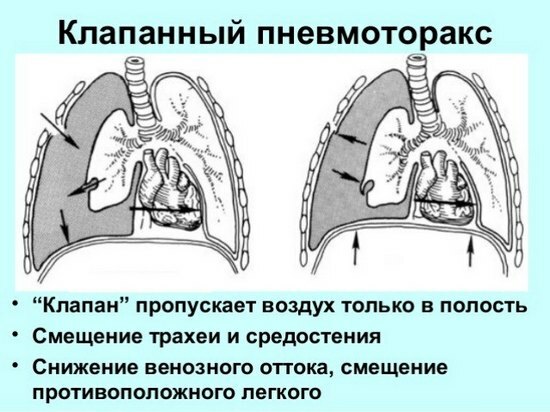
Dry pleurisy: symptoms, treatment, prevention
 Dry pleurisy( hereinafter referred to as pleurisy) is an inflammatory process of pleural leaves, in which the pleural cavity remains dry.In comparison with other diseases of the respiratory system, this pathology differs relatively benign course, but its clinical manifestations can significantly affect the quality of life and performance of patients.
Dry pleurisy( hereinafter referred to as pleurisy) is an inflammatory process of pleural leaves, in which the pleural cavity remains dry.In comparison with other diseases of the respiratory system, this pathology differs relatively benign course, but its clinical manifestations can significantly affect the quality of life and performance of patients.
Causes and mechanisms of development
Pleura is:
- primary - develops independently, without binding to other diseases;
- secondary - occurs due to diseases of organs( often those that are in close proximity to pleural sheets).
Secondary pleurisy develops:
- more often - with lung diseases;
- is less common - with pathology of the chest wall, mediastinum, diaphragm and subdiaphragmatic space.
In most cases, "dry" lesions of pleural sheets are a secondary process.Virtually all reactive or inflammatory changes in the pleura were preceded by a "push" - the defeat of other organs. And in a number of cases, only due to dry pleurisy, diagnosed the diseases provoking it, as they themselves passed without distinct symptoms.
Peloritis is divided into 2 large groups:
- non-infectious, or aseptic - initially inflammatory changes in the pleura occur without the participation of pathogens.
- is infectious.
The most common causes of aseptic pleurisy:
-
 hit the blood in the pleural cavity( for example, with trauma or during surgery - this is the so-called traumatic pleurisy).The discharge may be small, hemothorax itself is not - but even a few milliliters of blood is enough to cause irritation of the pleura and trigger an inflammatory process;
hit the blood in the pleural cavity( for example, with trauma or during surgery - this is the so-called traumatic pleurisy).The discharge may be small, hemothorax itself is not - but even a few milliliters of blood is enough to cause irritation of the pleura and trigger an inflammatory process; - irritation of pleural sheets of digestive enzymes in the pancreas that can enter the pleural cavity when developing acute pancreatitis( enzymatic pleurisy);
- dissemination on pleural sheets of tumor cells( carcinomatous pleurisy).
Less often dry pleurisy can occur in such diseases as:
- infarction of the lung ;
- rheumatism and other connective tissue damage;
- leukemia( malignant damage to blood cells);
- granulomatosis( autoimmune inflammation of the vessel walls);
- hemorrhagic diathesis( increased bleeding);
- some kidney and liver diseases( often autoimmune).
In some cases, the causes of pleurisy are not established - it is called idiopathic.
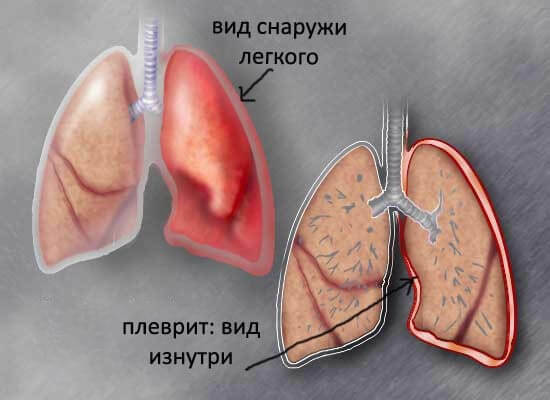
In case of an aseptic variant, the infectious agent may join later - the pleural sheets are compromised, the respiratory act is broken, the tissues are deprived of oxygen, this exacerbates the weakening of the organism, resulting in the activation of the infection.
Most commonly, infectious pleurisy is caused by:
- pneumococci;
- of staphylococci;
- gram-negative rods;
- less often - Koch sticks( mycobacterium tuberculosis), which mainly provoke exudative pleurisy( inflammation of the pleural sheets with the formation of fluid in the pleural cavity);
- in some cases - pathogenic fungi that cause blastomycosis, coccidoidosis and other fungal diseases.
Infection is capable of penetrating into the pleural cavity in several ways:
-
 is hematogenic - with blood flow;
is hematogenic - with blood flow; - lymphogenous - with a current of lymph;
- contact - directly from the organs affected by infection( including from the basal lymph nodes - most often it occurs in cases of tuberculous lesion);
- direct - during medical manipulations( surgeries, thoracoscopy, pleural puncture, if septic and antiseptic rules were violated) and traumatic injuries.
Often in order to have an infectious pleurisy, one infection on the pleural leaflets is not enough - it requires specific sensitization( hypersensitivity) of the tissues. Its role is confirmed by the fact that in some patients infectious pleurisy was not observed even with massive infectious agent invasion( for example, with chest injuries with extensive contamination of pleural sheets), while in others it arose when an insignificant number of microorganisms hit the pleura.In this case, isolated a separate form of this disease - infectious-allergic pleurisy.
Mechanisms for the development of aseptic pleurisy are not fully understood until the end.Basically, it occurs as a pleural reaction to various non-infectious factors.
 A separate form of lesions of pleural sheets that is observed in the presence of infectious foci in the body is described, but is non-infectious.These are the so-called sympathetic( or sympathetic) pleurisy - they arise from the fact that the infectious agent does not act on the pleura( it is not in the pleural cavity, but remotely), but the toxic products of its vital activity.
A separate form of lesions of pleural sheets that is observed in the presence of infectious foci in the body is described, but is non-infectious.These are the so-called sympathetic( or sympathetic) pleurisy - they arise from the fact that the infectious agent does not act on the pleura( it is not in the pleural cavity, but remotely), but the toxic products of its vital activity.
Dry pleurisy can be transformed into exudative - with the formation of fluid in the pleural cavity.This happens if lymph drainage is difficult. Most often, such a turn of the disease happens in cancerous diseases - tumor cells block the way out of the lymph flow in the chest( bringing the blood vessels), the lymph seeps into the pleural cavity.
The development of exudative pleurisy from the dry is inhibited if the suction capacity of the pleura is well developed and the effusion does not accumulate in the pleural cavity.This is a kind of borderline between two types of pleurisy, which is difficult to identify on the basis of clinical data - they simply are not observed.
The opposite clinical situation is less common: a dry lesion of the pleural sheets can develop after the exudative process, when the pleural suction capacity is activated, and on the surface of the pleural sheets from the exudate, which is actively absorbed by the pleura, a thick layer of fibrin falls out.So in the pleural cavity spikes are formed: the fibrin precipitated from the exudate becomes denser, so-called moorings arise.This explains the paradoxical phenomenon, when after rather harmless pleurisy there is a pronounced respiratory failure - the adhesions prevent the lungs from fully decompressing . Sometimes the adhesive process is so pronounced that partial or complete overgrowth of the pleural cavity occurs.
Symptoms of pleurisy
The following symptoms are most typical for pleurisy:
-
 chest pain;
chest pain; - superficial rapid breathing;
- less often - cough;
- signs of impaired ventilation( ventilation) of the lungs;
- general condition deterioration;
- rarely - fever;
- swelling of the cervical veins;
- sometimes - swelling of the skin in the lower parts of the breast can be swollen, its fold is thicker than on the healthy half of the chest.
The parietal pleura( the leaf that lining the chest wall from the inside) is characterized by a large number of nerve receptors.During the excursion of the chest( movements associated with the act of breathing), the pleura leaves rub against each other, which leads to the appearance of quite sharp painful sensations .
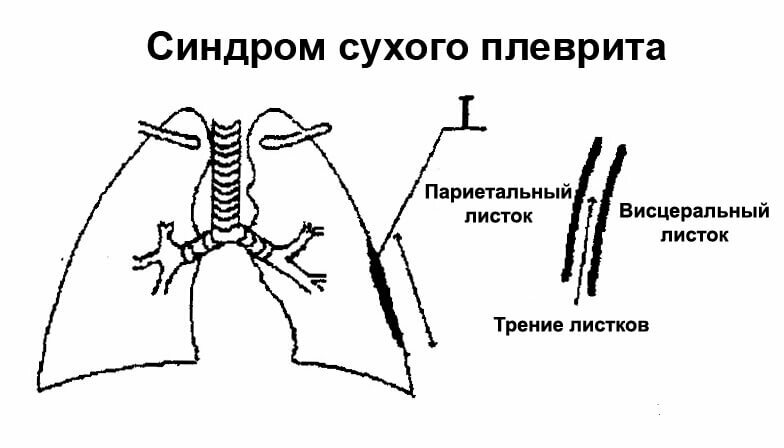
The more fibrinous deposits on the pleura, the more pronounced friction and pain. Unpleasant sensations increase when tilted to the healthy side - the affected pleura stretches, the nerve receptors are irritated by . To ease the pain, the patient can lie on the sore side, thereby limiting her movements.
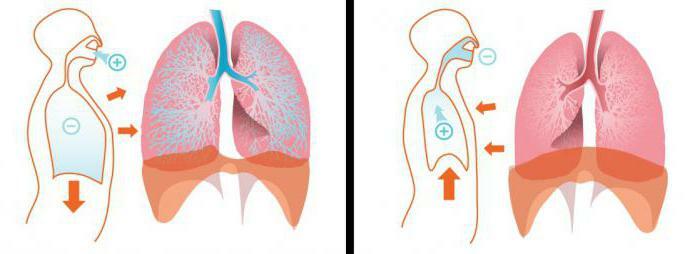
Because of the pain, breathing becomes more superficial.The patient begins to breathe more often to compensate for the lack of oxygen.
Cough occurs reflexively, due to irritation of the pleura sheets.But the patient tries to curb coughing movements, as they increase pain in the chest.
Restriction of respiratory movements of the chest leads to a deterioration in the ventilation of the lungs - they do not give off carbon dioxide and are poorly saturated with oxygen.As a consequence, at later stages of pleurisy development there may be signs of hypoxia - cyanosis of the skin and visible mucous membranes . Hypoxia in pleurisy is moderate and can lead to critical consequences only if chronic untreated neglected pleurisy.
Deterioration of the general condition( weakness, decreased performance, lethargy) occurs due to oxygen starvation, which is explained by the deterioration of the lungs due to pain and adhesions in the pleural cavity.
Depending on how pronounced the symptoms, pleurisy are:
- acute - marked peak symptom severity;
- subacute - with moderate manifestations of symptoms;
- chronic is a sluggish process that can last for weeks and does not cause special subjective sensations, but be resistant to treatment.
Dry pleurisy is not so often total - mostly affects some part of the pleura: apical, parietal, diaphragmatic or interlobar.If the apical segments are affected, there may be soreness when feeling the trapezius and pectoral muscles. With extensive pleural lesions in the patient's chest, noise is heard from the side, resembling creaking of snow or new skin products( Shchukarev's symptom). This clinical effect is observed in patients with asthenic physique.
If the patient does not seek help, with prolonged chronic, recurrent pleurisy, gradual exhaustion of the body occurs.Half of the chest on the side of the lesion decreases in size, the intercostal spaces become narrower. Chronic respiratory failure worsens the work of all organs and systems. In the most neglected cases, the so-called pleurogenic cirrhosis of the lung develops - irreversible proliferation of connective tissue in the lung, the occurrence of which provoked a chronic inflammatory process in the pleura and which, in turn, critically worsens the respiratory function of the lungs.
Diagnosis of dry pleurisy
The diagnosis of dry pleurisy in most cases is based on clinical manifestations.Alertness should cause severe pain and worsening of the excursion of the lungs against a background of a more or less satisfactory general condition.
Additional diagnostic methods give quite a scant information and are used in doubtful cases in order to exclude other diseases - in particular, pathologies with severe pains in the chest. X-ray examination, which is one of the most popular in pulmonology, with pleurisy is not informative : even with a pronounced clinic, an x-ray picture can be like a healthy person.Some informativeness is present, if expressed, considerably condensed moorings( spikes) are formed - they are manifested mainly in the lower part of the radiographic picture when they are filled with diaphragm pockets.With a different location, spikes are difficult to identify.
On the part of the blood, typical signs characteristic of the inflammatory process of completely different localization can be manifested:
- a slight increase in the number of leukocytes;
- increase in ESR( ESR).
A distinctive diagnosis should be made between pleural inflammation in the lower parts and pathological lesion of the subdiaphragmatic space of the .In the second case, the following symptoms are possible:
- pains in the neck or anterior abdominal wall;
- develops anterior abdominal wall tension;
- in a number of cases appears painful hiccups.
With pleurisy such effects are not observed.
With lesions of the lower parts of the pleura pleurisy can be confused with diseases of the abdominal cavity.
The absence of other signs on the part of the abdominal organs and the constant alertness of surgeons regarding the condition of the acute abdomen can lead to unreasonable laparotomy( autopsy, which is often performed for diagnostic purposes with complicated diagnostics).
Confusion in the diagnosis can cause prolonged pleurisy.Normally it lasts from a few days to several weeks.If it lasts a rather long time, does not respond to nonspecific treatment, the periods of remission alternate with relapses - one should suspect a tuberculous lesion.
 Also, a distinctive diagnosis should be made if the patient finds a sudden reduction in pain in the chest and related relief of - but they may not come from the fact that a competent treatment for pleurisy was made, and when switching from a dry form toExudative, when the fluid lubricates the pleural sheets and eliminates the painful friction between them.Discomfort in the chest does not go away - it acquires other characteristics: instead of sharp sharp, sometimes unbearable pains, the patient begins to feel a peculiar feeling of heaviness in the chest and its overflow.
Also, a distinctive diagnosis should be made if the patient finds a sudden reduction in pain in the chest and related relief of - but they may not come from the fact that a competent treatment for pleurisy was made, and when switching from a dry form toExudative, when the fluid lubricates the pleural sheets and eliminates the painful friction between them.Discomfort in the chest does not go away - it acquires other characteristics: instead of sharp sharp, sometimes unbearable pains, the patient begins to feel a peculiar feeling of heaviness in the chest and its overflow.
If the pleurisy remains dry due to the increased absorption capacity of the pleura, diuresis( daily urine output) may be increased.In , this is followed by a differential diagnosis of kidney disease - orienting will help:
- urine analysis;
- blood test - in addition to leukocytosis and increased ESR, there will be an increase in the number of certain blood cells - neutrophils, monocytes and eosinophils;
- instrumental methods of studying the kidneys( ultrasound and others).
If a pleural puncture was performed with a diagnostic purpose but no effusion was obtained, the pleural cavity can be rinsed and the liquid obtained after rinsing can be sown to nutrient media - thus it is possible to clarify:
- is infectious pleurisy or aseptic;
- in the infectious nature of pleurisy by sowing is determined by the infecting agent, it is important for the selection of antibiotics.
- is also flushed out for cytological analysis - in case of tumor lesions of the pleura, tumor cells and erythrocytes are found in it.
In case of doubt, thoracoscopy is used to confirm the diagnosis of dry pleurisy. In addition to examining the pleural sheets, during it, a pleurobiopsis is performed( pluck a fragment of pleural sheets in different places) followed by a cytological study of the biopsy under a microscope.
The diagnosis of dry pleurisy of tuberculosis origin is given with a combination of such data:
-
 Relatively young patients;
Relatively young patients; - contacts with patients with tuberculosis;
- chest pain;
- is a non-intensive cough;
- moderate temperature increase;
- prolonged course with the formation of adhesions in the pleural cavity;
- positive tuberculin test ;
- pathological changes in the lungs and radical lymph nodes, characteristic of the tuberculosis process.
Treatment of dry pleurisy
Regardless of the origin of pleurisy, patients should adhere to such medical prescriptions as:
-
 bed or half-bed mode;
bed or half-bed mode; - a balanced diet( is especially important for consuming enough protein, but the use of carbohydrates, salts and liquids should be limited to );
- anti-inflammatory drugs( in the acute period - intramuscular and intravenous, with residual effects - tableted);
- desensitizing agents;
- with severe pain syndrome - pain medications;
- to increase the body's resistance - hyperimmune plasma, polyglobulin and their analogs.
Treatment for secondary pleurisy should primarily be aimed at eliminating the cause of inflammatory changes in the pleura:
- cytotoxic agents for oncological diseases;
- antituberculosis drugs for tuberculosis;
- antibiotics for pneumonia, taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms;
and so on.
After consultation with your doctor, you can apply old, but quite effective methods of traditional medicine:
- warming compress;
- tight bandaging of the lower parts of the thorax;
- application of iodine strips to the skin of the chest
and so on.
In complicated or neglected cases with a pronounced inflammatory process, as well as violations of the protein and water-salt balance, the following are used:
- hormonal preparations;
- protein preparations;
- solutions of electrolytes.
Introduction of antibacterial drugs into the pleural cavity is theoretically possible, but as a method with dry pleurisy it did not stick.
Prevention
Prevention of the occurrence of pleurisy is primarily the prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions that provoke their occurrence - in particular, those that can lead to inflammatory changes in the pleura:
- timely cureTuberculosis, pneumonia and other diseases, competent medical tactics in oncolonology;
- Compliance with aseptic and antiseptic rules during pleural puncture, thoracoscopy and thorax surgery;
- high-quality sanation for injuries of the chest.
In order to prevent the formation of adhesions in the pleural cavity, it is recommended that:
- a respiratory gymnastics complex under the supervision of a physician;
- massage - classical or vibrating;
- physiotherapy methods of treatment( primarily - ultrasound exposure).
These measures are carried out after remission of acute manifestations.
Pleural prognosis
The prognosis for dry( fibrinous) pleurisy for life and health is generally favorable . Irreversible changes in the pleura that impair breathing occur in the case of neglected or improperly treated pleurisy.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician