How is pelvic ultrasound done in men?
Ultrasound diagnosis is the gold standard for determining and confirming the pathologies of internal organs. The technique visualizes the organs in norm and under such pathological conditions as abscesses, tumors, cystic formations and helps to determine the amount of fluid( inflammatory exudate) in various cavities inside the body.
Contents of
- 1 Which organs are examined?
- 2 Indications for ultrasound
- 3 Types of ultrasound of the small pelvis
- 3.1 Transabdominal method
- 3.2 Transrectal method
- 3.3 Doppler examination
- 4 Preparation for ultrasound of the pelvis
- 5 Procedure for ultrasound of the pelvic organs
- 6 What is detected on ultrasound of pelvic organs?
Which organs are examined?
Diagnostic examination of the small pelvis and its organs includes visualization:
- of the bladder;
- of the parietal peritoneum of the small pelvis;
- seminal vesicles;
- of pelvic lymph nodes;
- of the prostate.
In the study, the size, location of the organs and their pathological conditions are determined. The organs of the genitourinary and reproductive system are located in the cavity of the small pelvis and are anatomically connected. That is why a comprehensive ultrasound diagnosis of all pelvic organs is carried out.
Indications for US
Ultrasound diagnosis in men is performed to confirm diseases of the genitourinary and reproductive systems. The data obtained by ultrasound diagnostics help to clarify the diagnosis and make differential diagnosis in complex cases. In addition, ultrasound is performed to prevent the detection of chronic diseases and latent sexual infections in men.
Frequent indications for ultrasound of the pelvic organs of men are:
- hematuria - the presence of blood( erythrocytes) in the urine;
- spermaturia - determination of the ejaculate in the urine;
- male infertility or suspicion of it;
- pain in suprapubic, inguinal area and perineum;
- erectile dysfunction or vice versa, a pathologically long erection of the penis( priapism);
- dysuria - a violation of the process of urination, which can result in pain during the emptying of the bladder, a large frequency of urination, difficulty or vice versa urinary incontinence;
- detection of tumors;
- prophylactic diagnostics for diseases of the genitourinary system;
- puncture and biopsy of any formations localized in the small pelvis, under the supervision of ultrasound.
Preventive studies significantly reduced mortality from oncology of male reproductive organs. They allow to identify diseases at early stages, which increases the effectiveness of treatment and speed of recovery.
Types of ultrasound of the small pelvis
In ultrasound examination of the male pelvis, two main directions are distinguished:
- transabdominal ultrasound;
- transrectal ultrasound( TRUS).
Each method found its justification and has its strengths in the diagnosis of diseases.
Transabdominal method
The method consists in carrying out ultrasonic waves through the anterior abdominal wall. To do this, use an external sensor, which is installed in the suprapubic region( see Figure 1).The area of the sensitive element allows you to capture more reflected ultrasonic waves. This method is excellent for preventive studies and does not cause discomfort to a man.

Fig.1 - Conduction of transabdominal ultrasound.
Unlike TRUS, the accuracy of the transabdominal technique is somewhat lower. In this connection, the method is suitable for determining the volume pathological formations in the cavity of the small pelvis and the bladder. It is worth noting that during the transabdominal ultrasound, the bladder must be in the filled state.
Transrectal method
Transrectal ultrasound( TRUS) is performed using a miniature ultrasound transducer to minimize discomfort to the patient. The sensor is inserted into the previously prepared and purified rectum.
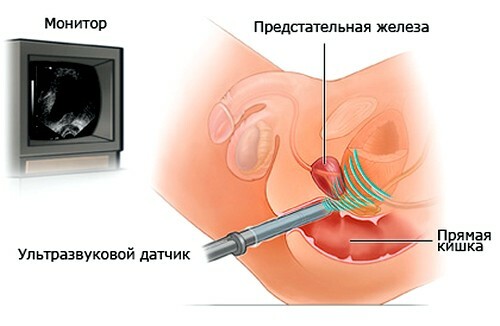
Fig.2 - Conducting transrectal ultrasound( TRUS).
In most cases, TRUZI is used for detailed examination of the prostate and determining the severity of the pathology in its tissues. Although the sensor has a small area of an ultrasound-sensitive element, it allows for a study in the immediate vicinity of the prostate( see Figure 2).This increases the accuracy of the data obtained: TRUS allows you to detect even the smallest cystic formations in the prostate gland - up to 0.2 cm.
Also TRUZI is the method of choice for such pathology as incontinence or small volume of the bladder, which makes it difficult to conduct standard ultrasound diagnosis.
Doppler ultrasound
Color Doppler is a supplement to the two methods described above. Dopplerography allows you to assess the degree of blood flow. For this, an image of the color pattern of blood flow in the vessels of the pelvic organs is obtained. Most modern ultrasound devices have this regime and help to identify vascular pathology from the urinary and reproductive systems.
Preparing for ultrasound of a small pelvis
The procedure for preparing a patient for a diagnostic examination depends on the technique of ultrasound diagnosis.
Preparation for transabdominal ultrasound:
- rejection of foods rich in fiber and legumes 2-3 days before the study, in order to minimize gas generation;
- it is advisable to refrain from eating for 5-6 hours before the study;
- drink half a liter of water without gas 2 hours before the study;
- 2 hours before the ultrasound should refrain from urinating. In case of strong urge you can urinate a little, but not completely. After that, drink an extra glass of water.
All the above stages of preparation are used for carrying out the TRUS, but the following are added to them:
- use of intestinal cleansers( Fortran and analogues).For this, the patient drinks 3-4 packs on the eve of the study. In case the study is scheduled for the second half of the day, two packets are drunk on the morning of the study day;
- cleansing enema is an alternative method and is performed on the morning of the day of the study. The volume of the liquid administered to the rectum should be at least 200 ml.
Procedure for ultrasound of pelvic organs
Transabdominal examination. The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall, with the bladder completely filled with liquid.
In transabdominal ultrasound, the size, shape, structure and position of the bladder is determined. All additional formations present in the walls or cavity of the bladder are fixed. Similarly, the size, shape, structure, contents of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles, as well as surrounding surrounding tissues, are examined.
The second stage is the emptying of the bladder with a re-examination. This allows you to estimate the residual volume of urine in the bladder.
TRUSI .At the TRUS, the sensor is inserted into the previously prepared and purified rectum. To the anterior wall of the rectum, the prostate gland is closely attached, which allows the miniature sensor to accurately visualize its size, shape and especially the structure with the formations.
In addition to TRUS, color Doppler mapping is possible. This method allows you to evaluate the blood flow in the pelvic organs and to identify vascular pathology, which is important for establishing the correct diagnosis.
What is detected on ultrasound of pelvic organs?
Thanks to ultrasound of the pelvic organs, there is an opportunity to establish an accurate clinical diagnosis, assess the severity of the disease and choose the tactics of treatment. Often, ultrasound can determine whether the patient needs surgical treatment. Ultrasound and TRUS can detect such diseases as:
- male infertility;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive and genitourinary systems;
- urolithiasis;
- vascular pathology of pelvic organs( see "Stagnation of blood in the small pelvis - causes and treatment");
- congenital anomalies of the genitourinary system;
- neoplasms( tumors, cysts, abscesses).
urologist / androlog evaluates and interprets the following settings:
- location organs and lymph nodes in the pelvis and in relation to each other;
- characteristic for inflammatory processes connective tissue formations. Including stricture of the prostate;
- thickness, volume, shape of the bladder, stones and neoplasms in it;
- residual volume of urine;
- consistency, shape, blood flow in the prostate gland, as well as tissue structure.
Due to its high accuracy of research and availability, ultrasound is the gold standard for diagnosis of diseases of the male reproductive and genitourinary systems.
See video about ultrasound of pelvic organs
Recommended for viewing: