Cyst of the jaw
 The jaw cyst is a neoplasm, the fibrous tissue in which it forms walls, the epithelium lining it from the inside, and the contents are filled with exudate. Cysts of the jaw are odontogenic, that is, formed from the remains of a developing tooth or from already erupted. In addition to odontogenic, there are false cysts( pseudocysts) that do not have an epithelial lining from the inside, this is their special feature. If you do not diagnose them in time and do not make the right treatment, complications can arise.
The jaw cyst is a neoplasm, the fibrous tissue in which it forms walls, the epithelium lining it from the inside, and the contents are filled with exudate. Cysts of the jaw are odontogenic, that is, formed from the remains of a developing tooth or from already erupted. In addition to odontogenic, there are false cysts( pseudocysts) that do not have an epithelial lining from the inside, this is their special feature. If you do not diagnose them in time and do not make the right treatment, complications can arise.
There are congenital cysts of the jaw that develop from the epithelial tissue of the nasal palatal canal. On the radiographic image, they are visualized as pockets of enlightenment, with clear outlines, located between the roots of the incisors of the upper jaw.
The cicatrix of the incisive gingival papilla is a variant of the jaw cyst formed from the mucous membrane. It gradually increases in volume without causing trouble for the patient. When jaws contact, trauma is possible, then its surface becomes painful, ulcerated, reddens, and can bleed during meals. Such cysts are excised operatively. Relapses occur rarely.
Causes of the jaw cyst
The causes of the cyst of the jaw are numerous. The first explanation of the occurrence of this pathology is infection during root canal treatment during endodontic treatment: pushing infected dentinal sawdust behind the apical hole, lack of medicamentous treatment of the root canal( passage and treatment of the canal should be done under the antiseptic tray).If you ignore these rules, the risk of complications in the apical tissues is much higher. Until now, dental doctors have not come to a consensus: what kind of filling material should be preferred and should retrograde be done? This issue remains very significant.
The oral cavity contains about 450 species of microorganisms. Among them are both pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic. If the oral hygiene of the patient is reduced, then the number of pathogenic microorganisms will increase, and against a background of a decrease in the immune system, growth of the tumor is possible. Factors that reduce the body's immunity: stress, lack of sleep, malnutrition, hypothermia, etc.).Difficult teething, trauma, transferred infectious diseases can provoke the development of the cyst of the jaw.
There are three main types of jaw cysts - keratokist( primordial), follicular and radicular cysts. Keratokista - formation, located more often on the lower jaw, the walls of which are formed by fibrous tissue. It is formed more often in the retromolar region, where the eighth tooth( the wisdom tooth) is erupted. The structure of the cyst is a single-chamber or multi-chamber. The cavity fluid contains a substance called cholesteatoma. Possible recurrence of the cyst.
Follicular cyst of the jaw or "eruption cyst".It is formed from the rudiment of an unbroken tooth. Its location is usually in the area of canines and premolars of the upper and lower jaws. At computer research in a field of these teeth the segment of an enlightenment with precise contours will be visible, inside the cyst there can be a formed or not formed rudiment of a tooth. Inside the follicular cyst is covered with epithelium.
The radicular cyst of the jaw is the most common. The frequency of occurrence is 80%.The radicular cyst of the jaw is located near the root of the tooth, more often it occurs with periodontitis. The walls of the parotid cyst are thin, fibrous, the lumen is lined with a multilayered flat non-geriatric epithelium, which includes lymphocytes and plasma cells. In the case of inflammation, cells grow into the wall, causing a feeling of raspiraniya and discomfort. With multiple and abundant overgrowth of the cyst of the teeth, the upper jaw can penetrate into the maxillary sinus, causing sinusitis.
Symptoms and signs of jaw cyst
Small formations for a long time may go unnoticed. Clinical symptoms do not show odontogenic cysts of the jaws. Usually, the cysts of the jaw are found during the X-ray examination of a person's teeth.
Odontogenic cysts of large jaws have a number of clinical signs. Patients will complain of the presence of cones, jaw swelling, deformation of the jaw bones. In the cyst of the posterior wall of the upper jaw, headaches are caused by compression of nerves, signs of sinusitis( a runny nose, a feeling of nasal congestion due to inflammation of the mucous membrane, a fetid odor.) When germinating into the lower nasal passage, the symptoms will be similar. With a slight pressure, a parchment crunch is characteristic.
Upon attachment of a secondary infection, the jaw cyst is suppurated. The clinical picture of the disease becomes brighter. There is swelling of the face due to the collateral edema of surrounding tissues, limiting the opening of the mouth when involved in the process of chewing musculature, the mobility of the causative tooth, soreness when biting tough food. A detachment of tissues is possible.
Symptoms of odontogenic cysts are very similar to those of osteomyelitis. But with osteomyelitis, mobility of several teeth is observed, a feeling of numbness in the tissues of the corresponding region( Vincent's symptom).
Cyst of the upper jaw
The cyst of the teeth of the upper jaw occurs quite often. The upper jaw is the twin bone of the facial part of the skull. In its composition, the bone has a compact and spongy substance. In terms of quantity, the spongy substance predominates, which facilitates the rapid spread of the cyst in the thickness of the bone. The anatomical feature of the upper jaw is that it is an air-sac. The maxillary sinus has an individual structure. The dimensions of the cavity are different, the roots of premolars and molars can penetrate into the sinus or be covered with a thin mucosa.
The causes of the cyst of the upper jaw are odontogenic and non-dentogenic. One of the causes of the cyst is the spread of infection through the root canal into the thickness of the tooth or through the periodontal pockets.
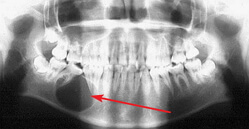
Symptoms of the cyst of the teeth of the upper jaw: the presence of education in the oral cavity, in case of suppuration of edema, pain with biting, raising the temperature to subfebrile digits, drowsiness, migraines. It is not difficult to diagnose this disease, it is enough to make an X-ray photograph. In the picture, the cyst of the upper jaw will be viewed as a darkened area.
The radicular cyst of the upper jaw is formed in the central teeth, usually as a result of inadequate endodontic treatment( fracture of the instrument) or trauma. Residual cyst is a kind of cyst that occurs after a complicated tooth extraction. The follicular cyst of the jaw is one of the unfavorable forms of the cysts of the upper jaw, in which the eruption of the permanent tooth and the risk of loss of the rudiment of the permanent tooth are possible, which can contribute to the development of partial adentia.
Cyst of lower jaw
The cyst of the lower jaw is a pathology in which a hollow formation forms in the thickness of the jaw. Over time, the cavity can be filled with liquid. Ill does not notice any deviations from the norm in the architectonics of the jaw, the state of health remains at the same level. The development of cystic education in this case continues, a cyst of the lower jaw is detected with a random radiographic examination.
The lower jaw( mandible) is an unpaired bone in the human body, consisting of compact and spongy components. In the lower jaw, the amount of compact matter predominates. In the area between the fourth and fifth teeth there is an orifice through which the output of the powerful mandibular nerve passes. With active growth of the cyst of the lower jaw, damage to this nerve is possible, which leads to severe consequences. As a result of nerve compression, the patient will experience severe pains that irritate half of the face.
Symptoms of the cyst of the lower jaw are varied: swelling, redness, pain. From the side of the lower jaw development of complications is possible, such as fracture, osteomyelitis, periostitis, fistula formation. The varieties of cysts are the same as for the upper jaw.
Treatment and removal of the jaw cyst
Treatment and removal of the jaw cyst are performed only by modern surgical methods. However, some cases may be an exception, and treatment is performed without surgery. In case of suppuration of the cyst, drainage is carried out, that is, surgical intervention is necessary.
There are two main types of surgical treatment of jaw cysts. These include cystectomy and cystotomy. Cystectomy is the complete removal of the cyst followed by the closure of the defect. The indication for cystectomy is:
1) small jaw cyst, located within 1-3 intact teeth;
2) the cyst of the upper jaw retaining the wall of the bottom of the nasal cavity and not having teeth in this area;
3) the cyst of the lower jaw, where there are no teeth and there is enough bone to prevent a pathological fracture.
The main goal of cystectomy is to preserve the causative teeth, as well as the teeth located next to the cyst. Teeth that provoked the development of the odontogenic cyst should be sealed with the removal of the material behind the tip of the root.
There is a variant of carrying out a tooth-saving operation - resection of the apex of the root. But often the teeth that are located 2/3 in the cyst cavity, after resection loosen and fall out. Preservation of such teeth is not advisable. Multi-rooted teeth are much more likely to be removed, since the passage of the root canals is much more difficult. Retenirovannye teeth are removed during the cystectomy, especially if they are the cause of the development of the cyst of the jaw. Before a cystectomy, the teeth should be subjected to an electrodontometry to determine the viability. If the tooth does not react to current, and the radiograph does not have an extension of the periodontal gap, the tooth should be depulled and sealed all the way before the operation.
The operation of the cystectomy is performed under the conductor and infiltration anesthesia, in the region of the jaw cyst make a cut corresponding to the size of the cyst, form and flake the mucosal periosteal flap in the form of a trapezium. Cut it out with the calculation of overlapping the future defect. Then trepanize the bone wall, expand the cutter to open the view and resect the tip of the root. Using a surgical spoon, peel the cyst and remove with the top of the root. The entire cyst shell must be removed completely to prevent relapses. After removal of the cyst of the jaw, the roots of adjacent teeth are exposed, their tips are also subjected to resection. Then the cavity is inspected, it is filled with a blood clot, which is the hope of a biological bandage. Introduction to the wound of antibiotics or washing with antiseptics is not indicated. It is admissible to introduce osteogenic preparations into the wound( bone sawdust, collapol).On the surgical wound, a flap is laid, fixed with catgut sutures. The patient is prescribed a sick leave for a week. Prescribe the use of antihistamines, analgesics, sometimes prescribed anti-inflammatory therapy. It is recommended to hold oral baths with solutions of chamomile, sage, etc.
In cystotomy, the main idea is to create an oral cavity message with the cavity of the jaw cyst. Anesthesia is also performed, an incision is made in the cyst area, the flap is flaked, and the wall is flipped. The front wall of the cyst and periosteum is cut with sharp scissors, the cyst is emptied, the fluid is aspirated or absorbed by gauze tampons, the flap is mobilized to the remaining wall of the cyst, the cavity is tightly plugged with iodoform turunda. Neighboring teeth are resected or depulpied with subsequent sealing. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity grows together for about a week, then the cavity is filled with a smaller swab. The cavity gradually decreases and disappears. Within 6-12 months the cavity disappears completely. In the first 2 months the patient needs to come to the dressings, after removing the swab the cavity should be washed with antiseptic solutions. Later, after the meal, the patient himself will wash the cavity with boiled water or a solution of weak antiseptics( chamomile, sage).