Pain in the thoracic spine
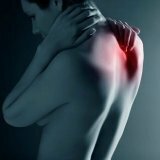
Osteoarthritis and osteochondrosis are dystrophic changes, usually the most common causes of pain in the spine, namely in the thoracic part of the spine. But it should be remembered that pain in the thoracic spine may arise for other reasons, which only a doctor can establish.
Consider the diseases in which pain may appear in the thoracic spine.
If suddenly there is persistent pain( especially if it's radicular girdle pain) in the thoracic spine and there are signs that the spinal cord is squeezed, first of all, a diagnosis should be performed to exclude primary or metastatic spinal tumors and infectious diseases( epidural abscess, tuberculousSpondylitis).
Shingles of the chest may appear due to the formation of herpes zoster, lesions of nerve trunks, in the case of vasculitis or diabetes mellitus.
More often such pains arise in the case of dystrophic intervertebral joints, the development of spondylarthrosis, affection of the rib-vertebra joints and rib joints with osteoarthritis, as a result of which the intervertebral foramen are narrowed. There is compression of sympathetic nerve fibers and nerve roots of the spinal cord, the appearance of pain syndrome. If the nerve roots of the spinal cord are squeezed, shingles appear in the area of innervation of the affected nerves and sensitivity is disturbed( numbness, sensation of the goose, burning sensation or increased sensitivity).If the sympathetic nerve fibers are squeezed, functional malfunctions of internal organs arise, the work of which they regulate. Typically, pains appear in the interlopar region of the spine or throughout the thoracic region and can be intensified during movement or breathing.
To clarify the diagnosis, X-rays are taken in 2 projections. They will be able to see various bony growths of the bodies and a decrease in the height of intervertebral discs. But such changes can often occur in people who do not feel such pain.
Pain sensations in the thoracic spine may also occur with a disc herniation in this department. However, in the thoracic region, intervertebral hernias appear in no more than 1% of the total number of cases of this disease. Most often, if the cause of the pain is a hernia, then it is located in the four lower discs. In this disease, much more often than in others, there is compression of the spinal cord, due to the middle location of the hernias and a decrease in the width of the spinal canal.
Any trauma to this part of the spine. In people aged with such pain, the cause can often be osteoporosis of the spine, accompanied by a compression fracture of the vertebrae.
Osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine can manifest itself in a variety of ways, but no symptom can be called clearly specific to it. Most often, the symptoms depend on where the main painful process is and how much it is expressed. After a prolonged stay in the same position or with tiring physical exertion, the pain can be intensified, causing the person to constantly change the position to at least somehow reduce the intensity of pain. One of the most noticeable symptoms in this case is a dull, aching or burning pain in the shoulder blades and between them. Often there is a feeling of mites that squeeze the back. Pain pains the procession of the processes of the vertebrae. Often the pain echoes respond even in internal organs.
In young people, pain in this part of the spine can be caused by the presence of Sheyermann-Mau disease, which manifests itself as a rapid increase in thoracic kyphosis and deformation of the lower thoracic vertebrae.
It is also very important to be able to exclude from the list of possible causes of pain injuries to the ribs, thoracic spine, sternum, aortic aneurysm, myeloma, pulmonary embolism, lung tumor, pneumonia, gastric ulcer, pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis, diaphragmatic abscess and cholecystitisAll these diseases can cause pain of this kind.