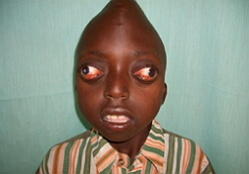
Charcot's disease
 Charcot's disease is a pathological process in which neurons of the central and peripheral CNS are affected. This pathological anomaly has a clinical and genetic heterogeneity, with a fatal outcome. Charcot's disease is one of the diseases called "motor neuron disease"( MND), in which the defeat of motoneurons in the first place.
Charcot's disease is a pathological process in which neurons of the central and peripheral CNS are affected. This pathological anomaly has a clinical and genetic heterogeneity, with a fatal outcome. Charcot's disease is one of the diseases called "motor neuron disease"( MND), in which the defeat of motoneurons in the first place.
This disease is very rare, in a ratio of 1: 100000 patients per year, for which endemic areas are not characteristic.
Charcot's disease is a degenerative pathology that selectively affects central neurons( cortical), and then - periphyric( anterolateral and bulbar).
Sharko's disease causes
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis( Charcot's disease) was discovered as far back as 1847, and the description of clinical symptoms dates back to 1869.But the most active disease of the nervous system began to study in the 90 years of the XX century.
Charcot's disease is considered a family pathology, although cases of a sporadic nature are known that have proved that the main cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is mutations occurring in the superoxide dismutase gene. Most of these mutations were found in 20% of families with this diagnosis, but the role of this gene in sporadic mutations has not yet been determined.
Charcot's disease is one of the most frequent progressive pathologies of motor neurons and is one of the most severe degenerative anomalies of the central nervous system. It is established that women in America and Europe suffer from this disease much less often than men. And cases of family etiology are found in 5-10% of cases, therefore the sporadic picture of the disease is mainly characteristic.
In the development of Charcot's disease, as well as other diseases in which motor neuron lesions are detected, the main cause is also considered infectious-toxic diseases caused by a certain virus that has a large neurotropism. In addition, Charcot's disease develops, as a rule, in 50 years.
Charcot's disease symptoms
One of the most important clinical symptoms of the initial stage of Charcot's disease is muscular atrophy with asymmetric progression. The disease can begin with any muscle group, then the lesion becomes generalized. There are several types of paralysis. These include cervicothoracic, pseudobulbar, bulbar and lumbosacral. The lethal outcome comes a few years after the involvement of the respiratory muscles in the progressive process.
Very often, in almost 40% of cases, a characteristic picture of Charcot's disease is the weakness of the muscles of one of the upper limbs. Defeat begins with a brush, followed by rapid progression of the disease. The patient experiences difficulties in the operation of the index finger and thumb, and also the fine motor control is disturbed. This is manifested in the difficult selection of objects during dressing, especially when buttoning buttons. During the defeat of the main hand, there are problems with writing, as well as in everyday life.
For the typical course of Charcot's disease is characterized by the steady involvement of the remaining muscles of the same limb, and then the lesion passes to the other arm. This precedes the paralysis of the lower extremities and bulbar muscles.
Sometimes Charcot's disease begins to develop with mimic muscles, affects the tongue or, conversely, the muscles of the trunk. Therefore, involving new muscles in the progressing process, the disease is characterized by a short duration of a person's life. This is especially true of the bulbar form, in which patients do not survive to paralysis of the legs. Relatively favorable is the lumbosacral form. Bulbar and pseudobulbar paralysis is manifested by symptoms of dysarthria and dysphagia, followed by respiratory disorders.
All forms of Charko's disease are characterized by an elevated mandibular reflex. Dysphagia is more often observed after swallowing liquid food than after a hard one. Gradually weakened chewing muscles, the soft palate hangs and the tongue atrophies. Patients with such symptoms can not swallow, pronounce sounds, they have generalized seizures.
Muscle atrophy is selective defeat. For example, on the hands - it's the muscles at the base of the thumb and forefinger, the interosseous and deltoid;On the legs - only those muscles that perform flexion from the back of the foot;Bulbar muscles of the palate and tongue.
Very infrequent clinical symptoms of Charcot's disease are the lesions of the eye muscles. In addition, patients with lateral amyotrophic sclerosis, even immobilized, do not have bedsores, which is a special sign of this disease. Also, cases are described where in the process of paralysis, even the upper and lower moths are uniformly involved, under which certain pyramidal or anterolone syndromes predominate.
Charcot's disease treatment
For the main treatment of Charcot's disease it is important to slow the progressing process of the disease and prolong the period at which the patient will retain self-service ability. And also it is necessary to reduce the characteristic expressed symptoms and to support as long as possible the stable level of life of the patient.
Patients are hospitalized if it is necessary to conduct an initial examination, for accurate diagnosis of the disease, or for gastrotherapy.
Currently, only one drug has been developed that significantly slows down the progression of Charcot's disease - this is Riluzole. The use of this drug prolongs the life of patients on average by three months. He is appointed strictly according to the testimony, after confirmation of the diagnosis, but excluding other causes of the defeat of the Mothiners, and if Charcot's disease is characterized by a duration of at least five years, there is no tracheostomy and a forced vital capacity of 60%.Assign Rizul for life for 100 mg per day, with a permanent control of liver transaminases every three months to avoid the attachment of hepatitis drug etiology.
Carrying out pathogenetic treatment of Charcot's disease with the use of Xaliproden, anti-Parkinson's drugs, immunomodulators, antioxidants, Cerebrolysin proved to be ineffective. Therefore, palliative therapy is trying to stop the progression of depression, dysphagia, fasciculations, spasticity and dysarthria. To improve the metabolism of muscles, appoint Carnitine, Levocarnitine, Creatine for two months three times a year. In order to make it easier for patients to walk, doctors recommend wearing only orthopedic shoes, and if necessary using a walking stick and walkers.
The appointment of gastrotomy improves the patient's condition and prolongs his life. But tracheostomy and artificial ventilation of the lungs is the verdict and the last stage of the disease. As a rule, they signal an imminent death.
Prognosis for Charcot's disease is always unfavorable. Lifetime in the lumbosacral form - up to three years, with bulbar - up to four, and mainly with this disease patients do not live more than five years.