Syndrome of prolonged compression: first aid to the patient

The syndrome of prolonged compression( traumatic anuria, Byuothers syndrome, traumatic rhabdomyolysis) is a pathological condition associated with the restoration of blood circulation in tissues that have been deprived of it for a long time.There is a VTS at extraction of victims from under blockages where they get during earthquakes, technogenic accidents, acts of terrorism.A variety of this pathology is the syndrome of positional compression, which arises in the limbs of people, which for a long time remain immobile( coma, alcohol intoxication).In this case, the compression of the limbs occurs under the mass of the patient's own body.
Table of Contents: Causes of Crush Syndrome Types of Long-Compression Syndrome What Happens in the Body with Crash Syndrome Symptoms of Crush Syndrome Diagnosis First Aid for Long-Compression Syndrome ComplicationsCauses of Crash Syndrome
 Most often people suffer fromCrash syndrome in the regions where fighting is being conducted, during earthquakes, in car accidents.In recent years, terrorism is becoming increasingly important as a cause of the SDS, in which explosions of buildings can lead to the fall of victims under the rubble.
Most often people suffer fromCrash syndrome in the regions where fighting is being conducted, during earthquakes, in car accidents.In recent years, terrorism is becoming increasingly important as a cause of the SDS, in which explosions of buildings can lead to the fall of victims under the rubble.
In all these cases, except for car accidents, there are situations with a large number of people who have been injured in medical institutions.Therefore, it is especially important to quickly identify the development of VTS and begin treatment at the pre-hospital stage.
Types of this pathological condition are classified according to several criteria:
- by its compression type it is divided into crushing( traumatic muscle damage), direct and positional compression;
- for localization - thoracic, abdominal, pelvic area, hand, forearm, hip, lower leg, stop in various combinations;
- in combination with damage to other parts of the body:
- internal organs;
- bones, joints;
- of the main vessels, nerve trunks;
- presence of complications;
- severity;
- combination with other types of injury:
- burns or frostbites;
- radiation sickness;
- poisonings, etc.
What happens in the body with a crash syndrome
The basis of this pathology is the mass death of muscle cells. There are several reasons for this process:
- their immediate destruction by a traumatic factor;
- termination of blood supply to the squeezed muscle;
- cellular hypoxia associated with hemorrhagic shock, often accompanying massive trauma.
While the muscle is compressed - there is no crash syndrome.It begins after the clamped part of the body is released from external pressure.In this case, the transmitted blood vessels are opened, and the blood, saturated with the products of the decomposition of muscle cells, rushes into the mainstream.Having reached the kidneys, myoglobin( the main muscle protein) clogs the microscopic kidney tubules, blocking the production of urine.Within a few hours tubular necrosis and death of the kidneys develop.The result of these processes is acute renal failure.
Symptoms of crash syndrome
The course of the disease directly depends on the duration of compression, and on the volume of affected tissues.So, if the forearm is squeezed for 2-3 hours, acute renal failure will not occur, although a decrease in urine production is still noted.There are no intoxication phenomena, inevitable with longer compression.Such patients almost always recover without consequences.

Extensive compression, lasting up to 6 hours, leads to a crash-syndrome of moderate severity.In this case, there are bright phenomena of endotoxicosis( intoxication) and violations of kidney functions for a week or more.The prognosis depends on the timing of first aid and the timeliness and volume of subsequent intensive care.
With more than 6 hours of compression, SDS develops in severe form.Endotoxicosis is rapidly increasing, the kidneys are turned off completely.Without hemodialysis and powerful intensive therapy, a person inevitably dies.
Symptomatic of crash syndrome depends on the period of development of pathology.
In the early period( 1-3 days), mostly there are symptoms of shock: pallor, weakness, tachycardia, low blood pressure.The most dangerous moment in this period is the immediate extraction of the victim from the debris.Once the blood circulation in the affected limb is restored, a large amount of potassium is released into the blood, which can lead to an instantaneous cardiac arrest.But even without this, with severe forms of SDS, already in the first day, the phenomena of renal and hepatic insufficiency and pulmonary edema develop, as well as cardiac arrhythmias.
For the early period, local manifestations of the affected limbs are typical:
- skin condition - tense( due to interstitial edema), pale, cyanotic, cold to the touch;
- on the skin there are bubbles;
- pulse on the peripheral arteries is absent;
- all forms of sensitivity are either depressed or absent;
- ability to actively move the affected limb reduced or absent.
More than half of the injured patients are also diagnosed with fractures of the corresponding bones.
In the interim period( 4-20 days), intoxication phenomena and acute renal failure come first.At first, the patient's condition stabilizes for a short period of time, but then starts to deteriorate rapidly, there are disturbances of consciousness down to deep stunning.Urine becomes brown, its amount drops to zero, and this condition can last up to 3 weeks.With a favorable course of the disease, this phase passes into the phase of polyuria, in which the amount of urine released increases sharply.It is during the interim period that most often infectious complications develop, prone to generalization( spread throughout the body), and also the appearance of pulmonary edema.
If during the interim period the patient did not die, then the third period comes - late.It lasts from 3-4 weeks to several months.At this time, the functions of all affected organs are gradually normalized - lungs, liver and, most importantly, kidneys.
Diagnosis
It is possible to suspect the development of the long-term compression syndrome at the scene of the accident.Information about the natural disaster, the long stay of a man under the rubble, suggests that he may develop a VTS.Objective data allows you to diagnose crash syndrome with a fairly high degree of certainty.
Under laboratory conditions, it is possible to obtain information on hemoconcentration( blood thickening), electrolyte disturbances, increase in glucose, creatinine, urea, bilirubin.A biochemical blood test reveals an increase in hepatic transaminases, a decrease in protein concentration.Analysis of the acid-base state of the blood shows the presence of acidosis.
In the analysis of urine, there are no changes at first, but then the urine acquires a brown color, its density rises, a protein appears in it, the pH shifts to the acid side.When a microscopic examination reveals a large number of cylinders, erythrocytes, leukocytes.
First aid for long-term compression syndrome and its treatment
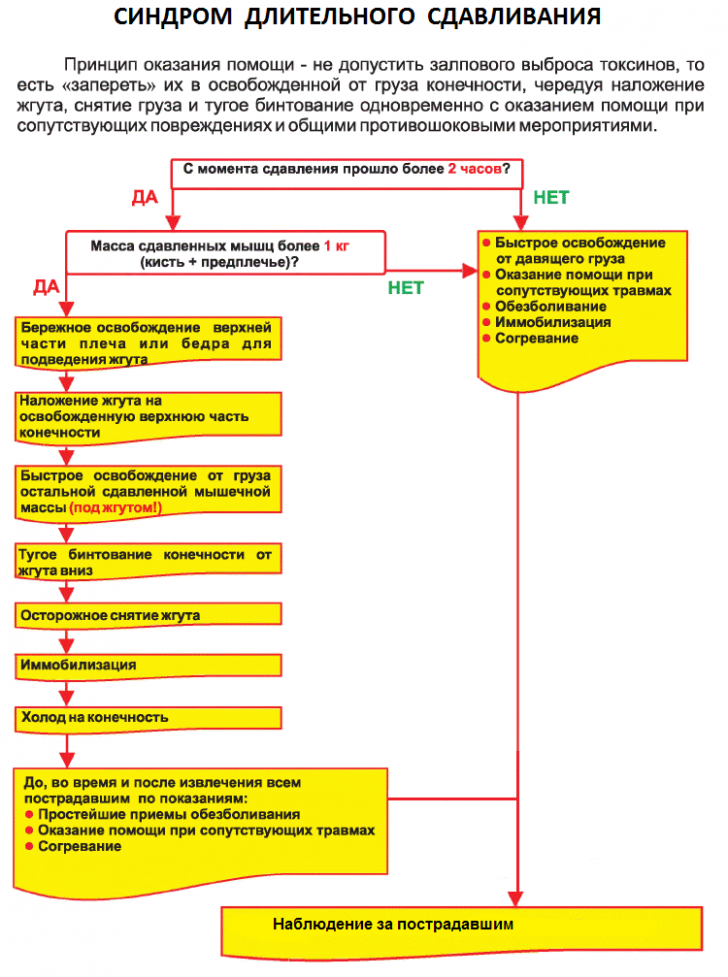
First aid measures for long-term compression syndrome depend on who provides them, as well as on the availability of the forces involved and the availability of qualified personnel.An untrained person can do little to prevent the development of serious complications, whereas professional rescuers by their actions seriously improve the prognosis for the patient.
First of all, the extracted from under should be moved to a safe place.Identified at a superficial examination of the wound, abrasions should be covered with aseptic bandages.If bleeding occurs, measures should be taken to stop it as soon as possible, and fractures are immobilized with special tires or improvised means.If the beginning of intravenous infusion is not possible at this stage, the patient must be provided with an abundant drink.These measures can be performed by any person participating in rescue operations.
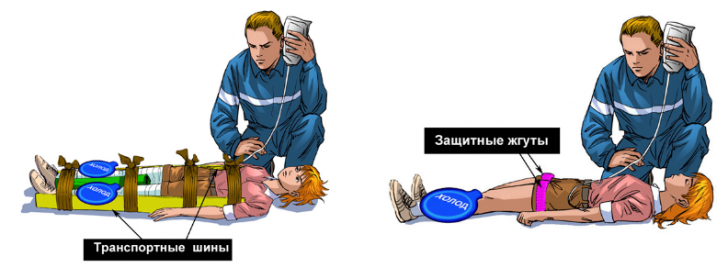
The question of imposing a tourniquet on the affected limb is currently being debated.Practice, however, shows the effect of this method when it is correctly applied.It is desirable to apply the tourniquet even before the victim is released, the place of application is above the site of compression.The tourniquet helps prevent the influence of large doses of potassium, which simultaneously reach the heart muscle and lead to the development of collapse and fatal cardiac arrhythmias. It is recommended to leave it for a long time only in two cases:
- with complete destruction of the limb;
- with gangrene.
The next stage is assisted by trained people - rescuers, paramedics, nurses.At this stage, the victim is required to install an intravenous catheter( although it is ideal to do this before liberation from the debris), by which infusion of saline blood-substituting solutions without potassium is started.Infusion therapy should last as long as possible, it is advisable not to interrupt it even when the victim is evacuated to a medical institution.Adequate anesthesia is mandatory.If the help is provided by a specialist, he can use narcotic analgesics( promedol), if not - the use of any painkiller like baralgina or ketorolac will be better than giving up analgesia.At this stage, you can cut clothes with the expressed swelling of the affected limb.
In parallel, intravenous sodium chloride solution for correction of acidosis, calcium chloride to neutralize excess potassium, glucocorticoids to stabilize cell membranes is administered intravenously.
In an inpatient setting, measures are being taken to stimulate the kidneys - the introduction of diuretics in parallel with the infusions of saline solutions and sodium hydrogen carbonate.It is possible to apply blood purification methods, with preference given to the most sparing of them - hemosorption, plasmapheresis.They should be used cautiously and only in case of an obvious onset of pulmonary edema or uremia.
Antibiotic therapy is used only with obvious signs of wound infection.Heparin prophylaxis helps prevent the development of DIC syndrome, an especially severe complication of VTS.
Surgical treatment of the syndrome of prolonged compression is the amputation of a non-viable limb.At the expressed edema leading to squeezing of the main vessels operation of fasciotomy in a combination to gypsum immobilization is shown.
Complications
The main complication of the crash syndrome is acute renal failure.It is the main cause of death in this pathology.
Pulmonary edema is a life-threatening condition in which pulmonary tissue is impregnated with a fluid emerging from blood vessels.This worsens gas exchange in the alveoli, increasing hypoxia.
Hemorrhagic shock due to massive blood loss is observed when large vessels are damaged.The situation is worsened by the fact that the ability of tissues to withstand the damaging effects of external factors is sharply reduced in the affected area.
DIC-syndrome develops as a consequence of bleeding, as well as due to direct damage to blood vessels by products of decay of affected tissues.This is the most severe complication of VTS with a high mortality rate.
Infectious-septic complications often accompany crash syndrome.Due to the reduced viability of tissues, the damage zone is easily affected by microorganisms, especially anaerobic ones.The result is severe diseases that worsen the course of the underlying pathology.
With crash syndrome, it is important to start the care.The earlier the victim is removed from the rubble, the fuller the volume of activities will be, the more likely he will have a chance to survive.
Bozbey Gennady Andreevich, ambulance doctor