Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
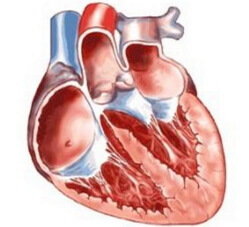 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a disease manifested by congenital pathology in the structure of the heart. This cardiac anomaly is characterized by antesistole of one ventricle, after which a reciprocal atrioventricular tachycardia is formed, which is manifested by flutter and atrial fibrillation, as a result of excitation by additional conducting beams. They are involved in the connection of the ventricles with the atria.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a disease manifested by congenital pathology in the structure of the heart. This cardiac anomaly is characterized by antesistole of one ventricle, after which a reciprocal atrioventricular tachycardia is formed, which is manifested by flutter and atrial fibrillation, as a result of excitation by additional conducting beams. They are involved in the connection of the ventricles with the atria.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in 25% has all the signs of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia. Since 1980, such a pathology of the heart is divided into the syndrome( WPW) and the phenomenon( WPW).The phenomenon is characterized by an electrocardiogram with signs of anterograde behavior, in which atrioventricular reciprocal tachycardia is not manifested at all.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a congenital heart disease in which the pre-excited state of the ventricles is accompanied by symptomatic tachycardia.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome causes
As a rule, this disease has no connecting lines between the structure of the heart and this anomaly, as it develops as a result of hereditary, family pathology.
In many patients, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is formed in other heart defects with a congenital etiology, for example, Ehlers-Danlos and Marfan syndromes( connective tissue dysplasia) or mitral valve prolapse. Sometimes the anomaly of this disease occurs in combination with defects in ventricular and atrial septa, or in patients with a congenital defect of the tetralogy of Fallot.
In addition, there is evidence that Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a consequence of familial cardiac pathologies. Also, the main reasons for the formation of this disease include the pathological development of the cardiac system involved in impulses, with the presence of an additional bundle of Kent. In the formation of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome this bundle performs one of the main functions.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
symptoms This disease is very rare and 70% of patients have any other cardiac pathologies. One of the main symptoms of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is arrhythmia, and tachyarrhythmias appear in most patients with this disease.
The clinical picture of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome basically consists of changes on the ECG in the form of certain ways of carrying out, additional character, between atria and ventricles. In this case it is a bundle of Kent, often found among some additional paths. He is the conductor of impulses, doing it retrograde and anterogado. In patients with this pathology, impulses are transmitted from the atria to the ventricles via the AV node or through additional ways of conducting that bypass this node. Pulses that propagate along additional paths manage to depolarize ventricles much earlier, in contrast to impulses through the AV node. As a result, characteristic changes are recorded on the ECG for the underlying disease in the form of a shortened PR interval associated with the absence of delays before the onset of ventricular excitation;Deformation of the ascending PR R-wave( delta wave) and wide QRS complexes as a result of joining pulses that enter the two paths into the ventricles. The available additional ways of conducting may sometimes not be accompanied by such characteristic changes on the electrocardiogram. This is due to retrograde impulses, which occurs in 25% of cases. Such ways are hidden, because all the signs of premature ventricular excitation are absolutely absent on the ECG.Despite this, they belong to the re-entry chain, which causes tachyarrhythmia.
The manifestation of the clinical picture of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome can occur at any age, but up to a certain time it can be asymptomatic. For this disease, heart rhythms are disturbed in the form of reciprocal tachycardia over the ventricles in 80%, atrial fibrillation in 25% and their flutter about 5% with a heart rate of 280 to 320 per minute.
Sometimes characteristic signs of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are arrhythmias of a specific action - this is ventricular tachycardia and extrasystole, both atria and ventricles. Such attacks of arrhythmias arise mainly from emotional or physical overstrain, taking alcohol or suddenly, for no apparent reason.
During arrhythmic attacks, patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome experience palpitations, cardialgias, cardiac fading, and lack of air. With flutter and atrial fibrillation, patients develop fainting, dizziness with increased blood pressure, dyspnoea, and impaired cerebral circulation. After the transfer of impulses into the ventricles, their fibrillation forms, which can cause sudden death.
In Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, paroxysmal arrhythmias sometimes occur up to several hours and can terminate either independently or after reflex actions. With prolonged attacks, hospitalization of patients and their examination by a cardiologist is necessary. During the course of the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, not only the paroxysmal tachycardia but also the mild systole noise, the strengthening of the first tone and the splitting of the first and second tone are determined.
Virtually all symptoms of this disease in 13% of patients are detected by chance. In thirty percent of cases, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome occurs with many pathologies of the heart. These include primary heart disease, subaortic stenosis, ventricular inversion, endocardial fibroelastosis, coarctation of the aorta, interventricular defect and tetralogy of Fallot.
Patients with a diagnosis of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome are sometimes noted for mental retardation. A shortened P-Q interval, an extended QRS complex directed to the left, forward or backward of the D-wave, the formation of the P j interval is revealed on the ECG for this anomaly. 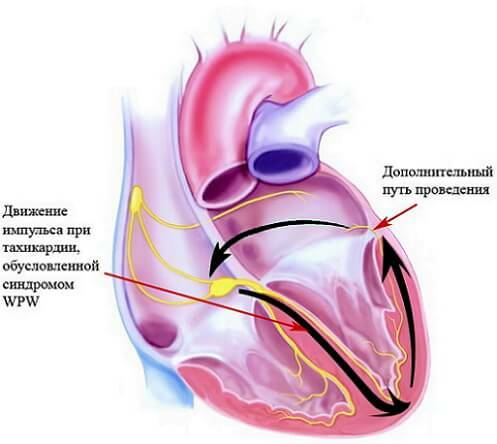
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome treatment
The absence of paroxysmal arrhythmia in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome does not require special treatment methods. A significant hemodynamic attacks, accompanied by signs of heart failure, angina pectoris, syncope and hypotension, require an electrical cardioversion of external action or through the esophagus pacing.
Sometimes Valsalva test and sinus massage are used to arrest arrhythmias, use reflex-vagal maneuvers, and intravenously enter ATP or Verapamil, blocking calcium channels, and prescribe antiarrhythmic drugs such as Novocaineamide, Aimalin, Propafenone and Cordarone. And in the future, such patients are shown lifelong therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs.
To prevent tachycardia attacks in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Amiodarone, Dizopiramid and Sotalol are prescribed to patients. When nadzheludochkovoy paroxysmal tachycardia, against the background of the main pathology, intravenously injected adenosine phosphate. Also, an electrodefibrillation is urgently prescribed in the development of atrial fibrillation. And then the destruction of the conducting paths is recommended.
Indications for surgery for Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome may be frequent attacks of tachyarrhythmias and atrial fibrillations, as well as young age or planned pregnancy, in which prolonged drug therapy is not possible.
With resistance of the body to these drugs and the formation of atrial fibrillation, the catheterization of additional routes by radiofrequency ablation with retrograde access or transseptal is prescribed. The effectiveness of this method of treatment can be achieved in 95% of cases with relapses of 5%.
Radiofrequency intracardiac ablation is currently considered to be the most effective and radical way in the treatment of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. This method of surgical intervention allows in the future to exclude repeated tachyarrhythmias, which are very dangerous for human life. Radiofrequency ablation can be performed without access to the heart. All this is done by a catheter and minimally invasive intervention, which has several types and depends on the principles of the same catheter. It is introduced, as a flexible conductor, through a blood vessel into the pathological cavity of the heart. Then a special frequency pulse is given, destroying exactly those areas in the heart that are responsible for the rhythm disturbance.
As a rule, patients with asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome have a more favorable prognosis. Persons who have a family history with aggravating consequences in the form of a sudden death or professional indications need constant monitoring and then treatment.
With existing complaints or life-threatening arrhythmias, it is necessary to perform diagnostic tests in full complex in order to choose the optimal methods of therapy.
Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome and those who underwent surgery should be observed by a cardiosurgeon and cardiologist-arrhythmologist.
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome requires prevention, which is characterized by antiarrhythmic treatment, in order to further prevent recurrent arrhythmias. Such prevention is mainly secondary.