Radiation therapy for prostate cancer: mechanism of effects and consequences
Prostate cancer is a malignant transformation of the glandular cells of the organ. During the pathological process, the transformation of cells occurs, their atypia increases. The altered tissues grow into surrounding organs and metastasize, forming foci of secondary lesion. This is an extremely aggressive and dangerous disease, standing at the first positions in frequency of occurrence. One of the methods of treatment is the so-called radiation therapy. What is it and when is it applied?

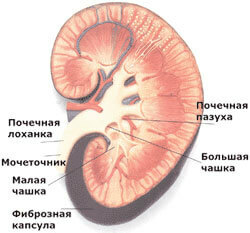
Radiotherapy - one of the methods for treating prostate cancer
Contents of
- 1 Indications for use
- 2 Mechanism of exposure to tissue
- 3 Basic methods and schemes of radiation therapy
- 3.1 Remote impact method
- 3.2 Contact method
- 3.3 Proton technique
- 3.4 Interstitial method
- 4 Consequences of treatment
Indications for use
Unlike many other organs, the prostate has an inhomogeneous structure. Therefore, it is simply impossible to determine the degree of malignant transformation and cancer invasion unequivocally. Even at the early, first stage of prostate cancer, total prostatectomy is shown - removal of the organ. However, the doctor may choose to wait and see tactics. In most cases, radiation therapy is prescribed according to the following indications:
- Preoperative preparation in 2-4 stages of the disease course. At these stages, the size of the cancerous tumor is significant, it is growing rapidly and is characterized by cellular instability. Radiation therapy in combination with chemotherapy is shown to stabilize the size of the tumor and reduce its vascularization.
- Nonoperability of the tumor. In this case, there is simply no alternative to chemo- and radiotherapy. They become the main methods.
- The presence of a well-delineated prostate tumor without invasion and with clear localization. The doctor seeks to maximize the patient's health: after all, prostatectomy is a serious and traumatic operation, destroying sexual health and placing a cross not of fertility. In such a situation, it is definitely worthwhile to try radiotherapy. It is possible that radiosurgery will put an end to the issue of the course of the disease.
- Postoperative period. Treatment is necessary to kill the remaining cancer cells if resection is performed, and not prostate removal.
Read also: Stages of prostate cancer: features of the development of pathology and prognosis
Mechanism of exposure to tissue
Radiation therapy is based on the harmful effects of radiation on tissues and cells of the body. The essence of the treatment consists in irradiating the affected area with high-intensity radiation waves, thanks to which cancer cells die and the tumor begins to disintegrate. At the same time, the more intense the nutrition of the tumor and the better its vascularization, the more lethal the radiation is for this new growth.
Basic methods and schemes of radiotherapy
Method of remote exposure
Comes in the patient's room under a special apparatus resembling an x-ray. The patient lies on a special table, under the radiator. This type of device produces high-intensity radiation. However, it does not act pointwise, but passes through soft tissues, including fatty deposits( in this case, the higher the body weight, the less effective the therapy and the more likely the development of side effects).There are two main methods of remote impact.
In the first case, the patient is placed under the radiator and begins to treat the tumor. This so-called. Stationary method. Both the apparatus and the patient in this case are immobile. Another method is to place the patient on the table. At the same time, the sensor is mobile and irradiates the tumor of the prostate gland in different projections radially( in a circle).
Both methods are very complex and give a lot of side effects. They are assigned before the operation and immediately afterwards for the destruction of pathogenic cells. The duration of the course varies from 2 to 7 weeks on average( 8-45 sessions).An important role is played by the choice of the optimal radiation dose.
Contact method
It is considered one of the most modern and safe. These are minimally invasive techniques that directly affect malignant growth. There are two ways to conduct contact treatment.
In the first case, the preparation in the form of small balls is inserted into the rectum or through the urethral canal into the bladder and left in a similar position. This so-called. Intracavitary method.
Another method involves the introduction of needle-shaped radio sources in the thickness of the tumor. This is interstitial therapy.
It is enough only 1-3 sessions for therapy. The contact method is shown instead of surgery, as the first or palliative measure of cancer treatment.
Proton technique
It is considered the most modern, not counting radiosurgery. It is enclosed in a patient's room under a special sensor. It has much in common with the remote method. However, the accuracy of irradiation in a proton radiator is several times higher. The effect is achieved due to the precise positioning of the patient and careful visual control of the effects of the rays. According to research, this is one of the most effective methods of treatment. The number of relapses does not exceed 1 case per 5000 patients.
Assigned instead of surgery, before surgery or immediately after, as a technique to prevent relapse with partial resection. The number of sessions varies from 3 to 30, the duration of the course is 1-6 weeks.
The interstitial method
is the introduction of a radioisotope substance into the prostate cavity. The effect is achieved through only 1-5 sessions.
Assigned to reduce tumor size before surgery.
Consequences of treatment of
All methods, except for proton therapy, have a lot of side effects. Among the most common:
-

Problems with urination and bowel movement - the most frequent consequences of radiation therapy
The occurrence of problems with urination. Instability of stool: alternation of constipation and diarrhea.
- Temporary, but significant impotence.
- Possibility of relapse.
In order to eliminate adverse effects or prevent them, it is recommended to adhere to a number of simple rules:
- Do not use alcohol at all.
- Smoking is excluded.
- After each radiation therapy session it is recommended to observe the rest regime, to lie for at least two or three hours.
- Clean teeth with a soft bristled brush only. A generalized manifestation of the fragility of the capillaries is possible.
- You need to consume as much plant food as possible. At the same time, the food should be fractional( up to 6-7 times a day).
- It is necessary to exclude the effect of solar radiation on the dermal cover.
- It is recommended to adhere to optimal physical activity, practice breathing exercises.
Radiation therapy is a dangerous technique and not always effective enough. Most often it is an auxiliary, but not the main way to treat prostate cancer. Nevertheless, radiation treatment has proved its effectiveness, therefore it is being improved and applied everywhere. However, the oncologist must weigh the pros and cons and only then decide the question of the appropriateness of prescribing such therapy. Otherwise, there will be no effectiveness.
Recommended for viewing: