Giardiasis: symptoms, treatment
Giardiasis is an intestinal infection caused by a single-celled parasite of lamblia( Lamblia intestinalis), which lives in the human body in the lumen of the small intestine.
Giardiasis is a very common disease. Basically it affects the small intestine. For giardiasis, allergic and neurological symptoms are characteristic, which should be treated by a qualified specialist.
You need to know.
Giardiasis is extremely common among rodents, cattle, dogs and cats. The main source of infection for a person is a person who secretes lamblia cysts. Also, the source of infection can serve as an animal, with which a person often communicates. The lamblias can be carried by flies and domestic insects.
Giardiasis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. The main factors contributing to the transmission of the disease include food, water, hands, soil, cysts infected with lamblia.
For example, in the US, Sweden, Colombia, Egypt and the United Kingdom, there are cases when the transmission factor is ordinary drinking water, which has not been filtered and properly treated at the waterworks. Repeatedly infection with lamblia occurred through the water of open pools and reservoirs. Water flares can occur during accidents at treatment plants. First of all, such outbreaks are dangerous because a huge number of people of all ages are infected.
In children's type institutions, the main cause of transmission of Giardiasis is the dirty hands of children or staff. Another cause of transmission of infection can serve as objects and objects of household conditions, parasite infected with cysts,( toys, pots, door handles, tables, chairs, etc.).
With regard to rural areas, the main factor in the transmission of the disease is soil, fertilized with contaminated feces and polluted by animal and human excrement.
If food workers do not comply with the sanitary-hygienic regime, the transfer factor of giardiasis can be food products. Do not use unwashed table greens, fresh vegetables and fruits because they can be carriers of the lamblia cyst.
Symptoms of Giardiasis.
A person infected with Giardia is susceptible to significant disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. The following symptoms occur in an adult:
- bloating;
- severe abdominal pain;
- stool disorders;
- presence of mucus in the stool.
Symptoms of giardiasis in children are:
- bloating;
- rumbling in the intestines and meteorisms;
- pain in the points of the gallbladder, in the right hypochondrium and slightly above the navel;
- enlargement of the liver.
With lambiosis in children in a period of active growth, the effect of parasites on the assimilation of essential nutrients becomes noticeable. First of all, there is a slowdown in growth and development. The child begins to lose weight and appetite. These symptoms of Giardiasis can also be found in adults. Most often, this manifests itself in the chronic form of the disease or general weakening of the body.
Course of illness .
The most dangerous intestinal infection is giardiasis. Symptoms caused by a unicellular parasite lamblia are very unpleasant. But the main threat of this disease is its adverse effect on the body as a whole. Lamblias literally steal nutrients from a person, sucking digested food in the small intestine.
The incubation period lasts from one to three weeks. In most cases, initially lambliasis is asymptomatic. But then begin to appear meteorisms, unstable stool, severe pain in the abdomen. This form of the disease is characterized as acute and is limited to five to seven days. After the majority of patients the symptoms of the disease disappear spontaneously. This can last from one to four weeks. The chronic course of Giardiasis occurs mainly in pre-school children and manifests itself in the form of constant repetition of the disease.
Lamblias produce metabolic products that are very toxic to the human body. Therefore, during illness, a person may have a bad dream, weakness, irritability.
Treatment of .
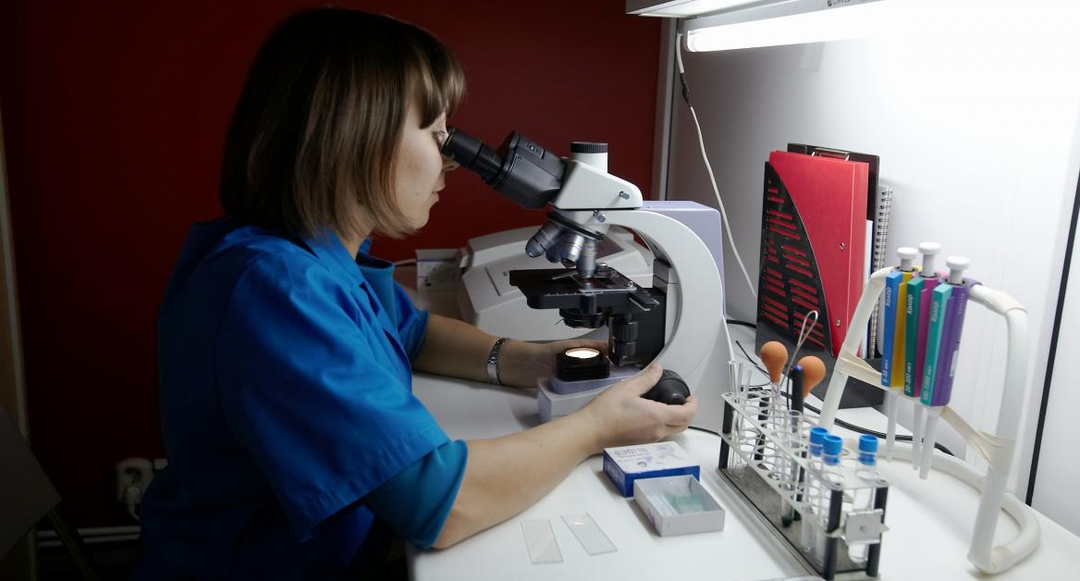
Giardiasis: the symptoms that are needed to treat this disease are very individual. As in the case of a clearly expressed diagnosis of "Giardiasis" and its asymptomatic manifestations, the medical worker takes measures to conduct the necessary specific treatment. Giardiasis is always accompanied by an intestinal disorder, as well as a violation of the liver. In order to timely identify the symptoms of the disease should be a complete laboratory examination of the patient.
Most often, ti-nidazole( fasizhin) and metronidazole( trichopolum) are used to treat giardiasis. Adults should take these drugs three times a day. The daily dosage should not exceed 300-500 mg. The duration of the course is from five to seven days. Preparations are taken after meals. Another patient may be appointed furazolidone. It is taken for five days to 0.4 grams per day. For children, the daily dose of drugs is slightly less, most often it is set individually.
As a rule, the effectiveness of prescription drugs is controlled immediately after the end of their admission and then in four to six months. Detection of lamblia can again say that a second infection has occurred or the disease has become chronic. In the event that the chronic form of the disease is confirmed, special treatment should be carried out, which will make it possible to attenuate the impact of the infection for four to five months. Together with taking medications, it is recommended to perform restorative treatment: take the necessary vitamins, enzyme preparations, as well as cholagogue.
Treatment of Giardiasis takes place solely under the supervision of a specialist in a stationary or outpatient setting.