Age androgen deficiency
Age androgen deficiency ( VAD, male menopause, age-related hypogonadism, PADAM syndrome, ADAM) is a syndrome caused by an age-related decrease in testosterone in the blood.
The following forms of VAD are distinguished:
- Relative VAD - androgen level is within the norm( more than 12 nmol / l).VAD is due to a decrease in the level of androgens relative to previous years.
- Absolute VAD - the level of sex hormones is less than normal values and is less than 12 nmol / l.
Contents of
- 1 Contents of
- 1 Aspect of pathology
- 2 Time of onset of VAD
- 3 Pathogenesis and clinical manifestation of VAD
- 4 Diagnosis of VAD
- 5 Treatment of VAD
- 5.1 Approaches to hormone therapy for VAD
- 5.2 Choice of hormone therapy method
- 6 Should hormone therapy be used in old age?
- 7 Conclusion
Pathology frequency
According to some authors, the incidence of severe androgen deficiency in men over 30 years varies from 7% to 30%.The percentage of patients with VAD strongly depends on the age group to which the man belongs. For example, men aged 40-49 years, suffer from VAD twice as often as men of the age group of 30-39 years.
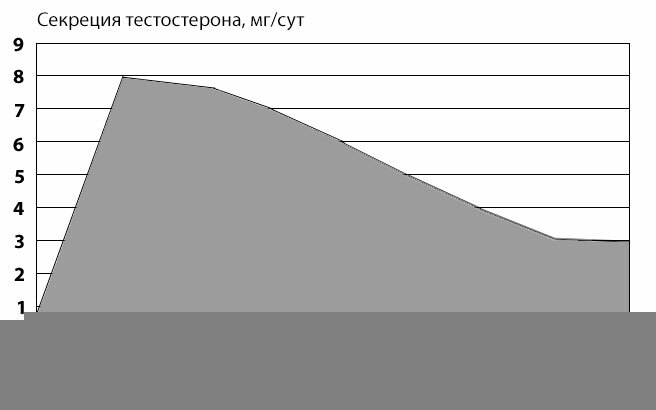
Fig.1 - Age dynamics of testosterone secretion in men.
Timing of the onset of VAD
In men's menopause, unlike women, there is no pronounced decrease in production of androgens, and therefore the age of diagnosis of VAD can vary from 35 to 70 years. Why is such a strong spread? Primarily this is associated with the initial level of the hormone at the age of its peak production( 20-25 years), with the so-called male sexual constitution( Figure 2).
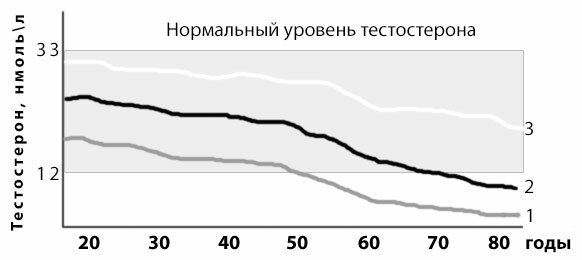
Fig.2 - Individual terms of the onset of age-related androgen deficiency depending on the sexual constitution( testosterone level in 20 years) 1 - a man with a weak sexual constitution, 2 - a man with a middle sexual constitution, 3 - a man with a strong sexual constitution.
Men whose hormone levels are closer to the upper level( 33 nmol / l) have a stronger sexual constitution, and with a decrease in testosterone production( 1% per year after 30 years), they later report symptoms of WAD,and in consequence, can only have a relative form of androgen deficiency.
Men with a low sexual constitution are much quicker to note the effects of natural androgen reduction. Moreover, in such men, the absolute form of age-related hypogonadism is diagnosed more often and earlier.
Thus, in men there is a strong individual indicator of the onset of androgen deficiency, due to its sexual constitution.
In addition to the male's sexual constitution, the following chronic diseases can lead to an early androgen deficiency:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypertension;
- ischemic heart disease;
- hypercholesterolemia.
In men with these chronic diseases, the testosterone level drops by 10-15% compared to healthy men of the same age, which approximates the reduction in the secretion of sex hormones on average by 5-7 years( Figure 3).But at the same time, the decrease in the level of androgens occurs at the same rate as in healthy men.
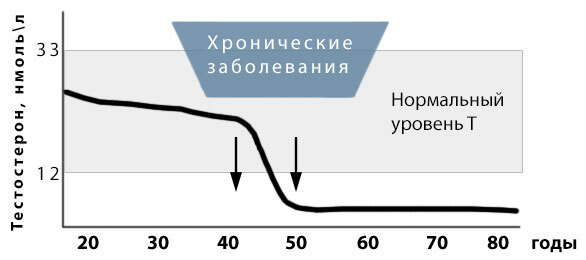
Fig.3 - Influence of chronic diseases on the onset of VAD.
Pathogenesis and clinical manifestation of VAD
The causes of the age-related decline of androgens are:
- decrease in the number of Leydig cells in testicles and responsible for the synthesis of sex hormones;
- decreased receptor density for luteinizing hormone( LH);
- decrease in enzymes of the metabolic pathway of testosterone synthesis;
- dysregulation in the hypothalamus-pituitary system;
- is a genetic predisposition associated with the amount of GAG-repeat in the receptor gene for androgens.
Table 1 - Clinical manifestation of VAD
| organs and systems | Clinical signs |
|---|---|
| Endocrine disorders |
|
| skin, hair |
|
| CNS |
|
| Cardiovascular system |
|
| musculoskeletal system |
|
| Genitourinary system and sexualFunction |
|
Diagnosis WAD
- Anamnesis history. The presence of characteristic complaints for several years, the completion of self-questionnaires of the WAD;
- Physical examination. Diagnosing symptoms of androgen deficiency, such as sagging the skin, losing its elasticity, increasing fat tissue mainly in the upper part of the trunk, reducing the volume of muscle mass and flabbiness of the muscles, gynecomastia, reducing the hair cover on the body and limbs( see Table 1);
- Laboratory diagnostics. The level of total testosterone is less than 12 nmol / l, and the GSPS parameters are increased.
- Instrumental examination. Diagnosis of osteopenia and osteoporosis - a decrease in bone density.
Treatment of VAD
The first attempts to treat androgen deficiency in elderly men were made back in 1940. However, they were not widely spread among doctors, for some reason: first, the drugs of that time did not possess all the effects of natural testosterone, and, moreover, Had significant side effects and toxic effects on the body;Secondly, the prevailing opinion of physicians on the physiological nature of the processes occurring during aging was another reason to refuse substitution therapy.
The emergence of new, more advanced testosterone preparations, as well as new data on the positive effect of androgens and the significant role of androgen deficiency in the aging process of the male body, prompted the interest of physicians and patients in hormonal therapy for men with age-related hypogonadism.
However, despite the acknowledged fact of the need for hormone replacement therapy for VAD, there is still no clear indication of its purpose.
Approaches to hormonal therapy for VAD
Treatment of age-related hypogonadism is aimed at normalizing the serum level of androgens in men. There are two approaches to treatment:
- hormone replacement therapy;
- stimulating therapy with chorionic gonadotropin( HG).
Table 2 - Types of hormone therapy for men
| DEPENDENT THERAPY | STIMULATING THERAPY | |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Can be used in any form of androgen deficiency( primary or secondary hypogonadism) | It is used only in the treatment of secondary forms of hypogonadism when the function of the testicles is maintained. |
| Influence on the synthesis of sex hormones | Exogenous administration of androgens may inhibit the production of its own sex hormones | Stimulation of the synthesis of androgens |
| Effect on spermatogenesis | Reversible inhibition of spermatogenesis during therapy | Does not depress spermatogenesis |
| Effect on testicle size | Reversible decrease in testes during therapy with injection forms of the drug | Does not cause a decrease in testicles during application, moreover, can lead to normalization of the original size reducedX testicles, after application of injection forms of the preparation |
| Preparations |
|
|
Choice of the method of hormonal therapy
As you can see from the table below,2 Substitution and stimulatory therapies have their advantages and disadvantages.
Therapy with drugs HG is a new form of hormone therapy, and has a significant advantage: stimulation of the production of their own sex hormones and spermatogenesis. To identify the possibility of using HG in treatment, an HG test is done: after a three-day injection of the drug at a dose of 1500 units, the patient should have a testosterone increase of at least 50% the next day. The drug has only an injection form. Frequency of injection is 2-3 times a week, starting with 1500 units and conducted in one month courses, followed by a month of interruption.
Substitution therapy is a proven and popular therapy for androgen deficiency. The main advantages of substitution therapy are, firstly, in the variety of forms of drug administration( see hormonal drugs for men), and secondly, in the convenience of therapy( thanks to Nebido injection, the therapeutic effect of which lasts 10-14 weeks), thirdly, Thirdly, substitution therapy will be effective regardless of the causes that caused the low level of androgens.
Do I need to resort to hormone therapy in old age?
Modern medicine has the latest products that meet stringent conditions, as well as extensive experience in their use. Despite this, there are questions about the effect of substitution therapy on some systems of the male body. The biggest controversy is the use of androgens in prostate cancer. Although there is no research proving a clear relationship between the pathological effect of androgens on the prostate, to date, prostate cancer is an absolute contraindication to the use of androgens and stimulant therapy.
On the other hand, there is accurate data on the positive effect of androgens on:
- libido;
- mineralization of bones;
- muscle mass and strength;
- adipose tissue;
- sexual function.
As a result, using androgen therapy, older men can avoid the characteristic diseases for this period and significantly improve the quality of life.
In conclusion
Today, older men have the opportunity to prolong their days of youth and avoid many ailments of old age. Such an opportunity was not with our fathers or grandfathers, but they lived in more "sparing" for health conditions. But no matter how optimistic the predictions of hormonal therapy are, the choice is always the patient.
Source:
Dedov I.I."Age-related androgen deficiency in men."
Recommended for viewing: