Varikotsele: clinic, treatment, diagnostics
 Varicocele is a disease that causes the veins of the spermatic cord to expand. Often this disease affects children aged 14-15 years. Almost 50% of patients with varicocele are aggravated by a violation of the spermatogenic function of the testicles. In thirty percent of men, the cause of infertility is often varicocele. In the article "Varikotsele: Clinic, Treatment, Diagnosis," we will take a closer look at the peculiarities of this ailment.
Varicocele is a disease that causes the veins of the spermatic cord to expand. Often this disease affects children aged 14-15 years. Almost 50% of patients with varicocele are aggravated by a violation of the spermatogenic function of the testicles. In thirty percent of men, the cause of infertility is often varicocele. In the article "Varikotsele: Clinic, Treatment, Diagnosis," we will take a closer look at the peculiarities of this ailment.
Varicocele: pathogenesis and etiology.
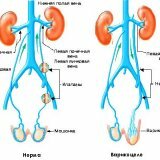
The cause of varicocele development is often the congenital absence of the valves of the testicular vein or their insufficiency. Increased retrograde blood flow down the testicle vein leads to an expansion and abundant development of the veins of the clustate plexus.
The cause of varicocele development can also be the entry of the internal spermatic vein( left) at a right angle into the renal vein( also correspondingly to the left vein).This, in its turn, on the left side complicates blood circulation, this is the reason for the higher incidence of spermatic cord vein enlargement on the left side.
Varicocele: classification.
The classification of this disease is based on changes in the trophism of the testicle and the severity of the enlargement of the veins of the clustate plexus:
- , the first stage of the disease - varicose veins are only palpable when the patient is strained vertically;
- the second stage of the disease - enlarged veins are determined visually, the consistency and dimensions of the testicle are not changed;
- the third stage of the disease is an increase in the veins of the clustellar plexus, a change in the consistency of the testicle, a decrease in size.
The severity and essence of such a clinical form determine not so much the severity of the enlarged veins of the spermatic cord, as the advancing failures of spermatogenesis. The dependence of the degree of failure of spermatogenesis on the duration of the carcocoelus, as well as the reversibility of spermatogenesis malfunction after surgical intervention, was observed.
Varicocele: clinic.
The initial stage of varicocele is revealed during medical examination of pre-conscripts, or during regular check-ups.
With varicocele, young people note: the lowering of the half of the scrotum on the left, the increase, pulling minor pain in the testicles, inguinal region and scrotum on the side of the lesion. When physical activity and walking, with sexual arousal, minor pain intensifies.
A significant varicocele leads to a scrotal scrotal that interferes with walking, except that the left testicle decreases. The enlargement of the left scrotum often occurs in the vertical position of the body, but disappears in the prone position.
If the disease starts, then the pain will become permanent. The scrotum will increase significantly, the left testicle will decrease, and contouring of the convoluted veins will occur. Referring to a doctor, young people often talk about infertility.
Varicocele: diagnosis.
During a clinical examination, the physician draws attention to the enlargement of the veins of the clustelliform plexus of the left scrotum, or from both sides. Nodularly enlarged veins of the clustate plexus are determined by palpation, the same method determines the consistency and size of the testicles.
Varicocele is characterized by permanent or orthostatic filling of veins. With this disease, a special laboratory examination is carried out, including ejaculate( the analysis is taken only in adults) for dynamic observation.
Reduction of motor function of spermatozoa is often the only manifestation of malfunction of spermatogenesis.
Subclinical varicocele forms( in preschool and early school children) are diagnosed with Doppler ultrasound.
Varicocele: treatment.
Surgery is by far the most effective treatment. Although the initial stage of the disease can do without surgery, nevertheless, with pain in the testicle, aesthetic defects of the scrotum and diagnosed male infertility surgery is simply necessary. Often, varicocele, especially in adolescents and children, surgery is seen as a preventive measure of infertility.
Currently, there are 4 types of operations performed with varicocele:
- Operation from the minidisc;
- Open( normal) operation;
- Microsurgical testicular revascularization;
- Endoscopic operation.
Operation from a mini-access( Marmar ).
This operation is based on a small incision in the projection of the outer ring of the inguinal canal( this is where the spermatic cord comes out) at a distance of one centimeter from the base of the penis. Then, after dissection, the surgeon bandages the veins of the spermatic cord. After this, the outflow of blood from the testicles is due to a network of superficial veins.
Open operation( conducted according to Ivanissevich).
The operation consists of an isolated dressing of testicular veins. The dressing is performed above the inner circumference of the inguinal canal. In the iliac region an incision is made, after the surgeon has cut the skin and subcutaneous tissue, it produces a cut of the tendon layer and the muscle layer. The operation is completed by vein ligation.
Endoscopic operation.
This type of operation has been a success for more than one year. Moreover, it is used to treat a variety of diseases. The effect was observed in the treatment of varicocele.
Operation is performed through 3 punctures, each with 5 mm each.
One puncture is done in the navel area, then a tiny camera is connected through it, connected to a video monitor, thanks to which the surgeon can observe the operation and see everything that is done in the operative zone with an increase up to 10 times and excellent illumination.
Two other punctures are necessary for the insertion of miniature clips and scissors, which are necessary to distinguish the artery and vein of the testicle from under the peritoneum. Further, the vascular bundle elements are carefully selected by the surgeon. Then veins of the testicle are tied with a surgical thread or special titanium brackets are applied. The operation lasts no more than 30 minutes.
Microsurgical testicular revascularization.
The operation is based on restoration through the testicle vein from a testicle of normal outflow of blood. During the operation, the testicular vein is transplanted into the epigastric.