Cavernitis - details of symptoms and treatment of pathology
Cavernitis is an inflammatory disease that involves the defeat of the cavernous( cavernous) bodies of the penis and the formation of painful seals on it.
It is accepted to distinguish between acute and chronic forms of the disease. The chronic form arises from an untreated acute inflammatory process or against the background of an inflammatory process near the cavern.
Content
- 1 reasons
- 2 disease symptoms kavernita
- 2.1 The appearance of the penis when the cavern
- 3 stages of the disease
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Treatment kavernita
- 6 Complications kavernita
reasons
disease causing kavernita is any viral or bacteriological pathogen that enters the cavity and begins to develop, growAnd multiply. The main causes of infection are:
- complication of urethritis specific or nonspecific;
- trauma of the urethral canal with damage to the cavernous bodies;
- surgery interventions involving the cavity of cavernous bodies;
- prolonged urinary catheterization;
- trauma of the penis;
- post-injection process of intracavernous drug administration;
- is a lymphogenic spread of bacteria from chronic foci of inflammation( osteomyelitis, caries, furuncles, carbuncles, sepsis).
Infection penetrates through a piercing and syphilitic route. Fracture cavernitis is characterized by infectious diseases of the urethra with further migration to the cavernous bodies. The syphilitic path implies the presence of foci of infection directly on the penis, without involving the urethra in the process.
Symptoms of cavernitis
The disease begins acutely. Intoxic focal syndrome extends to the entire body:
- increases body temperature;
- a feeling of weakness and weakness;
- man is quickly tired;
- body temperature can reach 38.1-39.0 degrees;
- there is a headache and chills, increased sweating.
Pain local, acute, is of a persistent type of bursting type, sometimes acquires a pulsating hue. It arises from the pressure of pus on the walls of the cavernous body, the irritation of the nerve endings, which is much larger in the penis than in any other organ. Also, the products of vital activity of pathogenic microorganisms( exotoxins) and the decay of non-living bacteria( endotoxin) can become a cause of constant pain. They affect both the nervous system and the vascular wall.
Appearance of penis with cavity
Penis becomes hyperemic( enlarged, swollen).If the cavernous bodies are affected from two sides, then the pus in the cavernous bodies and the blood flowing to the foci of the infection lead to the appearance of a noncontiguous erection. The bulk of pus is not bacteria, but the body's immune bodies. This erection is painful and makes it difficult to urinate, sometimes completely stopping it. After the fall along the cavern, a painful infiltration is felt. If the process is one-sided, then the penis is bent towards the lesion.
The lymphatic system also does not stand aside and reacts to infiltration, as to any other inflammation. The penis becomes edematous, a lymphogenous reaction is observed - the inguinal lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged.
Stages of the disease
The disease develops rapidly:
- After the stage of acute inflammation, an abscess is formed. All external signs are preserved, only the erection subsides. With an abscess in the cavernous bodies, all partitions are destroyed, the erection worsens, in the erect condition, the penis is warped( Peyronie's disease).
- The abscess breaks into the urethra. A man feels relief from the condition, body temperature returns to normal, soreness goes away. When the hearth is opened, the fetid pus exits through the urethra along with the necrotic tissue.
- After natural sanation the affected cavernous bodies are emptied, and during further sex life, the blood does not enter them at all, or in insufficient quantities.
In chronic form of cavernitis, a man may not notice a deterioration in general condition. The disease will respond with dull constant pain, impaired erectile capacity, and during palpation a dense infiltrate is found.
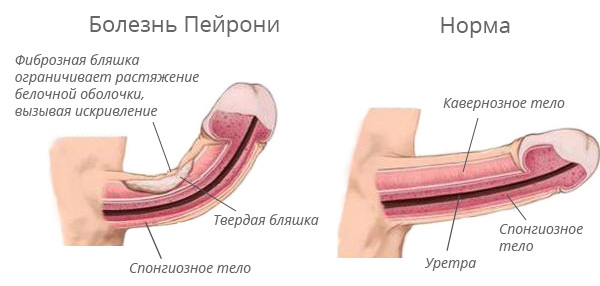
Fig.1 - One of the complications of cavernitis and its signs - Peyronie's disease - the curvature of the penis.
Diagnosis
Painful sensations in the penis - the main reason for prompt treatment of the andrologist or urologist.
The doctor in detail asks about complaints, about early infectious diseases, problems with erectile function, suffered sexually transmitted diseases. After the history is collected, a local examination and palpation is performed, during which a preliminary diagnosis is made. Also, the specialist outlines a scheme for conducting laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Laboratory diagnostics includes:
- blood sampling for general analysis,
- general urine analysis and planting on flora,
- bacteriological scraping from the urethra to bacterial remnants.
- analysis to determine the sensitivity of the environment to an antibiotic for more effective treatment.
Instrumental diagnostics involves carrying out an ultrasound of the penis or radiography of cavernous bodies( urethroscopy, cavernography).These studies will help the doctor to see the stage of the disease, neglect and the presence of complications, as well as confirm the diagnosis and more carefully predict the course of the disease.
If a pathogenic agent from a group of sexually transmitted diseases( gonococcus, pale treponema) is detected in a bacteriological study, then a consultation of the venereologist and a more thorough examination for the presence of other foci are necessary.
Treatment of cavernitis
The main therapy is aimed at sanitizing the body from the source of infection. The doctor prescribes broad-spectrum antibiotics: carbopenems, aminoglycosides, protected penicillins, macrolides, nitrofurans. If the process is sluggish and has signs of chronicization, it is advisable to use tools that stimulate the immune system.
As a symptomatic therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are administered orally and topically in the form of instillations and injections. To improve the overall and emotional state, analgesics in the form of injections or tablets are allowed.
Therapy is carried out for 10-14 days before the disappearance of a dense infiltrate and the above symptoms.
It is also useful local sanation of the bacterial focus by the introduction of antibacterial solutions( hydrocephalus, decasane).
Physiotherapy procedures - magnetotherapy, laser therapy, UHF, electrophoresis - can accelerate recovery and avoid unpleasant consequences.
Complications in the form of curvature of the penis are corrected by plastic surgeries and falloprosthetics.
Forecast of cavernitis treatment is favorable: 95% of acute cavitites are completely cured without transition to complicated forms. Everything depends on properly selected therapy and all the prescriptions of the doctor.
Complications of cavernitis
In severe cases, the lack of necessary treatment will suffer erectile function and male sexual activity. Sclerosed cavernous bodies are not able to perform their functions, so sexual intercourse becomes difficult or impossible. Fibrinous tissue in cavernous bodies results in:
- Peyronie's disease;
- of erectile dysfunction;
- male infertility.
Recommended for viewing: