Contusion of the elbow joint

The contusion of the elbow joint may result from a shock, squeezing or impact. In this case, isolated damage to the components of the joint itself is possible, but more often one can find a combined one. Sometimes synovial membranes and fibrous capsules of articular cartilage and bone tissue are damaged.
Symptoms of
In case of trauma to pararticular tissue, a necrosis foci, hemorrhage, release of chemically active substances - serotonin, histamine, bradykinin, play a leading role in the pathological process. Recently, more and more interest is caused by the action of prostaglandins Ei and Er, released when soft tissue is damaged. They are able to increase vascular permeability, have the ability to increase pain and increase swelling. In addition, prostaglandins can stimulate the process of collagen biosynthesis, so that scar tissue develops after injury.
There is a high reactivity of the joint, leading even after a small injury to excessive development in the place where there was damage, scar or ossification. The reason for this is the peculiarity of the circulation, as well as the innervation of the joint.
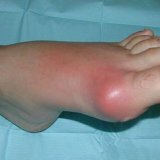
The manifestations of the clinic of a paraarticular tissue injury are expressed by local pain, swelling and bruising. The function of the joint may be impaired due to hemorrhage.
Contusion can often be accompanied by hemarthrosis, which develops as a consequence of hemorrhage with damage to the synovium, as well as a fibrous capsule. Blood, stretching the joint capsule, squeezes, and this disrupts the nutrition of the cartilage and causes the death of some of the chondrocytes. As a result, there is a disruption of the cartilaginous cover, the result of which is deforming arthrosis - the reason for this is the lack of regenerative proliferation of chondrocytes for the recovery process in the damaged site.
Clinical hemarthrosis syndrome initially manifests itself in pain. The articular contours are smoothed, the circle is enlarged. The extremity is forced to assume a bent position at an angle of 120 degrees. Movements, both active and passive, are very painful and difficult. The capsule in the region of the cleft in the humerus arches.
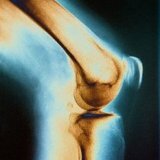
A characteristic symptom of an X-ray is a positive symptom of the posterior and anterior fat pads. In the normal state, they are not visible - the posterior is in the pit of the elbow, and the anterior in the coronary fossa. They seem to amortize the flexion-extensor movements in the joint. If there is an effusion, the fluid pushes the fat pads to the capsule, so they can be seen on the radiograph.
Injury treatment
In case of injury, damage to the cartilaginous tissue of the joint surface, as well as subchondral hemorrhage, is possible. When the compression forces and the rotational component are combined, this can lead to a tangential detachment of certain parts of the cartilage that form the intraarticular bodies. The main symptom is hemarthrosis.
In this situation, the puncture is considered both therapeutic and diagnostic. It is carried out along the posterior surface, passing through a gap located between the head elevation and the head of the radius bone. The point located in the very center of the triangle formed by the tip of the outer shoulder epicondyle and the middle of the head of the radius, as well as the tip of the ulnar process, and is considered the place for the puncture.
The patient sits while the puncture is sitting, and the sore arm in the elbow joint is bent to 90 degrees, the brush rests against the table. The implementation of this procedure is facilitated by the position of the limb, as it contributes to a larger expansion of the gap.
In the presence of hemarthrosis, the blood is removed, the joint cavity is rinsed with a solution of novocaine, and corticosteroids are administered. To ensure complete rest, a soft bandage is applied on the limbs. Corticosteroids reduce edema of the synovium, stop the development of fibroblasts, stop pain. Since the first day, active movement of the fingers of the bone is recommended, due to which edema and hemorrhage dissolve.
For any bruises and hemarthrosis of the elbow joint, Indomethacin is prescribed, which has analgesic and anti-edematous effects, it is also capable of blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins. Indomethacin compresses are applied daily until the acute events subsided.