Hypertrichosis: how it is inherited, signs of disease, treatment

Hypertrichosis - this is excessive hair.The pathology is manifested by excessive hair growth, atypical for sex, age or a certain area of the body.The congenital form of this disease is more often diagnosed in males, since it can be associated with the sexual Y-chromosome.
Table of contents: Classification Reasons for hypertrichosis Symptoms of hypertrichyosis Methods for treating hypertrichyosisClassification
Clinically, two main forms of pathology are recognized: congenital and acquired.
Disease types:
- heterogeneity( in women with hormonal reconstruction, hairy formation is formed in the male type);
- heterochrony( formerly the appearance of hair as secondary sexual characteristics against the background of endocrine disorders);
- heterotypy( active hair growth in atypical areas).
Species of hypertrichosis:
- gun( congenital or acquired);
- is limited;
- lumbosacral;
- symptomatic;
- medicinal;
- non-tailed.
Note: congenital form is currently considered incurable.

Causes of hypertrichosis
The main cause of the congenital form of the disease is genetic pathology. Mutations lead to a change in the structure of epithelial cells and their transformation into epidermal elements.The cause of the mutations may be infections that were suffered by the expectant mother during the first trimester, as well as the irregular course of pregnancy. The altered gene has a property to be fixed in the genome, therefore the hereditary conditioned hypertrichosis often appears in offspring, including through many generations.
 Important: congenital hypertrichosis is in some cases diagnosed with fetal alcohol syndrome, i.e., is a consequence of intrauterine pathologies of development caused by chronic intoxication.
Important: congenital hypertrichosis is in some cases diagnosed with fetal alcohol syndrome, i.e., is a consequence of intrauterine pathologies of development caused by chronic intoxication.
Symptomatic disease can develop against a background of dermatomyositis, bullous epidermolysis, porphyria, pre-bacterial myxedema, anorexia nervosa, or after suffering craniocerebral injuries of various degrees of severity.
Please note: as one of the reasons for the acquired hypertrichosis, calls insufficient nutritional intake of nutrients.
The most common etiologic factor of the acquired form is the dysfunction of certain endocrine glands .Hypertrichosis is associated with ovarian pathology( for example - polycystosis), pituitary gland, epiphysis, thyroid gland and adrenal cortex.Functional disorders on the part of these organs lead to a pronounced hormonal imbalance.
Changes in the hormonal background that provoke hypertrichosis can develop during puberty, pregnancy and menopause, and also with prolonged drug treatment with corticosteroid drugs or androgens( male sex hormones).
Excessive hair is often caused by disorders of the nervous system.They can be caused by organic pathologies( damage to nerve trunks and neoplasms in the brain), as well as epilepsy and the effects of chronic stress and serious mental trauma.
Among the possible causes of the acquired variety of pathology include breast tumors, metabolic disorders and long-term use of streptomycin in the fight against infections.
It is believed that excessive focal hairs can cause some exogenous factors that increase blood circulation in certain areas of the body.Active hair growth is observed with local use of funds for the treatment of skin diseases( Antipsoriatikum, Psoriazin) and ointments with corticosteroid components.
Note: hypertrichosis can provoke ordinary mustard plasters, especially - with frequent use.
Excessive hair is sometimes caused by physiotherapy( warming up, paraffinotherapy, ozocerite treatment), local massage, cryotherapy( local exposure to low temperatures). Hair can begin to grow more actively against the background of regular shaving( depilation) or skin irritation with an immobilization dressing( gypsum).
Drugs resulting in excess hair:
- antibiotics of the penicillin and cephalosporin series;
- streptomycin;
- hormones-glucocorticoids;
- Diazoxide;
- Minoxidil;
- Psoralen and its analogues( drugs for skin photosensitivity).
Possible etiologic factors of hypertrichosis include chronic dermatitis.
Traumatic variety of pathology often becomes a consequence of the regular pulling of fuzzy hairs on the face.Over time, their growth is activated, and the rods coarsen and become darker.
Signs of hypertrichiosis
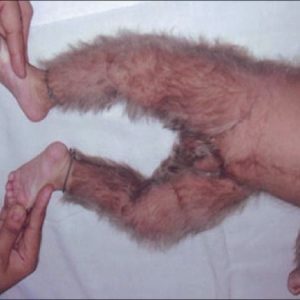 Note: is important in differentiating hypertrichosis and hirsutism.The second disease occurs only in women, and is characterized by excessive growth of so-called."Androgen-dependent" hair.Hirsutism is caused by a pathological increase in the level of male sex hormones and is usually accompanied by a coarsening of the voice, an increase in muscles and the appearance of other signs of masculinization.
Note: is important in differentiating hypertrichosis and hirsutism.The second disease occurs only in women, and is characterized by excessive growth of so-called."Androgen-dependent" hair.Hirsutism is caused by a pathological increase in the level of male sex hormones and is usually accompanied by a coarsening of the voice, an increase in muscles and the appearance of other signs of masculinization.
The main symptom of pathology is the extensive hairiness of those parts of the body where hair is short, rare or even practically absent from the body of .Instead of gun hairs, long and coarser rods with intense pigmentation appear.
The diagnosis takes into account the ethnicity of the patient.In particular, in some South European countries, hair growth in the femur in females is regarded as a variant of the norm.For representatives of Asian ethnic groups, this is pathology.
In congenital cannon-shaped( can be considered as atavism), the embryonic hair is not replaced by terminal and gun hair, but continues to grow further .In newborn boys, they cover the whole body, including the palms.
Note: fused eyebrows - this is also a symptom of hypertrichosis.
In lumbosacral hypertrichosis against a background of spinal dysraphia, a bunch of long soft hair grows in the projection of the affected area( non-extension of the vertebral column with the cleavage of the vertebral arch).
To the limited hypertrichosis is the antero-thoracic form.This is one of the clinical manifestations of neurofibromatosis( progressive hereditary disease).Often the depression of the sternum bone is detected in parallel.
 When the gun type is purchased from bulbous bulbs, embryonic hairs begin to appear.
When the gun type is purchased from bulbous bulbs, embryonic hairs begin to appear.
Important: conducted studies have shown that the pathological "awakening" of hair bulbs is often a distant harbinger of oncology.According to medical statistics, almost 90% of patients with excessive hair follicle subsequently develop malignant tumors.
Non -oidal hypertrichosis is a large birthmark, of which the hair is growing.
Methods for the treatment of hypertrichiosis
 Pathogenetic therapy is effective if it is possible to diagnose and eliminate the etiologic factor;Otherwise - the treatment of hypertrichosis is only symptomatic .When revealing the dysfunction of the endocrine glands, treatment with an endocrinologist is indicated.Women additionally need to consult a gynecologist.With polycystic ovaries resort to hormone therapy.
Pathogenetic therapy is effective if it is possible to diagnose and eliminate the etiologic factor;Otherwise - the treatment of hypertrichosis is only symptomatic .When revealing the dysfunction of the endocrine glands, treatment with an endocrinologist is indicated.Women additionally need to consult a gynecologist.With polycystic ovaries resort to hormone therapy.
The plan of therapeutic measures is made exclusively individually after consultation with specialized specialists.Patients suffering from excessive hair, you need to undergo examination not only in the dermatologist, but also with a neurologist in order to identify possible problems with the nervous system.
From treatment procedures that can increase the intensity of hair growth, as well as from mechanical effects on the skin, it should be kept as far as possible.
With a limited form of hypertrichosis in the absence of hormonal disorders, electrocoagulation( electric shock) of hair follicles is shown. The technique involves exposing each individual follicle to a discharge by means of a deeply inserted thin curved needle.In one session, you can remove up to several dozen hairs if the patient tolerates manipulation well.The total duration of the procedure is usually about half an hour.
 For hypertrichosis, women need about 60 sessions for chin hair removal( this takes about a year).Treatment of the area above the upper lip will take from 3 to 6 months.Repeated procedures will not be required later - this method of treatment is the most radical and reliable.If the patient does not tolerate unpleasant sensations arising from diathermocoagulation, local anesthesia is used.After manipulations, mild hyperemia and swelling of the soft tissues may appear, but they disappear without a trace in the next 24 hours.In order to avoid the emergence of foci of point hyperpigmentation for the duration of treatment, it is strongly recommended to apply sunscreens on the treated areas of the skin.
For hypertrichosis, women need about 60 sessions for chin hair removal( this takes about a year).Treatment of the area above the upper lip will take from 3 to 6 months.Repeated procedures will not be required later - this method of treatment is the most radical and reliable.If the patient does not tolerate unpleasant sensations arising from diathermocoagulation, local anesthesia is used.After manipulations, mild hyperemia and swelling of the soft tissues may appear, but they disappear without a trace in the next 24 hours.In order to avoid the emergence of foci of point hyperpigmentation for the duration of treatment, it is strongly recommended to apply sunscreens on the treated areas of the skin.
Please note: conventional hair removal is ineffective, because the hair grows again and, often, even more intensively.In addition, it can cause irritation of the skin, which provokes dermatitis.To remove hair follicles, it is more appropriate to use a safe, or better, electric shaver.
For aesthetic reasons, many patients are recommended to discolour thick and dark hair with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
If drug hypertrichosis is diagnosed, the replacement of a pharmacological drug with an analogue is mandatory.
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer