Options for surgical treatment of prostate adenoma
Prostate adenoma ( also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia) is a complex disease in which nodal formations form in the structure of the glandular organ. In most cases, doctors take wait and see tactics. Dynamic observation is designed to determine the development of the pathological process.
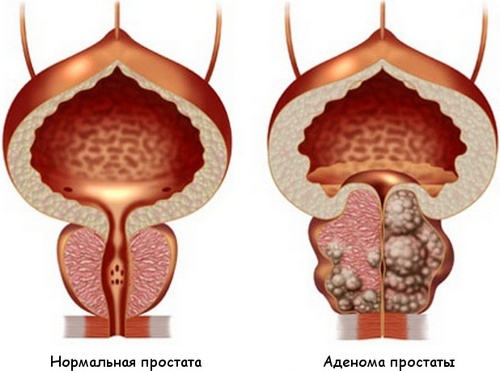
Prostate adenoma is a disease in which the nodular formations
are formed in the prostate structure. Contents
- 1 Indications for surgical treatment
- 2 General contraindications
- 3 Options for operation
- 3.1 Open operation
- 3.2 Transurethral resection
- 4 Can prostatic hyperplasia be treated with non-surgical methods?
- 5 Rehabilitation period
Indications for surgical treatment
Despite the fact that surgery is the main method of therapy, they resort to it last. There is a clear list of indications of for surgical treatment:
- The discovery of severe bleeding .Bleeding during prostatic hyperplasia is possible as a result of ischemia of the adenomatous node. Since the glandular organ is well-blooded, a copious discharge of blood from the urethral canal is possible. This is dangerous for health and life, and it is fraught with obstruction of the urinary tract by a clot.
- Chronic infectious-inflammatory processes, caused by hyperplasia. These are prostatitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis and other diseases of the urinary system of a secondary nature.
- Development of concrements in the bladder area.
- Stenosis of the urethral canal with inability to exit urine( chronic urinary retention).In this case, a complex operation is performed to remove the hypertrophied nodes of the prostate gland and expand the urethra.
- Acute urinary retention .At the advanced stages of the pathological process of iron, it grows to considerable dimensions, preventing the normal evacuation of urine from the body. This condition is urgent and requires urgent medical correction.
- Renal failure caused by congestion in the urinary tract( see here).
In all other cases, dynamic observation is shown.
General contraindications
Not always an operation can be performed. Contraindications include:
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems in the stage of decompensation. In this case, the risks associated with the introduction of the patient into a state of anesthesia.
- Acute inflammatory diseases of the urinary tract: kidneys, bladder. Also, it is not recommended to perform an operation during the period of acute prostatitis.
- Infectious diseases. Acute renal failure.
- Aortic aneurysm.
Surgical intervention is postponed until correction of the underlying disease or condition that caused the impossibility of the operation.
Operation options for
There are many options for operation. Classical methods are:
- Transurethral resection( TUR).
- Open operation.
Both methods have their testimony, features of the conduct. All other techniques are considered modifications of the two.
Open operation
This kind of surgery is considered universal, because it allows you to remove the formation of any size and location. Important, however, remains the question of expediency. A few decades ago, there was no alternative to open adenomectomy. At the moment, the operation is performed on the following indications :
- Significant adenomatous node size( over 8 cm in diameter).
- Presence of stones in the bladder.
- Bladder diverticulitis.
- Probability of malignancy( malignancy) of tumor-like structure.
Adenomectomy is a highly traumatic operation. The duration of the manipulation is from 40 minutes to 2-3 hours. During the intervention, the abdominal wall, the bladder is dissected. Through this access, nodal education is removed. After the end of the manipulation, the excised tissues are necessarily sent for histological examination to the laboratory.
Advantages of operation:
- Radicality. Volumetric formations are removed completely, the risk of recurrence is minimal.
- Efficiency.
Cons :
- Probability of complications development.
- Long term rehabilitation.
- The complexity of the implementation.
- Necessity of long stay in stationary conditions.
Complications :
- Main - prolonged bleeding. They are dangerous not the risk of loss of blood, but the probability of thrombosis. A blood clot can cause obstruction of the urethra. Such a state does not pass by itself.
- Infection of a postoperative wound.
- Possibility of developing a secondary infectious cystitis.
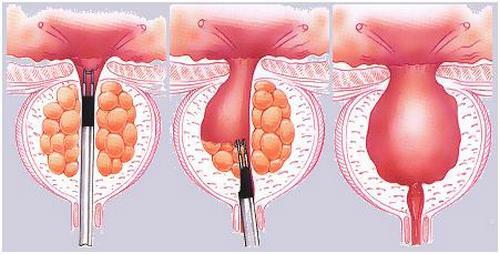
Transurethral resection
It is considered the most preferred method of treatment of prostatic hyperplasia, the "gold standard" of urology. However, such an intervention is very complex and requires perfect skills from the surgeon. The main indication for TUR is adenomatous nodes of small size( up to 8 cm in diameter).In all other cases, especially when a doctor has doubts about the origin and nature of education, a hollow operation is indicated.
Transurethral resection involves the introduction of instruments through the urethra to the prostate gland. Then the tumor is excised and removed. As in the previous case, the tissues are sent for histological examination.
Advantages of the method:
- Low-invasiveness. The surrounding tissues do not suffer.
- A short rehabilitation period.
- Absence of postoperative sutures.
The duration of the operation is about an hour.
Cons techniques:
- Impossibility of radical removal of large-sized assemblies.
- High complexity of intervention, huge requirements for the qualification of the operating surgeon.
- Need to use expensive equipment.
Probable complications :
- Narrowing of the urethral canal( stricture).
- Minor bleeding from the urethra.
- Pain syndrome.
Can prostatic hyperplasia be treated with non-surgical methods?
Conservative therapy can normalize the outflow of urine and inhibit the growth of adenoma; however, such treatment is considered symptomatic, i.e.the root cause does not disappear anywhere. For early treatment, the use of medicines is indicated:
- Alpha-blockers. They relieve spasm of the smooth muscles of the bladder and urinary tract, normalizing the outflow of urine. Alfuzozin, Doxazosin, Omnik, etc.
- Inhibitors of 5 alpha-reductase. Suspend the process of increasing the tumor in size. Stabilize the course of the pathological process. Proscar, Dutasteride, Alfinal.
- Phytotherapeutic agents. They are used exclusively at the initial stage of the process flow. Afala, Spemann, Gentos, etc.
In addition, the non-pharmacological methods of are practiced. But they can not be called completely surgical. Among the procedures for the elimination of adenoma:
- Electrocoagulation of the tumor.
- Cryodestruction.
- Laser ablation.
- Thermotherapy.
- Vaporization.
Access to the tumor is also transurethral.
Rehabilitation period
Regardless of the type of surgical intervention, in the rehabilitation period, a number of recommendations should be observed :
- Refuse from intensive physical exertion for a month and a half.
- Perform the selected complexes of therapeutic gymnastics.
- Exclude sexual contact for 30-40 days, until the wound is fully healed.
- Rationalize your own menu: as little as possible food of animal origin and, conversely, as much as possible of plant products on the table. From spices, salt, coffee and strong tea should be discarded.
- Take enough fluids, regularly empty the bladder( every two hours), not allowing urine stagnation.
- Regularly visit a surgeon or doctor to treat postoperative sutures( if a cavity operation is performed).
Treatment of prostatic hyperplasia is a difficult task. As a rule, in the early stages, a complex medication approach is chosen. In the future, without surgery, simply can not do. The technique of surgical intervention is chosen by the doctor, based on the size and nature of the tumor. In any case, it is impossible to delay with treatment. If you have anxious symptoms, you should contact your urologist.
Recommended for viewing: