Methods of treatment of hernia of the esophagus
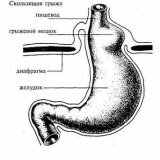
Hernias can be both congenital and acquired with age. Cases of congenital hernia are quite rare, and are accompanied by such a physical anomaly as a shortening of the esophagus. While the acquired hernia occurs much more often, and depends on the impact of certain conditions.
Methods of treating a hernia will also depend on many factors. But let's deal with this issue in order.
Reason.
The basis of any disease is its cause, with the elimination of which it is accepted to begin treatment. Treatment of hernia of the esophagus was no exception.
There are many reasons why a completely healthy person can develop a hernia. First, it is age-related degenerative changes. Usually in such cases potential patients will have thinning of connective tissue ligaments, which can also lead to the usual inguinal hernia.
Secondly, the frequent cause of a hernia is constipation, more precisely not the fact of constipation, but the increase in intra-abdominal pressure that it creates.
Third, usually among patients with hernia of the esophagus, there are more people who are obliged to constantly perform heavy physical work or lift weights. Here, intra-abdominal pressure will play an important role, namely, its increase.
Fourthly, people who have chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are also at risk.
So it can be concluded that the possibility of the formation of a hernia of the esophagus in the first place will be affected by frequent, or a sharp increase in intra-abdominal pressure, as well as the presence of chronic diseases of the abdominal cavity.
Diagram of the development of the disease.
Usually the pattern of the development of this disease is repeated in all patients. Under the influence of unfavorable factors, the result is an expansion of the aperture opening. Because of what, just in the presence of certain conditions the stomach can get from the abdominal cavity into the thoracic cavity. If you do not react in time, the chest cavity can also move part of the intestines, which will bring a lot of complications of the disease.
Usually, such a disease is accompanied by heartburn, pain, especially when eating, tilting forward, horizontal position of the body and lifting the gravity. Pain sensations usually occur in the abdominal region, and can be given to the chest, neck or shoulder blade and carry a squeezing character. Because of this, a hernia is often confused with a heart attack or the so-called "angina pectoris".It also happens that a person develops a sliding hernia, which does not give him any special discomfort, and is detected accidentally during a planned examination.
As for the symptoms of a hernia, we can relate belching, dysphagia, difficulty in the passage of food.
To date, hernia of the esophagus is well studied and easily diagnosed. If this is not done in time and the appropriate measures are not taken, the patient's health may deteriorate sharply, there is a risk of various complications that may necessitate surgical intervention.
The main complications of hernia include: shortening of the esophagus, bleeding, erosion, ulcers of the esophagus, anemia, esophageal cancer, cicatrical narrowing of the esophagus.
Methods of treatment.
Methods of treatment of hernia of the esophagus will depend directly on the type of hernia, as well as the level of neglect of the disease. In practice, there are two main methods of treatment:
Conservative method of treatment of a hernia: is to achieve a stable state of the patient without surgery, as well as to prevent further progression of the disease. With this method of treatment, the patient is prescribed drugs whose action is aimed at lowering the acidity of gastric juice, reducing gastric secretion, protecting the mucosa of the esophagus. As a mandatory item of treatment, a special diet becomes, and with mild forms of hernia - therapeutic gymnastics, to strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and diaphragm. Also, in the treatment of hernia of the esophagus, the treatment of concomitant diseases that could become the root cause is not performed in an operative manner in parallel.
The operative method of treatment is used in cases when the patient finds: fixation of the hernia of the esophagus in the hernial gates, large dimensions of the hernia, dysplasia of the esophagus mucosa, deterioration of the patient's condition, absence of the results of conservative treatment of the complication.
With this symptomatology, the operation becomes necessary. Also, surgical intervention is carried out in cases where the patient exhibits a near-esophageal sliding hernia. Basically, the recommendations for surgery with such a hernia are associated with a greater risk of infringement of the hernia.
There are exceptions, when a sliding hernia found in the patient does not cause any symptoms. Then the surgical intervention is not applied, and the patient simply must adhere to the diet and limit himself from the factors that will contribute to increasing intra-abdominal pressure.
People who undergone esophageal herniation and undergoing treatment are also obliged to continue at home to maintain the result. Such people are forbidden to lift weights, eat large portions( usually meals are divided into several times), overeat, perform heavy physical work, consume alcohol and heavy fatty foods.
Only in this case, it is possible to stop the progression of the disease and avoid complications. The same recommendations can be given to people who, for one reason or another, are predisposed to a hernia of the esophagus. After all, the prevention of the disease is better than its treatment.