Dwarfism
 Dwarfism( nanism, nanosomy, microsomy) is a clinical syndrome characterized by a delay in the physical development of a person( hence the name of the disease: nanism from the Greek is a "dwarf").Allocate proportional dwarfism and disproportionate dwarfism.
Dwarfism( nanism, nanosomy, microsomy) is a clinical syndrome characterized by a delay in the physical development of a person( hence the name of the disease: nanism from the Greek is a "dwarf").Allocate proportional dwarfism and disproportionate dwarfism.
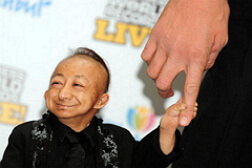
The main reason for the detection of dwarfism is the violation of the pituitary gland pituitary growth hormone( somatotropin, somatotropic hormone, STH).People with this syndrome have a low growth: men do not exceed 130 cm, the growth of women reaches no more than 120 cm. At the same time, dwarfism is found approximately 2 times more often in the male population than in the female population. Occurs disease infrequently: an average of 10 000 people 1-4 cases of dwarfism.
Dwarfism causes
Dwarfism can develop for several reasons:
is a genetic factor. If there are cases of dwarfism in the family, the probability of transferring the dwarfism gene to the next generation is about 50%;
- abnormalities in embryonic development( congenital defects of the pituitary gland, leading to its underdevelopment and abnormal functioning),
develops primordial dwarfism of ;- various tumors located in the central nervous system( chromophobic adenoma of the pituitary gland, craniopharyngioma, glioma);
- head trauma during labor and in the postnatal period, which disrupt blood circulation and the work of the hypothalamus and / or pituitary gland;
- complications during the course of infectious diseases,( syphilis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis), since pathogenic bacteria or viruses can penetrate into the central nervous system;
- autoimmune diseases, leading to the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the pituitary gland and deterioration of the synthesis of somatotropin;
- radiation therapy, chemotherapy;
- surgical intervention in the hypothalamus, pituitary;
- a decrease in the sensitivity of various tissues to the action of growth hormone, although the content of somatotropin in the blood in some cases remains normal;
is a deficiency of somatomedins synthesized in the liver. There is a correlation between somatomedine and somatotropins. Thus, with reduced synthesis of somatomedins, the activity of growth hormone decreases, although the functioning of the pituitary gland is not disturbed;
is a multiple pregnancy;
As for factors contributing to an even greater deterioration in physical development in dwarfism, include: poor patient care, various environmental factors, unbalanced nutrition, simultaneous occurrence of additional somatic diseases.
Despite a decent etiology of dwarfism, more than 60% of cases of this disease remain without explanation.
Dwarfism symptoms
The endocrine system is represented by organs synthesizing and secreting biologically active substances into the blood. This system includes the central and peripheral part. The central organs are represented by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, the composition of the peripheral organs includes the thyroid gland, testes, ovaries, adrenals, etc.
The hypothalamus is responsible for the synthesis of releasing factors that affect the pituitary hormone production responsible for the regulation of internal organs. Such hormones include somatotropin, with the violation of the secretion of which is associated with the appearance of dwarfism in humans.
Compared with other hormones that affect first the peripheral glands of internal secretion( and those already through their hormones ensure the normal functioning of the body), the growth hormone directly affects the development, the work of internal organs, organ systems:
- has a stimulating effect on protein synthesisIn cells, retards the disintegration of protein molecules;
- affects the development, growth of bone tissue, strengthens the mineralization of bones;
- stimulates the synthesis of liver and kidneys of somatidenins;
- when fat burning increases the content in the bloodstream of fatty acids;
- affects carbohydrate metabolism in the body.
The weight and height of newborn children with dwarfism do not differ from these indicators in healthy children. The first signs, indicating the presence of dwarfism in the child, begin to appear in 2-3 years. At this age, the growth begins in a child with dwarfism( adding 3-4 cm annually in growth instead of normal 7-8 cm annually).Nevertheless, children with dwarfism retain normal body proportions.
Growth delay is combined with the appearance of a child with dwarfism:
- the face is small, rounded, protruding forehead, the back of the nose is slightly flattened( the baby looks like a doll);
- dryness, pale skin. Skin thin;
- uneven distribution of subcutaneous fat: a large degree of fat deposits in the area of the mammary glands, abdomen, thighs, pubis;
- mild muscle development;
- underdevelopment of the genitals. In the male with dwarfism, the sex glands are diminished, like the penis, the development of the scrotum is not completed, the secondary sexual characteristics are poorly developed or completely absent. The female does not have menstruation, the mammary glands are underdeveloped, the secondary sexual characteristics( or absent) are practically not expressed. However, in the case of primordial dwarfism( primordial - "primary", "primary", is formed in utero) secondary sexual characteristics are formed in a timely manner, the girls have menstruation( sometimes with delays), people with this kind of dwarfism are able to have sex life, possibly conceiving a child.
is a good memory.
In addition, the symptoms of dwarfism include slowing the process of ossification, dysplastic development, underdevelopment of the genitals, impaired vision in the presence of a tumor in the pituitary gland or surrounding areas of the brain, predisposition to arterial hypotension, early appearance of wrinkled skin and its agingTreatment), lack of secondary hair, late teeth change, splanchnomycria( small size of internal organs), bradycardia, hypotension, muted heart sounds. Possible secondary hypokorticism.
Since under the influence of the pituitary gland are organs of the peripheral endocrine system, with the development of pituitary dwarfism it is possible to disrupt not only the synthesis of growth hormone. Then the clinical picture of the disease is manifold. There are several types of pituitary dwarfism:
- a pure form. It is characterized only by a decrease in the quantitative content of somatotropic hormone in the blood, as well as the absence of the influence of growth hormone on the development of tissues and organs;
- mixed forms. In addition to lack of somatotropin, there is an insufficient content of thyroid hormones, a small amount of sex hormones, which determine the normal development of the reproductive system.
When combined with pituitary dwarfism and thyroid hypothyroidism( hypothyroidism), patients are noted:
- thickening of the skin, cold to the touch. Because of the dryness of the skin, they note their peeling on the palms;
- impregnation of the subcutaneous fat layer with edematous fluid, hence the round shape of the face and narrowing of the eye slits;
- fineness, brittle hair;
- disorders in the cardiovascular system: bradycardia, rare pulse;
- mental retardation( however, this is observed in case of severe thyroid insufficiency).
Sexual underdevelopment( infantilism) against the backdrop of dwarfism is manifested:
- In adolescent boys - the infectious genitals, the small size of the penis, the underdevelopment of the scrotum with the possible undescension of the testicle,( one- or two-sided non-admission), the lack of hair in the axillaryDepressions, faces, pubes. The children's voice is preserved.
- In adolescent girls - small labia, later they never increase, lack of hair in the pubic area, small breasts, lack of menstruation.
Dwarfism treatment
In the diagnosis of dwarfism, attention is drawn to the presence of the corresponding symptomatology: the presence of a lag in growth, starting from 2-3 years, with the preservation of proportional constitution and mental abilities( proportional dwarfism).For the diagnosis of "dwarfism" various laboratory analyzes and instrumental methods of research are used.
Among the laboratory tests, one of the leading positions is occupied by diagnostic tests that are carried out to establish the content in the bloodstream of the growth hormone. The essence of the test is to determine the level of blood hormones after taking a certain type of medicine. The following samples are common: insulin test, sample with clonidine, test with glycine / insulin.
An important place is occupied by X-ray methods for studying the patient's skull, the condition of the Turkish saddle( the location of the pituitary gland).If there are any violations of the Turkish saddle( size, not corresponding to the norm, damage, deformation), then they will be clearly seen on the roentgenogram. A more complete picture will be obtained by computed tomogram( CT) and magnetic resonance imaging( MRI), with the help of which the physician can detect underdeveloped ossification zones in which the so-called ossification points remain throughout life in the event of a congenital disruption of the synthesis of growth hormone.
Successful treatment of dwarfism depends entirely on the cause that caused the disease. In the case of transfer of the dwarfism gene to the child from parents, early recognition of the disease will allow the use of substitution therapy, which will slow the progression of dwarfism.
Pituitary dwarfism caused by brain tumors( lesions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland), due to the hard-to-reach areas of the lesion is harder in terms of treatment. Usually people with this form of dwarfism receive a certain group of disabilities, since low growth and limitations in physical abilities significantly narrow the range of employment areas for such people.
In general, the treatment of dwarfism relies on:
- hormone replacement therapy with the use of somatotropin. It is prescribed at the age of 13-14 years, the effect of growth hormone on the increase in the content of somatidenins in the bloodstream is taken into account. If after a certain period of time the concentration of somatidenins increased, then treatment is considered successful. To simplify the determination of dosage and the administration of hormone, the patient was provided with special syringes-pens for injection of growth hormone injections;
- use of steroid hormones. These hormones, though not complete analogs of somatotropin, but significantly increase the growth and development of skeletal tissue, assist in the development of internal growth hormone. Begin such treatment from 5-7 years, not later than 18 years of age;
- correction of the inferior functioning of sex hormones. Such treatment of dwarfism is prescribed in the adolescent period. Boys are recommended to take Chorionic Gonadotropin within 3 months and Methyltestosterone together with the first drug at its low efficiency. Girls are prescribed estrogens( sex hormones, female) in accordance with the physiological sexual cycle. The latter factor must be taken into account to prevent complications: delay in menstruation or excessive menstrual function. Synestrol( in the first half of the menstrual cycle) and Chorionic gonadotropin( from the second half of the menstrual cycle) are also used;
- diagnosis and appropriate treatment of the underlying disease;
- use of thyroid hormones( with hypothyroidism);
- vascular drugs( in case of CNS disorders);
- the appointment of restorative therapy, vitamin A and vitamin D, various drugs( containing calcium, zinc and phosphorus), diets high in protein and vitamins.
In most cases, people with dwarfism syndrome with proper treatment achieve normal growth. Patients quite successfully adapt to conditions and are able to lead a full life.