Details about colliculitis: symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment
Colliculitis is an inflammation of the seminal tubercle. According to leading urologists, colliculitis is a special case of posterior urethritis, a pathological process in the posterior( prostatic) part of the urethra. In the absence of treatment, the disease can lead to the development of cystitis, pyelonephritis and other serious complications from the urinary system.
Anatomy prostate
Content
- 1 excursion into the anatomy
- 2 Forms colliculitis
- 3 causes of pathology
- 3.1 main reasons
- 3.2 Risk Factors
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 Complications
- 6 Diagnostics
- 6.1 Finger prostate study
- 6.2 Ureteroscopy
- 6.3 Laboratory diagnosis
- 7 PrinciplesTreatment
- 8 Prevention
Excursion to the Anatomy
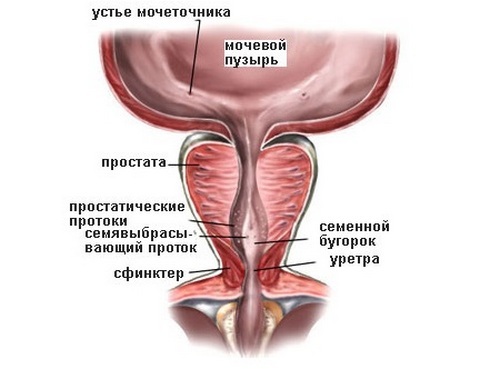
Seed tubercle is a small formation in the form of a mound, located in theDays of the part of the urethra( urethra).The seminal tubercle consists of muscle and connective tissue. The organ is well-blooded, has a branched network of small capillaries and veins. During erection, filling of the venous plexus of the tubercle occurs, due to which it significantly increases in size.
The seminal tubercle is involved in the realization of normal ejaculation and erection. On its surface open the ducts of the prostate gland and the vas deferens. Through the seminal tubercle, the secretion of the prostate and spermatozoa takes place. Inflammation in this department leads to a shortening of the time of sexual intercourse and other health problems.
Forms of colliculitis
There are two forms of colliculitis:
- Primary colliculitis - occurs as an independent disease in the violation of blood supply and innervation of the organ.
- Secondary colliculitis - occurs as a complication of urethritis, vesiculitis, prostatitis and other inflammatory diseases of the male sexual sphere.
Causes of pathology
The main causes of
The main cause of secondary colliculitis is infection with pathogenic and opportunistic flora. When the survey is most often identified such microorganisms:
- gonococci;
- ureaplasma;
- mycoplasma;
- chlamydia;
- intestinal flora.
A quarter of the urologist's patients have a mixed infection - infection with several microorganisms. Against the background of bacterial inflammation it is possible to attach a fungal infection and lengthen the terms of recovery.
Risk Factors

Non-compliance with personal hygiene rules is one of the most common causes of colliculitis
Colliculitis development risk factors:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- refusal to use condoms;
- non-compliance with personal hygiene;
- supercooling;
- viral infections and other diseases leading to a decrease in immunity;
- genital tract injury;
- instrumental studies of the urethra( catheterization, etc.);
- foreign bodies in the urethra.
All these factors significantly increase the risk of colliculitis and weight the course of the disease. The likelihood of a problem is also increased with the already existing inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary tract.
Symptoms of
The disease usually begins acutely with a sudden appearance of unpleasant sensations in the groin. Perhaps a gradual increase in symptoms. The asymptomatic course of colliculitis is rare. In the absence of specific symptoms, the disease can be detected accidentally during a planned examination in a urologist.
The main symptoms of colliculitis:
- pain in the groin( aching or stitching);
- sensation of foreign body in the anus;
- discomfort when urinating( pain, burning);
- appearance in the urine of impurities of blood or pus.
Inflammatory changes in the area of the seminal tubercle are accompanied by considerable discomfort in sexual life. For colliculitis, the following typical symptoms are typical:
-

When the first symptoms appear, immediately consult a doctor
for pain during intercourse( during or immediately after orgasm);
- appearance in the ejaculate of impurities of blood or pus;
- priapism - a prolonged erection, not associated with sexual arousal;
- involuntary ejaculation during defecation( due to mechanical stimulation of the inflamed seed tubercle by passing caloric masses);
- decrease in the strength of orgasm;
- decrease in sex drive;
- erectile dysfunction( inability to maintain an erection for a full sexual intercourse).
Complications of
Untreated colliculitis can cause cystitis and pyelonephritis. From the urethra, the inflammatory process gradually passes into the bladder and then into the kidneys. It is not excluded the occurrence of prostatitis - inflammation of the prostate gland. A prolonged sluggish infection does not add health to a man and does not in any way contribute to a full-fledged active life. In the future, such a condition can lead to erectile dysfunction and other problems in sexual life.
Diagnosis
The appearance of any discomfort in the groin, discomfort during urination and during sex is an occasion to visit a urologist immediately. At the first appointment, the doctor will assess the general condition of the patient, find out the main complaints and conduct an examination of the external genitalia. During the examination, the doctor pays attention to the color of the skin of the penis and the presence of discharge from the urethra. Mandatory palpation of the foreskin, scrotum, inguinal lymph nodes is performed. Based on the results of the initial examination, the doctor will be able to set a preliminary diagnosis and conduct additional diagnostics:
Finger prostate examination
Manipulation is carried out through the rectum. Finger research allows you to assess the condition of the prostate and identify pathological changes in the organ. The procedure is indicated for suspected concomitant prostatitis and prostate tumors. With the prophylactic purpose, finger examination of the prostate is recommended for all men over the age of 40.
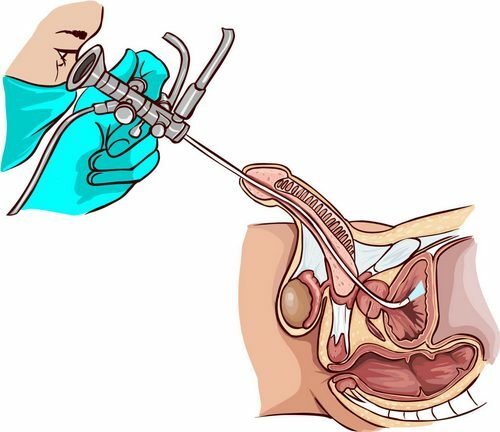
Urethroscopy
Inspection of the urethra with a special probe allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the body, identify ulcers, strictures, tumors, stones. It is necessary to examine the site of the localization of the seed tubercle, its dimensions are estimated. During the procedure, the doctor can take a portion of the mucosa for histological examination( biopsy).
Laboratory diagnostics
For the detection of a pathogen, the following is carried out:
- smear examination from the urethra;
- bacteriological seeding of ejaculate;
- PCR diagnostics for sexually transmitted infections.
This approach allows us to find out the cause of colliculitis and choose the treatment taking into account the detected pathogenic microorganisms.
Principles of Treatment of
The treatment of colliculitis and concomitant pathology is performed by a urologist. The choice of therapy will depend on the form of the disease, the cause and the infection. Do not self-medicate and postpone visit to the doctor. Not cured in time colliculitis can lead to the development of serious complications and significantly disrupt the normal course of life.

Complex therapy includes the use of antibiotics, antimicrobial and antiseptic drugs
Conservative treatment of colliculitis includes:
- systemic antibacterial therapy;
- topical treatment;
- physiotherapy.
Antibiotic therapy is prescribed taking into account the causative agent of the disease. Before receiving the results of bacteriological research, antibiotics of a wide range of action, harmful for many pathogenic microorganisms at once, can be used. The course of treatment lasts from 5 to 10 days. The dosage of drugs is determined by the doctor based on the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Antimicrobial and antiseptic drugs are prescribed not only inwards, but also locally. Medications are injected through the urethra by a special instrument. With this approach, medicines are delivered directly to the inflammatory focus and work only where it is needed. Side effects of drugs with topical application are minimized.
Surgical treatment of colliculitis is indicated in the long course of the disease and complete replacement of the organ with a non-functional connective tissue. The operation is also performed in the presence of polyps or other formations on the surface of the seminal tubercle. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia. During surgery, the doctor removes excess tissue and excises polyps. With the development of irreversible changes, transurethral resection is shown - excision of the seminal tubercle by access through the urethra.
Prevention of
Is it possible to prevent the development of colliculitis? Yes, if you follow some simple recommendations:
- Refusal of casual sexual relations.
- Using a condom during intercourse.
- Timely treatment of any diseases of the genitourinary sphere.
- Compliance with personal hygiene.
- Perform any instrumental interventions in the lumen of the urethra only on indications.
When the first signs of colliculitis appear, you should contact a urologist. The sooner the treatment is started, the easier it will be to cope with the disease and avoid the development of serious complications.
Recommended for viewing: