Signs and treatment of kidney tuberculosis
Renal tuberculosis is an infectious disease of the kidney( renal parenchyma) tissues with a Kocha rod( microbacteria of tuberculosis).This form of the disease accounts for more than 30% of cases of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. This is a significant figure. In urological and nephrological practice, tuberculous renal disease is considered one of the most difficult to treat. Due to the peculiarities of the structure and circulation of the parenchyma tissues, the process proceeds aggressively and carries a considerable danger to the life and health of the patient.
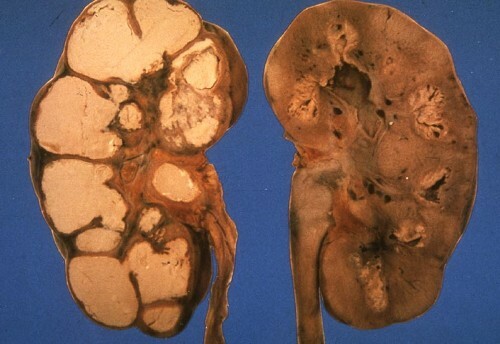
Tuberculosis kidney( nephrotuberculosis) - extrapulmonary infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and affecting renal parenchyma
Content
- 1 Transduction
- 2 clinical picture
- 3 Examinations
- 3.1 Laboratory studies
- 3.2 Instrumental investigations
- 4 Treatment
- 5 Complications
- 6 forecast
Transduction
Hotbed of tuberculosisLesions in the kidney is always secondary. The source of the infection lies in the lungs. It is paradoxical, but not always, patients suffering from the described ailment suffer from pulmonary tuberculosis: the microbacterium affects the lung tissue, however, immunity has time to encapsulate the pathogenic focus in a timely manner. With the blood flow, single bacteria are carried throughout the body. Kidneys:
- Well vascularized( have a rich blood supply).
- Tightly in contact with blood vessels throughout the volume.
- Have a slow blood flow( which is due to the filter function of the paired organ).
The process can then proceed according to one of three schemes:
- A slight inflammation of the cortical layer affected by the kidney process is formed. If the immune response is strong enough, the focus is encapsulated, and for many years does not make itself felt. There is a spontaneous regress of the pathological process.
- Cicatricial changes in the paired organ develop with cell death and decreased kidney function. In this case, the pathology also regresses, but leaves visible damage to the parenchyma and deep tissues.
- There is a melting of tissues( represented by the formation of liquid necrotic masses).In this case, it is difficult to predict the outcome of the disease. Possible complete destruction of anatomical structures or encapsulation of microbacterial focus.
After all this, the question arises: is tuberculosis of the kidneys contagious? Koch's wand is transmitted from the individual to the individual by airborne droplets. Therefore, contact with the patient can lead to infection( in fact, as it turned out, a person is a carrier of pulmonary tuberculosis, although he himself may not get sick).Bacterial pathogen can also go with the current of urine. Therefore, contact with the excrements of the patient is undesirable( especially this applies to medical workers).
Clinical picture
Clinic of the disease depends on the stage of development of the process. In the early stages, when infection has only just occurred in the first few years from the onset of pathology, kidney tuberculosis does not manifest itself and proceeds in a latent form. This is the most favorable time for treatment, but in view of the absence of symptoms, it is extremely difficult to identify an ailment in the early stages.
Over time, the following layers are layered :
- Pain syndrome. It is localized in the lower back, from the side of the location of the affected organ. Has a weak character. As the process worsens, the pain intensifies. In advanced stages of the disease, renal colic occurs due to a spasm of smooth muscles.
- Hematuria. Blood in the urine. It is explained by the destruction of the blood vessels of the kidneys. At developed stages, massive bleeding occurs.
- Isolation of pus with urine. It is observed when the kidneys are destroyed.
- Common symptoms: weakness, drowsiness, malaise, fever to subfebrile-febrile values.
- Renal failure. It is manifested, first of all, by oliguria( a decrease in daily diuresis), skin rashes.
With , the complicated process of is noted:
- Imperative urge to empty the bladder. Are false. Urine either does not go away at all, or comes out drop by drop.
- Increased blood pressure. The so-called malignant hypertension. Develops in response to a violation of the kidneys.
The clinical picture even on the started stages of the disease is not specific enough and masks for other diseases: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, kidney failure, nephritis. A specialist requires a fair amount of attention, so as not to miss such a terrible pathology.
Diagnostic measures
The survey is carried out by nephrologists and urologists. Tuberculosis itself is diagnosed and treated by phthisiatricians. It is extremely important to identify the disease in the early stages: so the forecast is most favorable. Primary consultation is conducted according to a typical scheme: the doctor interrogates the patient for complaints, collects an anamnesis of life. An important role is played by the presence of pulmonary tuberculosis in the patient or his relatives, contact with infected persons. If the patient does not suffer from excess weight, palpation of the kidney is possible. Then he appoints a number of instrumental and laboratory studies.
Laboratory tests
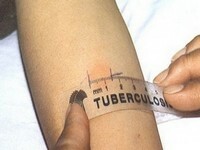
Tuberculin test( Mantoux test)
- Tuberculin test. A universal diagnostic method that has sufficient informativeness.
- General analysis of urine. Gives a classic picture with an increase in the acidity of urine, leukocytosis, high concentration of proteins, pus and blood in the urine.
- PCR diagnostics.
- Bacterial culture of urine. It makes it possible to identify the microbacteria of tuberculosis.
Instrumental Research
- Radiography of the kidneys. It gives an opportunity to see changes in the structure of the paired organ.
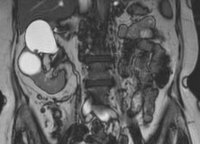
MRI of nephrotuberculosis
- CT / MRI.Provides detailed images of the kidney structures.
- Scintigraphy( radioisotope study).Allows to assess the functional state of the organ.
- Cystoscopy. It is indicated for suspicions of a complicated process.
It is not so difficult to detect tuberculosis of the kidneys. It is important to do it in a timely manner.
Treatment of
Mainly medicamentous. Assignments of the following groups are prescribed:
- Specific anti-tuberculosis drugs: Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Prothionamide and others. The duration of the course of therapy is about a year.
- Fluoroquinolones. Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Preparations for the protection of blood vessels( angioprotectors).
Complications of
Many complications are associated with the descent of infection through the urinary tract:
- Tuberculosis of the genitals. Men suffer from penis, testicles, prostate gland. In women - the uterus, fallopian tubes, appendages.
- Inflammation of ureters, urethra.
In advanced cases, complete purulent melting of the affected kidney tissue is possible with the development of peritonitis, shock.
Forecast
Conditionally favorable for identifying the process in the early stages( when there is no destruction of the kidney structures).If the ailment is "neglected" - the prognosis is much worse. However, it is still favorable. It is unfavorable in the bilateral lesion of the paired organ.
Renal tuberculosis is a complex pathology requiring early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. Otherwise, it is not necessary to count on a favorable outcome. In order not to miss the moment, it is necessary to regularly undergo preventive examinations with a nephrologist and urologist.
Recommended for viewing: