Hypogonadism in men
Hypogonadism is a syndrome in which the development of sex hormones is impaired or observed.
Depending on the level of lesion distinguished:
- Primary( hypergonadotrophic)
hypogonadism Primary( testicular) hypogonadism - arises from testicular tissue lesion that leads to disruption of testicular function as the main body responsible for the production of male sex hormones;
In primary hypogonadism feedback principle, is an increase in levels of gonadotropins( LH, FSH), so it is called hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Secondary
- ( hypogonadotrophic) hypogonadism
Secondary( central, hypothalamic-pituitary) hypogonadism - violation gonadal function occurs due to disturbances of hypothalamo-hypophysial system. In this case, the production of hormones responsible for the synthesis of androgens with testicles is disrupted.
In secondary hypogonadism levels of gonadotropic hormones are reduced, which leads to a decrease in secretion of hormones by the testicles, therefore it is called hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
- normogonadotropic hypogonadism
normogonadotropic hypogonadism( hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism, hyperprolactinemia) - violation of hypothalamic-pituitary function, wherein the level of gonadotropin hormones are normal and prolactin levels increased.
Recently, the following are also singled out:
- Age-related hypogonadism associated with age-related androgen deficiency;
- Hypogonadism, due to obesity.
Depending on the timing of the onset, the following are distinguished:
- Congenital hypogonadism;
- Acquired hypogonadism.
content
- 1 Etiology and pathogenesis
- 2 symptomatology
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 treatment of hypogonadism
- 4.1 Treatment of primary hypogonadism
- 4.2 Treatment secondary hypogonadism:
Etiology and pathogenesis
cause primary hypogonadism may be:
- Congenital underdevelopment gonads( anorchia, monorchism, cryptorchidism);
- Chromosomal pathologies( Klinefelter syndrome, de la Chapelle syndrome, XYY syndrome);
- Injuries, diseases of the testicles;
- Endocrine diseases;
- Infectious Diseases;
- Diseases of the liver, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract;
- Medicaments, radiation, poisoning with poisonous vapors.
reasons secondary hypogonadism may be:
- Hereditary pathology( Kalman syndrome, Laurence-Moon-Bardet-Biedl syndrome, Prader syndrome - Willy);
- Tumor processes;
- Post-traumatic changes;
- Systemic diseases.
Regardless of the causes of the development of pathology, there is a marked decrease in androgens in the patient's blood.
Symptoms Symptoms of hypogonadism is highly dependent on the timing of its occurrence, and therefore emit dopubertatnogo( before puberty boys( 11-12 years)) and post-pubertal hypogonadism form.
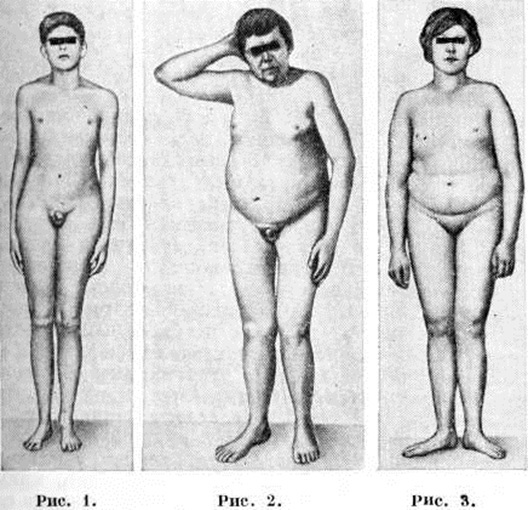
Features of the symptomatology of the adipative form of hypogonadism:
- Eunuchodism( high growth, long limbs, lack of pronounced muscle mass, high voice);
- Absence of secondary sexual characteristics( strengthened scalp on the body and face, presence of muscle mass, low voice, etc.);
- Underdevelopment of the genitals;
- Osteoporosis.
Symptoms of post-pubertal hypogonadism:
- The presence of symptoms of androgen deficiency against the background of normal genital size( see the normal size of the penis and the size of the testicles);
- Main complaints: decreased sexual desire and impaired sexual function.
General symptomatology of hypogonadism, characteristic of the pre-pubertal and post-puertata forms of hypogonadism:
- Decreased muscle mass;
- Hairy pubis by female type;
- The deposition of excess adipose tissue;
- Mood decline, depressive states;
- Violation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism;
- Cognitive impairment( decreased mental capacity and memory, loss of concentration, etc.);
- Vegetative-vascular disorders;
- Reduction of testes.
Diagnosis
General examination includes:
- Definitions of the nature of pubic hair. When expressed hypogonadism in men is characterized by pubic hair in the female type( there is a horizontal line of hair growth);
- Determination of the nature of secondary sexual characteristics( hair and body, the presence of muscle mass, etc.);
- Measures the difference between the width of the shoulders and the pelvis. For measurements, a measuring tape is used, the indications of which are compared to each other - normally the width of the shoulders should be 10-12 cm more than the width of the pelvis;
- Definition of waist circumference and body mass index;
- Assessment of the development of genital organs. Includes measurement of the penis( in the erect and / or relaxed stretched state), palpation and measurement of the testicle volume( ochometer);
- Definitions of the patient's gynecomastia.
Laboratory tests:
- Assay for hormones: testosterone, LH, FSH, prolactin, estradiol, gonadoliberin( GnRH);
- Spermogram.
Treatment of hypogonadism
Regardless of the etiology of the disease, in each case, hormone therapy is prescribed.
Treatment of primary hypogonadism
The only possible treatment is exogenous hormone therapy( Table 1).
Table 1 - Exogenous preparations of testosterone( S. Yu. Kalinchenko, IA Tyuzikov, 2009)
| GROUP PREPARATIONS | CHEMICAL NAME TRADE NAME | DOSAGE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injectables | Testosterone cypionate | Depo-testosterone cypionate | 200-400 mg every 3-4 weeks Testosterone enanthate |
| Delasteril Testosterone depot | 200-400 mg every 2-4 weeks | ||
| Mixture of testosterone esters | Sustanol-250 Omnadren-250 | 250 mg every 2-3 weeks | |
| Testosterone unedecanoate | Nebido | 1000 mg once every 3 months | |
| Oral forms | Fluoxymesterone * | HaloTestin | 5-20 mg daily |
| Methyltestosterone * | Metadrene | 10-30 mg daily | |
| Testosterone undecanoate | Andriol | 120-200 mg daily | |
| Mesterolone *** | Proviron Vistinone Vistimon | 25-75 mg daily | |
| Buccal tablets | Stridant | 30 mg 3 times daily | |
| Subcutaneous forms | Implants | Testosterone implants | 1200 mg every 6 months |
| Transdermal forms | Testosterone gel | Androgel | 25-75-100 mg daily |
| Plasters with testosterone(Scrotal and cutaneous) ** | Androderm Testosterum | 2,5-7,5 mg daily | |
| Testosterone Cream | Andromen | 10-15 mg daily | |
| Dihydrotestosterone gel( DGT gel) | Andractim | Individually |
Notes: * -Hepatotoxicity and in a number of countries are prohibited;** - not registered in Russia;*** - withdrawn from production.
Treatment of secondary hypogonadism:
- therapy with exogenous hormonal drugs;
- stimulating therapy with chorionic gonadotropin( HG).
Stimulating therapy HG is aimed at stimulating the production of its own testosterone and spermatogenesis. Carrying out of stimulating therapy is considered possible, if after a three-day injection of HC in a dose of 1500-2000 ED the level of initial testosterone in the patient is increased by 50-60%.
Preparations HG: Chorionic gonadotropin, Bigagonil, Horagon, Pregnil, Profazi, Ovitrel, Luveris.
| PREGNANCES OF CHRIONAL GONADOTROPINE | |
|---|---|
Gonadotropin chorionic ( 500, 1000, 5000 units per 1 bottle)  | Prophase ( 500, 1000, 2000, 5000 units per 1 bottle)  |
Pregnil ( 100, 500, 1500, 3000 units in 1 bottle)  | Ovitrel * ( 6500 units in 1 bottle)  |
* Not approved for use in men
Recommended for viewing:



