Kidney: location, structure and functions of the paired organ
Kidneys are a paired organ located in the retroperitoneal space at the sides of the spinal column. Kidneys promote the removal of metabolic products, participate in the blood formation of many parts of the metabolism. The successful functioning of the kidneys affects the work of the whole organism and largely determines the life span of a person. 
content
- 1 structure
- 2 Perfusion and innervation
- 3 kidney functions
- 4 regulation of renal function
- 5 Assessment of renal function
- 5.1 Urinalysis
- 5.2 Biochemical blood test
- 5.3 Functional tests
- 5.4 Instrumental methods
structure
Kidneys are part of the urinary systemTogether with the ureters, bladder and urethra( urethra).Localized kidneys in the lumbar region on both sides of the spine at the level of the last XII thoracic and first three lumbar vertebrae. The right kidney is slightly lower than the left( 1-2 cm), which is explained by the pressure of the overlying liver. The kidneys of a man have a bean-shaped form. The upper pole of each kidney reaches the level of the last thoracic vertebra. The lower pole is 3-5 cm from the spine. All the boundaries of the kidneys are variable and depend on the individual features of the structure of the human body. Deviations are allowed for kidney localization on 1-2 vertebrae in any direction.
Kidney Dimensions:
- Length: 12 cm;
- width: 6 cm;
- thickness: 4 cm.
Three sections are distinguished in the kidney structure:
- connective tissue capsule;
- parenchyma;
- system of accumulation and excretion of urine.
The capsule of each kidney with a dense cover envelops the organ from the outside. Parenchyma is divided into two sections: cortical( external) and cerebral( internal).The cortical part includes renal corpuscles formed from capillary glomeruli. The brain layer of the kidney is represented by tubules. The tubules, connecting, form pyramids of the kidney, which in turn open into small cups from 6 to 12. Small cups merge and form 2-4 large cups. Together, the large calyx form the renal pelvis. All this together - a renal pelvis, large and small cups are a system of accumulation and excretion of urine.
The structural unit of the human kidney is nephron. The nephron consists of a glomerulus( interlocking capillaries), Shumlyansky-Bowman capsules and a system of convoluted and straight tubules. Each kidney contains up to 1 million nephrons, most of which are located in the cortical layer. In the nephron there is a formation of urine and it is ensured the maintenance of homeostasis in the body.
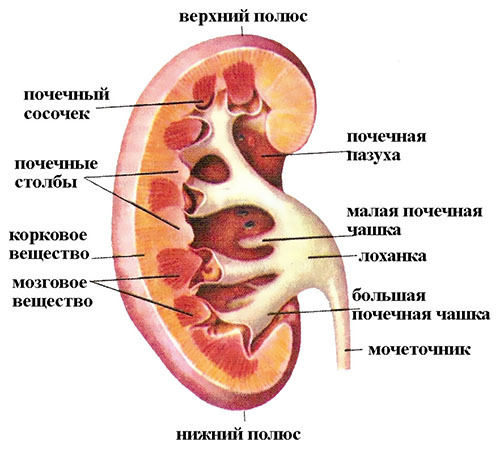
Kidney structure
Blood supply and innervation
In the gate area, vessels to each kidney are suitable: the renal artery and veins. There also pass the lymphatic vessels, as well as the ureter. Blood supply to the kidney occurs from the aorta. Passing the renal gates, the artery divides into two branches to each of the poles of the kidney. In the parenchyma of the organ, the vessel is divided into small branches, braided by the renal tubules and then passes into the veins. The outflow of venous blood is carried out through the renal vein and then into the inferior vena cava.
Kidney innervation is performed from the branches of the renal plexus, which in turn proceeds from the celiac plexus. In the interweaving of nerve fibers, the branches of the vagus nerve and the processes emerging from the spinal nodes are marked.
Kidney function
In the human body, the kidney performs such functions :
- excretory;
- metabolic;
- homeostatic;
- endocrine( endocrine);
- protective.
Excretory, or excretory is the main function of the kidneys. In the renal tubules blood plasma under pressure enters the capsule Shumlyansky-Bowman, forming the primary urine. Further, the primary urine moves along the nephron tubules, where a gradual absorption of nutrients back into the plasma takes place. The secondary urine formed in the filtration process emerges into the renal pelvis and then proceeds along the urinary tract.
Metabolic kidney function plays no less a role in maintaining adequate functioning of the body. In the kidneys, many substances are made necessary for the proper functioning of all internal organs. In particular, the transformation of vitamin D and its transformation into an active form( D3) occurs precisely in the kidneys. Kidneys also participate in the synthesis of glucose, the breakdown of fats and proteins, the synthesis of certain enzymes and other compounds.
The homeostatic function of the kidneys is to ensure the constancy of the internal environment of the body, including:
- water balance( due to changes in the volume of excreted urine);
- osmotic balance( due to excretion of osmotically active substances, including glucose and urea salts);
- acid-base equilibrium( due to a regular change in the excretion of various ions);
- constancy of hemostasis( due to the synthesis of clotting factors and participation in the exchange of anticoagulants).
Due to the continuous filtration of blood, the stability of the acid-alkaline balance of the plasma is ensured, conditions are created to maintain a constant concentration of osmotically active substances. Thus, the kidneys support the water-salt balance in the body and prevent any significant changes in this area.
Endocrine kidney function is equally important for the human body. In the kidneys produced some biologically active substances, including renin( a hormone that regulates blood pressure), erythropoietin( a substance that stimulates the production of red blood cells).Kidneys also participate in the production of prostaglandins, which affect all key processes in the human body.
The protective function is to remove foreign substances and toxins from the body. Thanks to the kidneys, a person has the opportunity to get rid of the dangerous elements trapped inside them naturally.
Read on: Improve kidney function in a natural way
Regulation of kidney function
Kidney activity is determined by the secretion of hormones produced by endocrine glands. In the regulation of kidney function involved:
- vasopressin;
- adrenaline;
- thyroxine.
Vasopressin is a hormone produced in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Under its influence, the volume of urine decreases significantly. Reducing the production of urine carries and adrenaline. With significant nervous shocks, injuries, and also during surgical operations, these hormones contribute to stopping urination up to anuria( complete absence of urine).The thyroid hormone thyroxine, on the contrary, enhances the production of urine and promotes the development of polyuria.
Assessment of renal function
The following methods help determine the functional activity of the kidneys:
General urine analysis
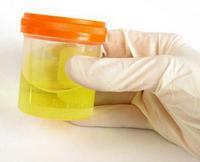
Urinalysis helps to quickly identify abnormalities in kidney function
A routine study that assesses the overall condition of the kidneys and identifies some common diseases. In the general analysis of urine special attention is paid to the density( specific gravity) of urine( in the norm of 1005 - 1025).The change in this indicator in either direction indicates a violation of the ability of the kidneys to concentrate or dilute urine.
Other indicators for the evaluation of renal function:
- protein;
- glucose;
- bilirubin;
- ketones;
- cellular elements( erythrocytes, leukocytes, cylinders).
Biochemical blood test
In a blood test, attention is drawn to the level of creatinine and urea. The determination of these parameters allows to determine the glomerular filtration rate and evaluate the excretory function of the kidneys. Many modern laboratories offer the determination of the level of cystatin C as a more accurate marker of the rate of blood filtration in the glomeruli of the kidneys.
Functional tests
Creatinine clearance( Redberg test) is one of the leading indicators of the ability of the kidneys to purify the blood and remove the products of metabolism with urine. For evaluation, blood and urine portions are taken. Decreased creatinine clearance indicates a serious impairment of kidney function.
Zimnitsky's trial is another important method for assessing the functional state of the kidneys. The sample allows to determine daily fluctuations in the specific gravity of urine, which is important in the diagnosis of many diseases of the urinary system.
Instrumental methods
Excretory urography is the main method for determining the excretory capacity of the kidneys. Introduction of x-ray contrast substance into the blood allows to evaluate urodynamics, as well as to reveal some pathological processes in the kidney structure( stones, tumors, etc.).
Assessment of the functional capacity of the kidneys is an important stage in the diagnosis of diseases of the urinary system. After conducting simple tests, you can identify various pathological processes in time, take all measures to eliminate them and prevent the development of complications.
Read: Kidney Disease and Symptoms
Recommended for viewing: