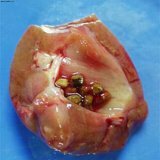
Polyp of the bladder

Polyp is an abnormal proliferation of tissues that protrudes over the mucosa of the bladder. It can be attached to the mucosa by an elongated stem or the rod may be absent. In most cases, this proliferation of the bladder is benign in nature. Polyp is one of the forms of bladder cancer, diagnosis is complicated by such a feature that often the disease does not manifest itself and in the absence of symptoms, it can be detected only with ultrasound( planned) study of the bladder.
Causes of bladder polyp formation
Usually polyps in this organ form against the backdrop of a long inflammatory process, combined with a hereditary predisposition to such a disease.
The polyp in the bladder can also form with prolonged chronic cystitis. In this case, during the remission of the disease, the mucosa grows. Since the condition of the bladder mucosa is disturbed by inflammation, the restoration of the mucosa is reproduced by the areas. If at one of the sites the mucosa grows strongly and protrushes into the lumen of the bladder, then we are talking about polyps. In most cases, the polyps are round in shape, sitting on a thin stalk. A polyp in the bladder can be one, but there can be many.
In some cases, a polyp is also called a benign tumor of the bladder. Sometimes the disease is completely asymptomatic and a person does not even suspect a polyp. Polyps( polyps) of the bladder can be regenerated into a malignant tumor( otherwise malignant), but this happens rarely, so they do not always remove it, sometimes( with a small polyp), just monitor its growth.
Signs, symptoms of bladder polyp
As already mentioned, symptoms may be absent. In case the polyp is large, it is often prone to destruction and in the urine, then blood can be observed. There can be little of it in the urine( when it is found in urine in the laboratory), and maybe a lot, the urine acquires a pink or red hue.
A large polyp that is located near the ureter or near the urethra can cover the lumen of these organs. This can cause the following symptoms: urge to urinate, when you can not urinate, severe pain.
The polyp in the bladder can also be complicated by tissue necrosis( dying) or bleeding, very frequent recurrences in the bladder of the inflammatory process.
Diagnosis of this bladder disease
When diagnosing polyps in the bladder, an ultrasound examination of the bladder itself is performed. This examination reveals the formation( soft tissue) in the wall of the bladder, which protrudes into its lumen.
Also to clarify the nature of education specialists conduct an endoscopic examination of the bladder - this is a cystoscopy.
In certain cases, X-ray examination of this organ with the introduction( preliminary) of contrast media into the cavity of the bladder is a cystography.
In addition, it is mandatory to conduct a laboratory study of urine, in which signs of the polyp can be found, as well as a biopsy of the material to exclude the degeneration of the polyp into malignant formation.
How is the treatment of polyp in the bladder
Treatment of this pathology of the bladder depends on the development of the disease, on the size of these sprouts, on the condition of the patients.
A polyp small in size of this organ, which does not manifest itself in any way, basically does not remove, just observe its growth. In case the polyp proliferates and there is a danger of closing the lumen of the ureters or the urethra, if it bleeds, it is removed.
Removal of the polyp of the bladder is mainly performed using an operating cystoscope under general anesthesia. In the cystoscope are special, very small, surgical instruments that allow for small operations. It is used when removing polyps diathermocoagulation. On the polyp itself, a loop is applied that heats up to a certain temperature and removes the polyp. This operation basically proceeds bloodlessly, because when exposed to a large temperature, blood vessels are simultaneously sealed.