The main symptoms of femoral hernia and its treatment
In femoral hernia, men develop an abdominal cavity( intestinal loops and peritoneum gland) through the deep femoral ring formed by the ligamentous apparatus( fascia) of the abdomen into a pathologically formed canal( normally there is a gap between the fasciae).
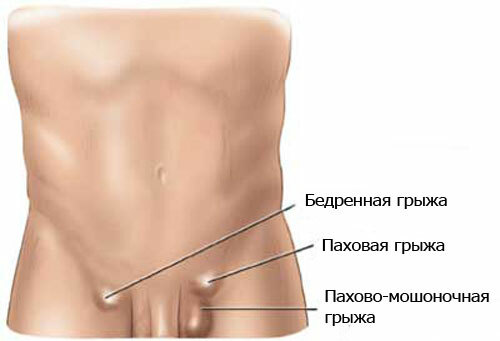
Fig.1 - Hernias of various localizations.
Contents
- 1 Symptoms and causes of
- 2 Symptoms
- 3 Features of treatment
- 4 Forecast
- 5 Prophylaxis
Predisposing factors and causes of
The main causes:
- increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity( with severe weight lifting, tightening with constipation, coughing tension);
- rapid weight loss( with loosening of the ligament apparatus and muscular system);
- damage to nerve fibers( weakness, weight loss and atrophy of muscle tissue, ligaments and fasciae);
- traumatic abdominal wall injuries.
Symptoms of
Clinical manifestations depend on the localization of the lesion and the presence of complications. With bilateral hernias protrusions are formed from two sides, the pain syndrome is more pronounced and can spread throughout the lower abdomen.
Main manifestations:
-
With a hernia, protrusion of the abdominal wall is observed.
discomfort, less often - pain in the upper and inner thigh, lower abdomen, worse with walking, muscle tension, physical activity;
- visible protrusion in the inguinal-femoral area of a small size, with a smooth surface;
- sonorous sound when tapping on the area of protrusion if there are intestinal loops in the hernial sac;
- enhancement of protrusion when coughing and tensing the abdomen;
- when the femoral vein of the femoral vein is compressed, the puffiness of the lower limb on the side of the lesion, the hip skin sensitivity disorder;
- violation of urination when a bladder enters the cavity of the hernial sac.
If the patient has a correctable hernia, then when the horizontal position is taken, the protrusion can disappear, and when the stomach tucks, it can increase. A feature of this pathology is the ease of restoring the contents of the hernial sac into the abdominal cavity. In case of irreversible hernias, complete correction does not occur, while the blood flow and the integrity of the organs in the hernial sac remain intact.
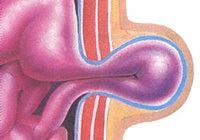
Strangulated hernia is most dangerous due to its complications.
With injured hernias, it is not only impossible to insert the contents into the abdominal cavity, but also damage the tissues of the intestine and peritoneum.
The most dangerous complications of the strangulated femoral hernia:
- necrosis of the intestinal or glandular loops as a result of abrupt discontinuance of nutrition;
- inflammation of the hernial sac;
- peritonitis( inflammation of the peritoneum);
- Acute intestinal obstruction( as a reaction to damage to the gut area).
The strangulated hernia gradually increases in size, sharp pains occur, which are amplified when the affected area is probed, the bowel function is disrupted: constipation occurs and the gas exhaustion worsens.
With inflamed femoral hernia, local signs of inflammation and general body reaction are observed. The area of the femoral hernia swells, the skin over it blush, the pain syndrome sharply increases, the body temperature rises.
With the development of intestinal obstruction, nausea occurs, which is accompanied by vomiting that does not bring relief, hiccough, pain from unexpressed permanent or periodic( with straining, coughing) go into sharp, intense, cramping.
With a large hernia, protrusion is observed not only in the subcutaneous tissue area of the inner thigh, but can also be located in the scrotum. In the latter case, it is important to distinguish the femoral hernia from diseases of the testis and appendages of vascular, inflammatory and tumor origin. For this, it is necessary not only to consult a surgeon, but also a urologist.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of examination and feeling of the area of the lesion, confirmed by the methods of ultrasound diagnosis.
Treatment features
The patient can be cured only by surgical methods. Conservative methods( wearing a bandage with uncomplicated hernias) are used only when contraindications to the operation, the extremely serious condition of the patient, when the risk of interference exceeds the risk of the consequences of the disease.
Operations are divided according to access and technical performance: open and endoscopic. When open, a cut is made of the skin, with endoscopic - 2-3 small incisions for the introduction of endoscopic instruments and surgical instruments. The subsequent stages are identical.
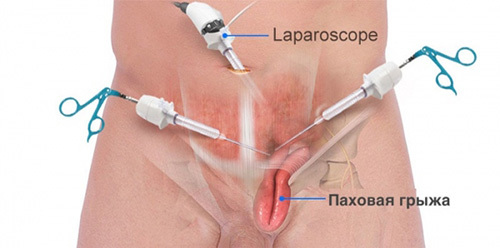
Fig.2 - The principle of carrying out laparoscopic surgery.
Depending on the type of plastic used, the closure of the pathological femoral canal is carried out using the patient's own tissues or a grid of synthetic materials.
The operation is carried out in several stages:
- Incision of skin and underlying tissues, opening of the hernial sac.
- Direction of intestinal tissues, omentum and mesentery in the abdominal cavity.
- Dissection and removal of tissues of the formed hernial sac.
- Plastic surgery of the hernial sac( own tissues or mesh implant).
If an operation is performed for a complicated( strangulated hernia), resection( incision and stitching within healthy tissues) of the intestine loops damaged during infringement is performed.
However, with bilateral lesions, complicated hernias, large sizes and a combination with inguinal hernia, open-access interventions are indicated.
Regarding the different types of plasty of the hernial femoral canal, the advantage of using synthetic nets is the hemming of the implant in front of the peritoneum without stitching the femoral canal lumen. Due to the less traumatic nature of this type of operation, hospital stay decreases( up to 1 day).Stitches for any type of surgery are removed on the 10th day. During the rehabilitation period, the patient is under the supervision of a surgeon of the polyclinic.
Forecast
With uncomplicated femoral hernia the prognosis with timely surgical treatment is favorable. If the patient refrains from surgical intervention, then the probability of an infringement of the hernia exceeds 80%.
Prevention of
The basis of prevention of femoral hernia is maintaining normal intra-abdominal pressure, the absence of traumatization of the muscular and ligament apparatus of the abdominal wall.
Mandatory measures:
- rational nutrition, prevention of constipation and bloating;
- timely treatment of diseases of the digestive system( especially the intestine and pancreas), urinary tract and respiratory system;
- quitting;
- maintenance in the normal tone of the abdominal muscles( regular physical activity).
Recommended for viewing: