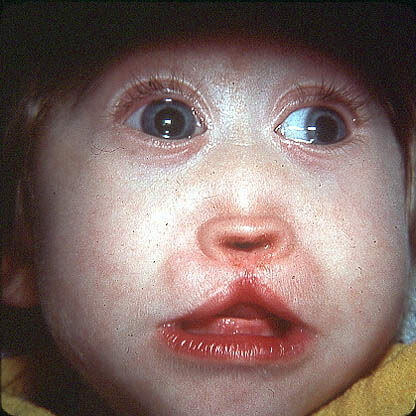
Congenital heart defect
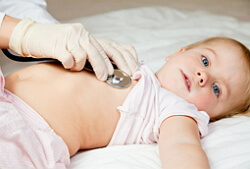 Congenital heart disease is a heart defect of an innate origin. Basically, this pathology affects the septa of the heart, affects the artery, which delivers to the lungs venous blood or one of the main vessels of the arterial system - the aorta, as well as the growth of the Botallov duct( OAP).With congenital heart disease, the movement of blood in the large circle of blood circulation( BPC) and small( ICC) is disrupted.
Congenital heart disease is a heart defect of an innate origin. Basically, this pathology affects the septa of the heart, affects the artery, which delivers to the lungs venous blood or one of the main vessels of the arterial system - the aorta, as well as the growth of the Botallov duct( OAP).With congenital heart disease, the movement of blood in the large circle of blood circulation( BPC) and small( ICC) is disrupted.
Heart defects are a term that unites certain heart diseases, the main preference of which is a change in the anatomical structure of the heart valve apparatus or its largest vessels, as well as the growth of the partitions between the atria or ventricles of the heart.
Congenital heart disease causes
The main causes of congenital heart disease are disorders from the chromosomes - it is almost 5%;Mutation of the gene( 2-3%);Various factors, such as alcoholism and drug addiction of parents;Infectious diseases in the first third of pregnancy( rubella, hepatitis), medication( 1-2%), and hereditary predisposition( 90%).
With various distortions of chromosomes, their mutations appear in a quantitative and structural form. If aberrations of chromosomes of large or medium size occur, this mainly leads to a lethal outcome. But when distortions occur with compatibility for life, it is then that there are various kinds of congenital diseases. When a third chromosome appears in the chromosome set, defects occur between the valves of the valves of the atrial and ventricular septa or a combination of them.
Congenital heart disease with changes in sex chromosomes are much less common than with trisomy autosomes.
Mutations of one gene lead not only to congenital heart disease, but also to the development of anomalies of other organs. The developmental defects of CVS( cardiovascular system) are associated with the syndrome of autosomal dominant type and autosomal recessive. For these syndromes is characterized by a pattern of damage to the system in a light or heavy degree of severity.
Various environmental factors that damage the cardiovascular system can contribute to the formation of congenital heart disease. Among them, one can identify X-ray radiation, which a woman could get during the first half of pregnancy;Radiation by ionized particles;Some types of medicines;Infectious diseases and viral infections;Alcohol, drugs, etc. Therefore, heart diseases that were formed under the influence of these factors, received the name of embryopathy.
Under the influence of alcohol, most commonly formed VSD( defect of the interventricular septum), OAP( open arterial duct), pathology of the interatrial septum. For example, anticonvulsant drugs lead to the development of stenosis of the pulmonary artery and aorta, coarctation of the aorta, OAP.
Ethyl alcohol is on the first place among toxic substances, which contributes to the occurrence of congenital heart defects. A child born under the influence of alcohol will have an embryophytic alcohol syndrome. Mothers who suffer from alcoholism give life to almost 40% of children with congenital heart disease. Alcohol is especially dangerous in the first third of pregnancy - this is one of the most critical periods of fetal development.
It is very dangerous for a child's future to have the fact that a pregnant woman has had rubella. This disease causes a number of pathologies. And the congenital pathology of the heart is no exception. The incidence of congenital heart disease after rubella is from 1 to 2.4%.Among the heart defects, the most common are found in practice: OAA, AVK, tetralogy of Fallot, DMZHP, stenosis of the pulmonary artery.
These experiments indicate that almost all congenital heart defects are fundamentally of genetic origin, which is consistent with multifactorial inheritance. Of course, there is heterozygosity of a genetic nature and some forms of UPU are associated with mutations of one gene.
In addition to the etiological factors, the causes of congenital heart disease, there is also a risk group, in which women fall into age;Having violations of the endocrine system;With toxicoses of the first three months of pregnancy;Who have stillborn babies in history, as well as already existing children with congenital heart disease.
Congenital heart disease
symptomsThe clinical picture of congenital heart disease is characterized by features of the structure of the defect, the process of recovery and the complications arising from a variety of etiologies. First of all, symptoms of congenital heart disease include shortness of breath, which occurs against a background of low physical exertion, increased heart rate, periodic weakness, pallor or cyanosis of the face, pain in the heart, swelling and fainting.
Congenital heart diseases can occur at regular intervals, and therefore three main phases are distinguished.
In the primary phase, adaptive, the patient's body tries to adapt to disorders in the circulatory system, which are caused by a developmental defect. As a result, the symptoms of the manifestation of the disease are usually not very pronounced. But during a severe violation of hemodynamics, cardiac decompensation develops rapidly. If patients with congenital heart disease do not die during the first phase of the disease, then after about 2-3 years, there are improvements in the state of health and their development.
In the second phase, relative compensation and improvement of general condition are noted. And for the second inevitably comes the third, when all the adaptive capabilities of the organism at the end, develop a dystrophic and degenerative nature of the changes in the heart muscle and various organs. Basically, the terminal phase leads to the death of the patient.
Among the most pronounced symptoms of congenital heart disease are cardiac noise, cyanosis and heart failure.
Noise in the heart of a systolic nature and different intensity is noted for almost all types of malformations. But sometimes they can be absolutely absent or manifest as impermanence. As a rule, noises of the best audibility are localized in the left upper part of the sternum or close to the pulmonary artery. Even a slight increase in the shape of the heart makes it possible to listen to cardiac noise.
During stenosis of the pulmonary artery and TMS( transposition of the main vessels) cyanosis is sharply manifested. And with other types of malformation, it may be completely absent or small. Cyanosis sometimes has a permanent character or appears during crying, crying, that is, with a periodicity. This symptom may be accompanied by a change in the terminal phalanges of the fingers and nails. Sometimes such a symptom is expressed by the pallor of a patient with congenital heart disease.
With certain types of malformations, cardiac dullness can change. And its increase will depend on the localization of changes in the heart. To make an accurate diagnosis, to ascertain the shape of the heart and the heart hump, resort to an X-ray, using both anti- ography and kymography.
With heart failure, spasm of peripheral vessels may develop, which is characterized by blanching, cold extremities and the tip of the nose. Spasm is manifested as an adaptation of the patient's body to heart failure.
Congenital heart disease in newborns
Infants have a fairly large heart, which has significant redundancy. Congenital heart disease is usually formed at 2-8 weeks of pregnancy. The cause of his appearance in the child are various diseases of the mother, infectious and viral;Work of the future mother in harmful production and, of course, hereditary factor.
Approximately 1% of newborns have cardiovascular disorders. Now, it is not difficult to accurately diagnose congenital heart disease at an early stage. Thus, it helps to save the lives of many children, using medical and surgical treatment.
Congenital heart disease is most often diagnosed in male children. And for different defects is characterized by a certain sexual predisposition. For example, OAA and VSD prevail in women, and aortic stenosis, congenital aneurysm, coarctation of the aorta, tetralogy of Fallot and TMA - in men.
One of the most common changes in the heart of children is the non-opening of the septum - this is an anomalous hole. Basically it is VSD, which are located between the upper chambers of the heart. During the entire period of the first year of the baby's life, some minor defects in the partitions may spontaneously close and not adversely affect the child's further development. Well, for major pathologies, surgical intervention is indicated.
The fetal cardiovascular system before birth is a circulation that bypasses the lungs, that is, blood does not flow there, but circulates through the arterial duct. When a child is born, this duct usually closes within a few weeks. But if this does not happen, then the child is put up by the OAU.This creates a certain strain on the heart.
The cause of severe forms of cyanosis in children is the transposition of two large arteries, when the pulmonary artery is connected to the left ventricle, and the aorta to the right ventricle. This is considered a pathology. Without surgical intervention, newborns die right away during the first days of life. In addition, children with severe congenital heart defects rarely have heart attacks.
Characteristic signs of congenital heart disease in children are poorly gained weight, rapid fatigue and pallor of the skin.
Congenital heart disease Treatment of
Congenital heart defects can sometimes have a different clinical picture. Therefore, the methods of treatment and care will largely depend on the severity and complexity of the clinical manifestations of the disease. Basically, when the patient is fully compensated for the blemish, then the way of life is absolutely normal, as in healthy people. As a rule, such patients do not need consultations of doctors. They can be given recommendations, the purpose of which is the ability to hold the defect in a compensatory state.
First of all, a patient suffering from congenital heart disease should be restricted to hard physical labor. That work, which will adversely affect the patient's well-being, is advisable to change to another type of activity.
A person with a history of congenital heart disease should refuse to engage in complex sports and participate in competitions. To reduce the burden on the heart, the patient should sleep for about eight hours.
Proper nutrition should be for life to accompany patients with congenital heart disease. Food should be taken 3 times a day in order that the abundant food does not lead to stress on the cardiovascular system. All food should not contain salt, and when heart failure occurs, salt should not exceed five grams. It should be borne in mind that only cooked foods should be eaten, since they are better suited for digestion and significantly reduce the burden on all digestive organs. Categorically you can not smoke and take alcoholic beverages so as not to provoke a cardiovascular system.
One of the methods of treatment of congenital heart disease is medication, when it is necessary to increase the contractile function of the heart, regulate water-salt metabolism and remove excess fluid from the body, as well as fight the altered rhythms in the heart and improve metabolic processes in the myocardium.
Treatment of congenital heart disease sometimes changes due to the peculiarity and severity of the defect. The patient's age and general health are also taken into account. For example, sometimes children with small forms of heart defects do not need treatment. And in some cases, immediately need to conduct surgical intervention even in infancy.
Almost 25% of children with congenital heart disease need urgent early surgery. To determine the location of the defect and its severity, in the first days of life, children are put a catheter in the heart.
The main operational method for treating congenital heart disease is the method of deep hypertension, in which a strong cold is used. This kind of surgery is done by babies having a heart in size with a walnut. Applying this method to heart operations, the surgeon has the opportunity to perform a complex operation to restore the heart, as a result of his complete relaxation.
At the moment, other radical methods of treatment of congenital heart diseases are widely used. Among them, commissurotomy can be distinguished, where the dissection of intergrown valves and prosthetics is used when the altered mitral or tricuspid atrioventricular valve is removed, and then the valve prosthesis is sutured. After such surgical interventions, especially mitral commissurotomy, the prognosis of surgical treatment is positive.
Basically, patients after operations return to their normal lifestyle, they are able to work. Children do not limit themselves in physical abilities. Nevertheless, all those who have undergone heart surgery should continue to be observed by the attending physician. A vice that has a rheumatic aetiology needs re-prophylaxis.