In detail about a tuberculosis of testicles: development of a pathology, treatment and complications
Testicular tuberculosis is an inflammatory infectious disease, during which the testicles are affected by the Koch's rod( tuberculosis bacterium).This is a relatively rare disease, most often of a secondary nature. Despite the relatively small prevalence, tuberculosis of the testicles is considered a dangerous disease, as it can cause formidable complications. What do you need to know about this serious pathology?
Tuberculosis Testicular
Content
- 1 Tuberculosis egg - definition
- 2 How is tuberculosis testicular
- 3 Clinical manifestations
- 4 Diagnostics
- 4.1 Instrumental investigations
- 4.2 Laboratory studies
- 5 Treatment
- 5.1 Drug therapy
- 5.2 Surgical therapy
- 6 Complications
Tuberculosis egg - definition
Testicular tuberculosis is an infectious pathology caused by the microbacteria of tuberculosis. It can be worn as primary( provoked by direct damage to the testicle by Koch's stick as a result of violations of hygiene rules, etc.), and secondary character, when the infectious agent penetrates the organ structure lymphatically from the primary focus in the lungs. The probability of a primary lesion, however, is not so great, and is about 5-10%.
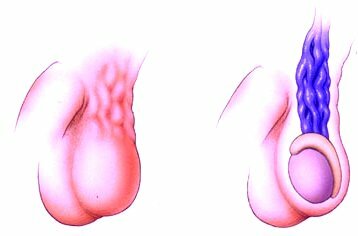
The disease is rarely found in isolation, where tuberculosis epididymitis is more common with tuberculous orchitis( inflammation of the testicle).And usually with the passage of time, the pathological process affects both the testicles and their appendage at once.
As tuberculosis of testis develops
The main immediate cause is the presence of tuberculosis in an anamnesis. Itcobacteria are never removed from the body completely, remaining in "sleeping" foci, from which they can again spread with weakening of the immune system. Indirect factors are:
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency;
- decreased immunity against the background of the transferred disease;
- asocial way of life.
As a rule, tuberculosis initially affects the lungs, because it spreads by airborne droplets. With the flow of lymph and / or blood( the so-called lymphogenous and hematogenous pathways of infection), the microbacterium from the primary focus penetrates the scrotum. There are two theories about how testicular tuberculosis spreads:
- Theory 1. According to the first point of view, the appendages initially suffer. With the passage of time, the infection penetrates the testicles from the appendages, and then into the prostate gland.
- Theory 2. According to another theory, the infectious agent first affects the prostate, and only then with the current of the seminal fluid the bacterium enters the testicle.
Many believe that tuberculosis can be transmitted through unprotected sex. This is a false idea. However, tuberculosis and unprotected sex life are still connected. Although the disease is not transmitted through sexual contact, the AIDS virus gets into the body sexually. As is known, tuberculosis and HIV are twins-brothers. Almost always, AIDS sufferers suffer from tuberculosis.
Clinical manifestations of
Most of the symptoms are meager, since most often the tuberculosis of the testicle proceeds in chronic form from the time it starts( the primary chronic process).The disease is indicated by:
- The presence of a seal in the structure of the testicles. It is detected by palpation of the testicles.
- Pain on the part of the lesion. The pain is weak, aching, "accompanies" the patient constantly. Strengthens during intercourse.
- Formation of fistula scrotum. Fistulas occur in the late stages of the disease.
- Redness( congestion) of the scrotum.
In an acute current process, there are manifestations of microbial intoxication:
- loss of appetite;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile values (37-38 degrees Celsius);
- sharp weight loss;
- night sweats;
- weakness;
- excessive fatigue.
If the pathology has arisen for a long time, the risk of damage to neighboring organs of the genitourinary system, including the kidneys, the bladder, and the prostate is high. In this case, there is a focal symptomatology: urination disorders, pain, hematuria, etc.
Diagnosis
Urologists are engaged in diagnostics, as well as treatment of testicular tuberculosis, in tandem with phthisiatricians. This is an interdisciplinary problem, so one specialist can not do it. Diagnosis is complicated by the absence in the early stages of specific symptoms.
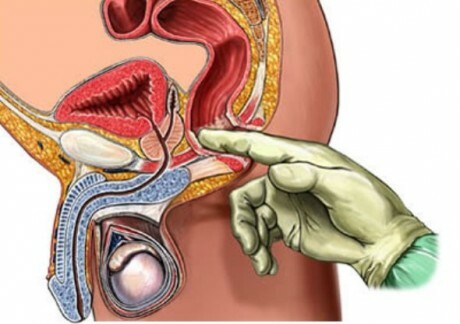
At the initial consultation, the doctor interviews the patient for complaints. Next, a visual evaluation of the testicles and palpation of the scrotum organs is necessary. The basis of diagnosis is a number of instrumental and laboratory studies.
Instrumental Studies
- Chest X-ray is used to identify the primary source.
- ultrasound of the scrotum. Detects nodules, calcinates.
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the scrotum.
- CT / MRI.Puncture of the testicle.
Laboratory testing
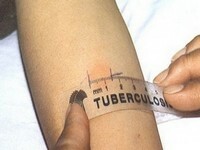
Tuberculin test( Mantoux test)
Includes:
- General blood test. Gives a characteristic picture of inflammation with leukocytosis, ESR, C-reactive protein.
- Biochemical blood test.
- Tuberculin test( classical method of diagnosis of tuberculosis).
- PCR diagnostics. Microscopy of smears from the urethra.
- Study of the secretion of the prostate for a Koch sticks.
The combination of these methods is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Treatment
Medication Therapy
Therapy, mainly medicamentous, consists in the admission of special anti-tuberculosis drugs:
- Prothionamide;
- Pyrazinamide;
- Ethionamide;
- Etambutola, etc.
Surgical therapy
Surgical treatment means removal of the affected organ:
- if the testis itself is damaged - then its complete removal;
- if the testicle along with the appendage - respectively, remove the testicle along with the appendage;
- if only the appendage of the testicle - then the testicle itself is not touched, only the amazed appendage is removed.
There are clear indications for surgical treatment:
- with suspicions of a malignant process in the scrotal area;
- in the absence of the effect of the treatment;
- in the presence of complications.
Complications of

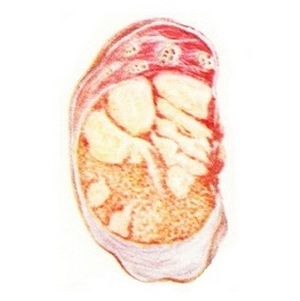
Complications of tuberculosis of testis - hydrocele
Complications always require surgical correction. Among them:
- testicular necrosis;
- fistula;
- hydrocele;
- abscesses.
Testicular tuberculosis is a serious illness that requires urgent medical attention. A frequent consequence of this condition is infertility( total violation of reproductive health).Therefore, it is so important to carry out the diagnosis in a timely manner and begin therapy. Self-management by domestic methods is impossible.
Recommended for viewing: