Diverticulum of the bladder
Diverticulum is a protrusion in the bladder, which in appearance looks like a sack. The diverticulum can be of various sizes and communicates with the bladder with a small isthmus.
Types and causes of the diverticulum
There are two types of diverticula: true and false.
True - this is one that is formed due to abnormal development of the urinary organ. A feature of the true diverticulum is that it consists of several layers of muscle tissue, like the bladder itself.
A false diverticulum is a formation that arises from the weakening of the muscles of the bladder. As a result, the muscles diverge, and through them the mucous membrane in the form of an overhanging sac emerges beyond the bladder.
In addition to this, the diverticula of the urinary organ can be both congenital and acquired. Congenital, this is when a person is already born with such an anomaly, and acquired arises in the course of a person's life, when there is an increased pressure inside the bladder. This happens when the patient has sclerosis of the neck of the bladder, stricture of the urethra, as well as prostate adenoma, in a word, such diseases that do not allow the urine to go out normally. As a result, the patient, in order to go to the toilet, is forced to push, and this provokes an increase in pressure in the bladder, which in turn leads to weakening and stretching with the formation of a diverticulum.
Symptoms of the diverticulum
Since the release of urine occurs with the diverticulum, this disease leads to inflammatory processes of an infectious nature, which then degenerate into pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc. The main symptom, which can be suspected diverticulum, is the release of the bladder in two sets. This suggests that first the bladder itself is emptied, and then the diverticulum. Also, the indicator of the diverticulum is haematuria, frequent and painful urination.
Diagnosis
Unfortunately, it's impossible to detect a diverticulum just like that. It can be detected during cystoscopy and ultrasound of the bladder.
Ultrasound examination allows to determine not only the presence of a diverticulum, but also its location and dimensions, as well as their number( may be the emergence of one protrusion, but several).
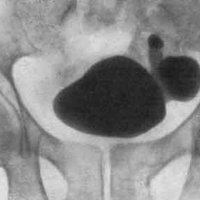
Cystography is carried out as follows. To begin with, a contrast medium( it can be either gaseous or liquid), pre-heated to body temperature, is injected into the bladder cavity.2 minutes after filling, an X-ray is taken, at which two photographs are taken. The first in the supine position, and the second - lying on the back, but after emptying the bladder. This scheme allows you to determine where the diverticulum is located. When emptying a small amount of contrast medium enters the diverticulum, resulting in its shadow is released against the background of the bladder.
By location, the diverticulum of the bladder is mainly localized on the posterior and lateral walls of the bladder, as well as at the mouth of the ureters. At the bottom of the bladder and its apex protrusion is extremely rare.
Complications of the disease
Diverticulum is complicated by the fact that its development can lead to cystitis, stones in the bladder, cystitis, the formation of stones in the diverticulum, pyelonephritis, as well as the rupture of the diverticulum.
Treatment of the disease
There is only one way to treat the diverticulum. For this, a surgical procedure is performed, in which the diverticulum is simply cut off, and the hole in its place is carefully sutured.
There are two ways to remove the diverticulum: extravascular and intravesical.
Extra-chubby removal of
Cut the skin and fat pad and expose the bladder. Then divide the diverticulum from surrounding tissues and cut off, and the formed hole is sewn with knotty seams in two rows.
Intravesical removal of
In this case, the bladder is cut, the diverticul is turned inside the bladder and cut off. The wall of the bladder is sewn with catgut sutures.
In case there is a ureter on the diverticulum, then cut off part of the bladder and diverticulum, and then connect part of the wall with the ureter with the bladder.